Open access in France
This article needs additional citations for verification. (August 2018) |

In France, open access to scholarly communication is relatively robust and has strong public support.[1] Revues.org, a digital platform for social science and humanities publications, launched in 1999. Hyper Articles en Ligne (HAL) began in 2001. The French National Center for Scientific Research participated in 2003 in the creation of the influential Berlin Declaration on Open Access to Knowledge in the Sciences and Humanities.[1] Publishers EDP Sciences and OpenEdition belong to the international Open Access Scholarly Publishers Association.[2]
Open Repositories[edit]
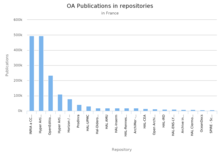
There are a number of collections of scholarship in France housed in digital open access repositories.[3] They contain journal articles, book chapters, data, and other research outputs that are free to read. The main open repository platform in use for French higher education and research institutions is HAL. It hosts over 520 000 fulltext documents and about 1.5 million references. More than 120 institutions have opened their own institutional portals on the HAL platform.
Open access publishing[edit]
France's main actor in open access publishing is Openedition. This set of publishing platforms is specialized in Human and Social Sciences. It hosts 490 journals, 5,600+ books, 2,600+ blogs and 39,000 events. Openedition is operated by an institutional unit called CLEO, and funded by the Centre national de la recherche scientifique, Ecole des hautes etudes en sciences sociales, Université d'Aix-Marseille, and Université d'Avignon et des Pays de Vaucluse. It uses for books and journals a "freemium" business model: most content is available in HTML format for free, and the other formats (pdf, epub) are available to the subscribed institutions.
Timeline[edit]
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (June 2018) |
Key events in the development of open access in France include the following:
- 1999
- Creation of the Revues.org portal by Marin Dacos, with 2 open access journals
- 2001
- 23 March: French Wikipedia, a French-language open educational resource, begins publication
- HAL repository platform launched, operated by the CCSD
- 2005
- HAL-Inria repository launched
- 2013
- Signature of a partnership agreement in favour of open archives and HAL by French higher education and research institutions[4]
- 2016
- Law for a digital Republic, creating a right for the researchers to submit their accepted manuscripts to institutional repositories, eventually with an embargo period, even if they've signed a copyright transfer agreement.[5]
- 2018
- Consortium Couperin cancels its subscription to a bundle of several journals published by Springer Nature.[6]
- 4 July: French Minister for Higher Education, Research and Innovation Frédérique Vidal announces a National Plan for Open Science[7]
- 4 September: Researchers from France take part in the Europe-wide Plan S initiative.[8][9]
See also[edit]
- Open data in France
- Internet in France
- Education in France
- Media of France
- Copyright law of France
- Science and technology in France
- Open access in other countries
References[edit]
- ^ a b "OA in France". Open Access in Practice: EU Member States. OpenAIRE. Retrieved 19 March 2018.
- ^ "Members", Oaspa.org, The Hague: Open Access Scholarly Publishers Association, retrieved 7 April 2018
- ^ "France". Directory of Open Access Repositories. UK: University of Nottingham. Archived from the original on 6 February 2009. Retrieved 15 April 2018.
- ^ "Convention de partenariat en faveur des archives ouvertes et de la plateforme mutualisée HAL" (PDF). Ministère de l'enseignement supérieur, de la recherche et de l'innovation. Retrieved August 4, 2018.
- ^ "New French Digital Republic Law boosts support for OA and TDM". OpenAIRE blog. Retrieved 5 August 2018.
- ^ "Big Deal Cancellation Tracking", Sparcopen.org, US: Scholarly Publishing and Academic Resources Coalition, retrieved 30 June 2018
- ^ "National plan for open science" (PDF). MESRI. Retrieved 5 August 2018.
- ^ "Plan S: Accelerating the transition to full and immediate Open Access to scientific publications" (PDF). Science Europe. 4 September 2018. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 September 2018. Retrieved 13 September 2018.
- ^ "European countries demand that publicly funded research should be free to all". The Economist. 13 September 2018.
Further reading[edit]
- Hélène Bosc (2008). "L'auto-archivage en France: deux exemples de politiques différentes et leurs résultats" [Self-Archiving in France: Two Different Policies and Their Results]. Liinc em Revista (in French). 4. Brazil. doi:10.18617/liinc.v4i2.280. ISSN 1808-3536.
- Open Access in France: a state of the art report (PDF), Ministère de l'Enseignement supérieur et de la Recherche, 2010
- Eelco Ferwerda; Frances Pinter; Niels Stern (2017), "Country Study: France", Landscape Study on Open Access and Monographs: Policies, Funding and Publishing in Eight European Countries, Knowledge Exchange, doi:10.5281/zenodo.815932
- Walt Crawford (2018). "France". Gold Open Access by Country 2012-2017. US: Cites & Insights Books.

External links[edit]
- "France". Global Open Access Portal. UNESCO.
- "Open Access France: Le site couperin de l'accès ouvert en France". Openaccess.couperin.org (in French). Consortium unifié des établissements universitaires et de recherche pour l'accès aux publications numériques. (Website launched in 2008).
- "Browse by Country: Europe: France". Registry of Open Access Repositories. UK.
- "(Search: Country of Publisher: France)". Directory of Open Access Journals. UK: Infrastructure Services for Open Access.
- Peter Suber (ed.). "(France)". Open Access Tracking Project. Harvard University. OCLC 1040261573.
News and comment from the worldwide movement for open access to research
- "Browse by Country: France". ROARMAP: Registry of Open Access Repository Mandates and Policies. UK: University of Southampton.
- "Our members: France". Sparceurope.org. SPARC Europe.
Scholarly Publishing and Academic Resources Coalition
