Consumer debt
This article needs additional citations for verification. (October 2009) |
| Part of a series on |
| Macroeconomics |
|---|
 |

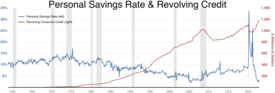

In economics, consumer debt is the amount owed by consumers (as opposed to amounts owed by businesses or governments). It includes debts incurred on purchase of goods that are consumable and/or do not appreciate. In macroeconomic terms, it is debt which is used to fund consumption rather than investment.[1]
The most common forms of consumer debt are credit card debt, payday loans, student loans and other consumer finance, which are often at higher interest rates than long-term secured loans, such as mortgages.
Long-term consumer debt is often considered fiscally suboptimal. While some consumer items such as automobiles may be marketed as having high levels of utility that justify incurring short-term debt, most consumer goods are not. For example, incurring high-interest consumer debt through buying a big-screen television "now", rather than saving for it, cannot usually be financially justified by the subjective benefits of having the television early.
In many countries, the ease with which individuals can accumulate consumer debt beyond their means to repay has led to a growth in the debt consolidation industry and credit counseling. Debt also leads to a lower credit score and may have effects on mental health.
The amount of debt outstanding versus the consumer's disposable income is expressed as the consumer leverage ratio. On a monthly basis, this debt ratio is advised to be no more than 20 percent of an individual's take-home pay.[2] The interest rate charged depends on a range of factors, including the economic climate, perceived ability of the customer to repay, competitive pressures from other lenders, and the inherent structure and security of the credit product. Rates generally range from 0.25 percent above base rate, to well into double figures. Consumer debt is also associated with predatory lending, although there is much debate as to what exactly constitutes predatory lending.
In recent years, an alternative analysis might view consumer debt as a way to increase domestic production, on the grounds that if credit is easily available, the increased demand for consumer goods should cause an increase of overall domestic production. The permanent income hypothesis suggests that consumers take debt to smooth consumption throughout their lives, borrowing to finance expenditures (particularly housing and schooling) earlier in their lives and paying down debt during higher-earning periods.
Personal debt is on the rise, particularly in the United States and the United Kingdom. However, according to the US Federal Reserve[when?], the US household debt service ratio is at the lowest level since its peak in the Fall of 2007.[3]
Debt-to-GDP ratio, consumer leverage ratio[edit]
A country's private debt can be measured as a 'debt-to-GDP ratio', which is the total outstanding private debt of its residents divided by that nation's annual GDP. A variant is the consumer leverage ratio, which is the ratio of debt to personal income.
List of countries[edit]
This section needs to be updated. (March 2021) |
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ "Consumer Debt Definition". Investopedia. Retrieved August 24, 2011.
- ^ "Alternatives to Filing for Bankruptcy". www.moneymanagement.org. Retrieved 2016-07-29.
- ^ US Federal Reserve. "Household Debt Service and Financial Obligations Ratios". Household Debt Service and Financial Obligations Ratios. Retrieved December 4, 2012.
- ^ "Domestic credit to private sector (% of GDP) | Data".
- ^ "Domestic credit to private sector (% of GDP) | Data".
External links[edit]
- Current rates from the World Bank
- U.S. consumer credit outstanding
- In-depth reports on debt and borrowing in the United Kingdom
