File:Signal Transduction Model for Embryonic Differentiation Waves.png
Page contents not supported in other languages.
Signal_Transduction_Model_for_Embryonic_Differentiation_Waves.png (635 × 455 pixels, file size: 307 KB, MIME type: image/png)
| This is a file from the Wikimedia Commons. Information from its description page there is shown below. Commons is a freely licensed media file repository. You can help. |
Summary
| DescriptionSignal Transduction Model for Embryonic Differentiation Waves.png |
English: This signal transduction model for the cell state splitter is a general one. There will be replacement or alternate proteins for some of the proteins in our model in some tissues or organisms. As embryogenesis proceeds there will be more feedback loops amplifying the contraction and expansion signals and additional inhibitory or excitatory interactions down the signal transduction pathways. In some cellular differentiations, highly specialized versions of these signal transduction pathways will exist such as where cells only one cell state splitter reaction can actually take place.
Nuclear State Splitter Participants: Wnt – Name is derived from “Wingless” and formerly considered “The Morphogen”, Wnt acts primarily as an autocrine protein that binds one or more transmembrane protein and affects their conformation and phosphorylation and thereby affects signal transduction pathways, often amplifying other signals. FzR- Frizzled transmembrane protein. Cdc42 – a cell cycle protein that takes part in signal transduction pathways and can signal the cell to enter mitosis. It is a member of the small Rho-kinase family that is known to affect microfilament contraction and also can stimulate pathways promoting cell division. A round of determination is often followed by cell proliferation as part of differentiation and this could be via Rho-kinase. PKC – Protein Kinase C is a protein normally found in the cytosol of the cell in an inactive form but when phosphorylated by other signaling molecules, in particular calcium ions and diaglycerols, translocates to the cell membrane where it interacts with other kinases, especially RACK (receptor for activated C Kinase). PKC continues to signal long after the calcium flux has faded and the diaglycerol signal has ended and so can be considered a signal amplifier. CaN – Calcineurin, which is known to dephosphorylate the trans- cription factor NFAT. This causes a conformation change which exposes the NFAT nuclear import signal allowing it move to the nucleus and bind to specific DNA sequences and change gene expression. β-catenin – Cadherin associated protein beta one, a dual function protein that is active in cell-to-cell adhesion as well as gene expression. JNK-c-Jun terminal kinase first found because they bind and phosphorylate c-jun forming a transcriptional activator domain on DNA. JNK is a form of mitogen activated protein. PLC – An enzyme which cleaves PIP2 to form two products, inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate (IP3) and diaglycerol both of which are second messengers that commonly affect opening and closing of membrane channels. Diaglycerol and calcium combined can trigger Protein Kinase C translocation. PIP2 – Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-biphosphate, a phospholipid that is the major constituent of membranes that is cleaved by PLC. Such cleavage can activate PKC. Dvl – Dishevelled, cytoplasmic phosphoprotein that is required for canonical and noncanonical Wnt pathway signal transduction and Wnt signaling. CK1 – Casein Kinase 1 involved in phosphorylation of Dishevelled. Axin- A dual domain cytoplasmic protein, with one domain binding the disheveled receptor and the other binding G proteins. APC – Adenomatous polyposis coli, so called because when one version is mutated in humans it is connected to development of colon cancer. It is a negative regulator which reduces β-catenin response and is also directly connected to e-cadherin. GSK3 – glycogen synthase kinase 3, phosphorylates β-catenin (thereby signaling for it to be degraded) in response to signaling from Axin. DAAM1 – Disheveled-associated activator of morphogenesis 1, a protein associated with microfilament polymerization, possibly by acting as a scaffold protein. It is activated by Rho. Rho – A member of the Ras homolog gene family, Rho is a kinase that is activated during microfilament contraction by directly stimulating microfilament polymerization undertaken by the formins. Formins recruit free actin monomers which are then used to elongate microfilaments. (They also capture and stabilize free ends of microtubules required for ruffling in forward movements of cells.) ROCK – Rho associated protein kinase, this protein works downstream to Rho and can either trigger stabilization or destabilization of microfilaments. It can also trigger contraction by activating specific myosins. Rac – a serine/threonine-protein kinase that interacts with multiple other kinases. MAPK – Mitogen activated protein type K. MAPs were originally called microtubule associated proteins because when they phosphorylate another set of proteins, MAP, that bind to microtubules. MAP – microtubule associated protein, bind to microtubules and can either stabilize or destabilize microtubules depending on phosphorylation signals from other proteins. When signalled by Wnt signal transduction they generally stabilize and elongate microtubules. |
| Date | |
| Source | Own work |
| Author | Bjorklund21 |
Licensing
I, the copyright holder of this work, hereby publish it under the following license:
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license.
- You are free:
- to share – to copy, distribute and transmit the work
- to remix – to adapt the work
- Under the following conditions:
- attribution – You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
This work was published in my book, Embryogenesis Explained, World Scientific, Singapore, 2016, figure 8.13, page 588-9 and I have approval from the publisher to release it here.
Captions
Add a one-line explanation of what this file represents
Items portrayed in this file
depicts
some value
2016
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 19:52, 6 November 2017 | 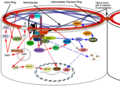 | 635 × 455 (307 KB) | Bjorklund21 | User created page with UploadWizard |
File usage
The following pages on the English Wikipedia use this file (pages on other projects are not listed):
Metadata
This file contains additional information, probably added from the digital camera or scanner used to create or digitize it.
If the file has been modified from its original state, some details may not fully reflect the modified file.
| Horizontal resolution | 59.06 dpc |
|---|---|
| Vertical resolution | 59.06 dpc |

