Joseph Saxton

Joseph Saxton (March 22, 1799 – October 26, 1873) was an American inventor, watchmaker, machinist, and photographer from Pennsylvania. A daguerrotype taken by Saxton in 1839 is one of the oldest surviving photographs taken in the United States.[1]
Early life[edit]
Joseph Saxton was born in Huntingdon, Pennsylvania, and first entered as an apprentice to a watchmaker when he was twelve years old.[2] Saxon was the son of a Mr. Saxton, a mechanic, and Elizabeth Ashbaugh, daughter of John Ashbaugh Sr.[3]
Career[edit]
Philadelphia[edit]
In 1817, aged 18, Joseph Saxton moved to Philadelphia, where he found employment as a watchmaker, engraver, and apprentice in the machine shop of Isaiah Lukens.[4] During this time, he made his first inventions: a machine for cutting the teeth of marine chronometer wheels and an escapement and compensating pendulum for clocks. He also helped Lukens with the construction of a clock for the newly rebuilt steeple of the Independence Hall.[5]
In 1884, an anecdote about Saxton's apprenticeship was published by George Escol Sellers, who worked with him in Lukens' shop:
"From the time of Saxton's coming to Philadelphia we were intimate and warm friends until his death. The first summer vacation of Lukens' after Saxton commenced to work with him, his shop was not closed as usual, but Saxton was left in charge, "to tinker," as Lukens said, with anything he liked. He planned, and was making for himself a cane gun. My elder brother and myself each concluded to make one ... I was in his shop beside Saxton doing that little job, when Lukens, who had unexpectedly returned from his summer trip, came in. He looked at, and asked what I was doing. On examining the plan, he suggested some slight alterations. Saxton showed his gun that was completed. He had worked out the plan himself and Lukens was greatly pleased with its simplicity."[4]
England[edit]
Looking to further his education, Joseph Saxton traveled to London, England, in 1828 and resided there nine years. For most of his stay he was employed by the Adelaide Gallery of Practical Science, a museum for the public that demonstrated new inventions and scientific principles.[6] While working for the gallery, Saxton invented the magneto-electric machine, an apparatus for measuring the velocity of vessels, a device for measuring the height of water in a steam boiler, the riflescope, and the fountain pen prototype.[7]
Return to the US[edit]
After almost a decade abroad, Saxton returned to Philadelphia in 1837 and accepted a position at the Philadelphia Mint, first as superintended the making of machinery and then as curator of weights and measures, accurate sets of which were furnished to national and State governments. Among his inventions of this time may be mentioned a mirror comparator for comparing standards of length and a new form of dividing engine; a self-registering tide gauge, and an immersed hydrometer.
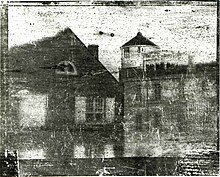
In the fall of 1839, either around September 25 or October 16,[8] Saxton took what is one of the oldest surviving photographs (daguerreotype) taken in the U.S. There were earlier photographs taken in the United States by the calotype process during spring 1839 and daguerreotypes in September of that year.[9][10][11]
The image was taken from the window of his office at the Philadelphia Mint and captured the cupola of Central High School and a portion of the State Armory building.[12] It was taken on a sheet of polished metal. A seidlitz powder box with a few flakes of iodine answered for a coating box, while a cigar box and burning glass were improvised for a camera. An iron spoon served to heat the mercury to develop the plate. The picture which was produced is owned by the Historical Society of Pennsylvania.[13] The first reference to the photograph appeared on 24 October 1839 in the United States Gazette.[12]
After Saxton took his first experimental images, he approached Robert Cornelius to supply him with better photographic plates. Cornelius took up an interest in photography and opened one of the first daguerreotype studios in May 1840.[14]
Later life[edit]
From 1843 until his death, three decades later, he was superintendent of weights and measures for the United States Coast Survey.[2] He died in Washington, D.C., on October 26, 1873.[12]
He was a member of the American Philosophical Society, the Franklin Institute and the National Academy of Sciences.[12] In 1843 he was awarded the John Scott Legacy Medal and Premium by the Franklin Institute for the invention of his reflecting pyrometer.[2]
See also[edit]
External links[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ Rung, Albert M. (1940). "Joseph Saxton: Pennsylvania Inventor and Pioneer Photographer". Pennsylvania History: A Journal of Mid-Atlantic Studies. 7 (3): 153–158. ISSN 0031-4528. JSTOR 27766416.
- ^ a b c "Joseph Saxton | The National Inventors Hall of Fame". www.invent.org. Retrieved 2019-01-04.
- ^ "Pioneer period and pioneer people of Fairfield County, Ohio : Wiseman, C. M. L. (Charles Milton Lewis), 1829-1904 : Free Download, Borrow, and Streaming". Internet Archive. Retrieved 2020-08-17.
- ^ a b Seller, George Escol (August 9, 1884). "Early engineering reminisces". American Machinist. 7 (32): 6.
- ^ Rung, Albert M. (July 1940). "Joseph Saxton: Pennsylvania Inventor and Pioneer Photographer". Pennsylvania History: A Journal of Mid-Atlantic Studies. 7 (3): 153–158. JSTOR 27766416.
- ^ "Record Unit 7056, Saxton, Joseph, 1799-1873, Joseph Saxton Papers, 1821-1856". Smithsonian Institution Archives. Retrieved 2019-01-04.
- ^ "Joseph Saxton". National Academy of Sciences. Retrieved 2019-01-04.
- ^ Stapp, W. (1983). Robert Cornelius - portraits from the dawn of Photography. National Portrait Gallery.
- ^ Keith, D. (2007). The Origins of American Photography: From Daguerreotype to Dry-Plate, 1839-1885: The Hallmark Photographic Collection at The Nelson-Atkins Museum of Art. Nelson Atkins. ISBN 978-0300122862.
- ^ Draper, John W. (1858). "Who Made the First Photographic Portrait?". American Journal of Photography. 1 (1): 2–6.
- ^ Beck, B. "First photo". Retrieved May 6, 2023.
- ^ a b c d Ambrose, Jenny (2008). Hannavy, John (ed.). Encyclopedia of Nineteenth-Century Photography. New York: Routledge. p. 1247. ISBN 9781135873271.
- ^ The Public Schools of Philadelphia: Historical, Biographical, Statistical by John Trevor Custis, Burk & McFetridge Co. Publisher, 1897, Pg. 132
- ^ Stapp, W. (1983). Robert Cornelius - portraits from the dawn of Photography. National Portrait Gallery.
