From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Chemical compound
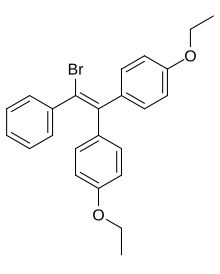
Estrobin , also known as α,α-di(p -ethoxyphenyl)-β-phenylbromoethylene and commonly abbreviated as DBE , is a synthetic , nonsteroidal estrogen of the triphenylethylene group that was never marketed.[1] [2] Chlorotrianisene , and subsequently clomifene and tamoxifen , were derived from it.[1] [2] lipophilic and hence very long-lasting in its duration of action.[1] [2] prodrug to a much more potent estrogen in the body.[2]
See also [ edit ] References [ edit ]
ER Tooltip Estrogen receptor
Agonists
Steroidal: 2-Hydroxyestradiol 2-Hydroxyestrone 3-Methyl-19-methyleneandrosta-3,5-dien-17β-ol 3α-Androstanediol 3α,5α-Dihydrolevonorgestrel 3β,5α-Dihydrolevonorgestrel 3α-Hydroxytibolone 3β-Hydroxytibolone 3β-Androstanediol 4-Androstenediol 4-Androstenedione 4-Fluoroestradiol 4-Hydroxyestradiol 4-Hydroxyestrone 4-Methoxyestradiol 4-Methoxyestrone 5-Androstenediol 7-Oxo-DHEA 7α-Hydroxy-DHEA 7α-Methylestradiol 7β-Hydroxyepiandrosterone 8,9-Dehydroestradiol 8,9-Dehydroestrone 8β-VE2 10β,17β-Dihydroxyestra-1,4-dien-3-one (DHED) 11β-Chloromethylestradiol 11β-Methoxyestradiol 15α-Hydroxyestradiol 16-Ketoestradiol 16-Ketoestrone 16α-Fluoroestradiol 16α-Hydroxy-DHEA 16α-Hydroxyestrone 16α-Iodoestradiol 16α-LE2 16β-Hydroxyestrone 16β,17α-Epiestriol (16β-hydroxy-17α-estradiol) 17α-Estradiol (alfatradiol )17α-Dihydroequilenin 17α-Dihydroequilin 17α-Epiestriol (16α-hydroxy-17α-estradiol) 17α-Ethynyl-3α-androstanediol 17α-Ethynyl-3β-androstanediol 17β-Dihydroequilenin 17β-Dihydroequilin 17β-Methyl-17α-dihydroequilenin Abiraterone Abiraterone acetate Alestramustine Almestrone Anabolic steroids (e.g., testosterone and esters , methyltestosterone , metandienone (methandrostenolone) , nandrolone and esters , many others; via estrogenic metabolites)Atrimustine Bolandiol Bolandiol dipropionate Butolame Clomestrone Cloxestradiol
Conjugated estriol Conjugated estrogens Cyclodiol Cyclotriol DHEA DHEA-S ent -EstradiolEpiestriol (16β-epiestriol, 16β-hydroxy-17β-estradiol) Epimestrol Equilenin Equilin ERA-63 (ORG-37663) Esterified estrogens Estetrol Estradiol
Estramustine Estramustine phosphate Estrapronicate Estrazinol Estriol
Estrofurate Estrogenic substances Estromustine Estrone
Etamestrol (eptamestrol) Ethinylandrostenediol
Ethinylestradiol
Ethinylestriol Ethylestradiol Etynodiol Etynodiol diacetate Hexolame Hippulin Hydroxyestrone diacetate Lynestrenol Lynestrenol phenylpropionate Mestranol Methylestradiol Moxestrol Mytatrienediol Nilestriol Norethisterone Noretynodrel Orestrate Pentolame Prodiame Prolame Promestriene RU-16117 Quinestradol Quinestrol Tibolone Xenoestrogens: Anise -related (e.g., anethole , anol , dianethole , dianol , photoanethole )Chalconoids (e.g., isoliquiritigenin , phloretin , phlorizin (phloridzin) , wedelolactone )Coumestans (e.g., coumestrol , psoralidin )Flavonoids (incl. 7,8-DHF , 8-prenylnaringenin , apigenin , baicalein , baicalin , biochanin A , calycosin , catechin , daidzein , daidzin , ECG , EGCG , epicatechin , equol , formononetin , glabrene , glabridin , genistein , genistin , glycitein , kaempferol , liquiritigenin , mirificin , myricetin , naringenin , penduletin , pinocembrin , prunetin , puerarin , quercetin , tectoridin , tectorigenin )Lavender oil Lignans (e.g., enterodiol , enterolactone , nyasol (cis -hinokiresinol) )Metalloestrogens (e.g., cadmium )Pesticides (e.g., alternariol , dieldrin , endosulfan , fenarimol , HPTE , methiocarb , methoxychlor , triclocarban , triclosan )Phytosteroids (e.g., digitoxin (digitalis ), diosgenin , guggulsterone )Phytosterols (e.g., β-sitosterol , campesterol , stigmasterol )Resorcylic acid lactones (e.g., zearalanone , α-zearalenol , β-zearalenol , zearalenone , zeranol (α-zearalanol) , taleranol (teranol, β-zearalanol) )Steroid -like (e.g., deoxymiroestrol , miroestrol )Stilbenoids (e.g., resveratrol , rhaponticin )Synthetic xenoestrogens (e.g., alkylphenols , bisphenols (e.g., BPA , BPF , BPS ), DDT , parabens , PBBs , PHBA , phthalates , PCBs )Others (e.g., agnuside , rotundifuran ) MixedSERMs Tooltip Selective estrogen receptor modulators ) Antagonists
Coregulator-binding modulators: ERX-11
GPER Tooltip G protein-coupled estrogen receptor
Agonists Antagonists Unknown