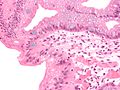
Glandular metaplasia

Glandular metaplasia is a type of metaplasia where irritated tissue converts to a glandular form.
An example occurs in the esophagus, where tissue becomes more similar to the tissue of the stomach.[1]
Another example occurs in the urinary bladder.[2]
See also[edit]
Additional images[edit]
-
Micrograph of Barrett's esophagus, an example of glandular metaplasia.
References[edit]
- ^ "Metaplasia". Archived from the original on 2008-08-01.
- ^ Ward AM (July 1971). "Glandular metaplasia and mucin production in transitional cell carcinomas of bladder". J. Clin. Pathol. 24 (5): 481. doi:10.1136/jcp.24.5.481-b. PMC 477052. PMID 5571853.