Architectural rendering

Architectural rendering, architectural illustration, or architectural visualization (often abbreviated to archviz or ArchViz) is the art of creating three-dimensional images or animations showing the attributes of a proposed architectural design.
Computer generated renderings[edit]


Images that are generated by a computer using three-dimensional modeling software or other computer software for presentation purposes are commonly termed "Computer Generated Renderings".[1] Rendering techniques vary. Some methods create simple flat images or images with basic shadows. A popular technique uses sophisticated software to approximate accurate lighting and materials. This technique is often referred to as a "Photo Real" rendering. Renderings are usually created for presentation, marketing and design analysis purposes.
- Still renderings
- 3D Walkthrough and Flythrough animations (movie)
- Virtual Tours
- Live Virtual Reality
- Floor Plans
- Photorealistic 3D Rendering
- Realtime 3D Renderings
- Panoramic Renderings
- Light and Shadow (sciography) study renderings
- Renovation Renderings (photomontage)
- and others
Common types of architectural renderings[edit]
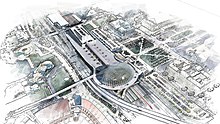
Architectural renderings are often categorized into 3 sub-types: Exterior Renderings, Interior Renderings, and Aerial Renderings.
Exterior renderings are defined as images where the vantage point or viewing angle is located outside of the building, while interior renderings are defined as images where the vantage point or viewing angle is located inside of the building. Aerial renderings are similar to exterior renderings, however, their viewing angle is located outside and above the building, looking down, usually at an angle.[2]
Education[edit]
Traditionally rendering techniques were taught in a "master class" practice (such as the École des Beaux-Arts), where a student works creatively with a mentor in the study of fine arts. Contemporary architects use hand-drawn sketches, pen and ink drawings, and watercolor renderings to represent their design with the vision of an artist. Computer-generated graphics is the newest medium to be utilized by architectural illustrators.
During the past 20–30 years, many professional architectural illustrators came from an education in architecture first, then moved into the profession as their (mostly self-taught) skills in illustration progressed.
Hand-drawn renderings or architectural illustration[edit]
Until 3D computer modeling became common, architectural renderings were generated by hand. There are still architectural illustrators who create renderings entirely by hand, as well as illustrators who use a combination of hand drawing/painting and computer generated color and/or linework. Common mediums for hand-done architectural renderings include: watercolor, colored pencil, gauche, and graphite or charcoal pencil.
Awards[edit]
- The Hugh Ferriss Memorial Prize is awarded by the American Society of Architectural Illustrators in recognition of excellence in the graphic representation of architecture. It is the Society's highest award.
- The CGarchitect Architectural 3D Awards are awarded by CGarchitect.com in recognition of outstanding achievement in the field of computer-generated architectural rendering. The awards were started in 2004 and award in five main categories: Best Architectural Image, Best Architectural Film, Best Student Image, Best Student Film, Best Interactive Presentation/Emerging Technology.
See also[edit]
Architectural animation[edit]
- Concept art
- Museum for Architectural Drawing, Berlin, Germany
References[edit]
- ^ "What Is Architectural Rendering? (with pictures)". Retrieved 2015-06-27.
- ^ "What Are Architectural Renderings?". Retrieved 2018-08-21.
This article needs additional citations for verification. (June 2015) |
