Supersampling


Supersampling or supersampling anti-aliasing (SSAA) is a spatial anti-aliasing method, i.e. a method used to remove aliasing (jagged and pixelated edges, colloquially known as "jaggies") from images rendered in computer games or other computer programs that generate imagery. Aliasing occurs because unlike real-world objects, which have continuous smooth curves and lines, a computer screen shows the viewer a large number of small squares. These pixels all have the same size, and each one has a single color. A line can only be shown as a collection of pixels, and therefore appears jagged unless it is perfectly horizontal or vertical. The aim of supersampling is to reduce this effect. Color samples are taken at several instances inside the pixel (not just at the center as normal), and an average color value is calculated. This is achieved by rendering the image at a much higher resolution than the one being displayed, then shrinking it to the desired size, using the extra pixels for calculation. The result is a downsampled image with smoother transitions from one line of pixels to another along the edges of objects. The number of samples determines the quality of the output.
Motivation[edit]
Aliasing is manifested in the case of 2D images as moiré pattern and pixelated edges, colloquially known as "jaggies". Common signal processing and image processing knowledge suggests that to achieve perfect elimination of aliasing, proper spatial sampling at the Nyquist rate (or higher) after applying a 2D Anti-aliasing filter is required. As this approach would require a forward and inverse fourier transformation, computationally less demanding approximations like supersampling were developed to avoid domain switches by staying in the spatial domain ("image domain").
Method[edit]
Computational cost and adaptive supersampling[edit]
Supersampling is computationally expensive because it requires much greater video card memory and memory bandwidth, since the amount of buffer used is several times larger.[1] A way around this problem is to use a technique known as adaptive supersampling, where only pixels at the edges of objects are supersampled.
Initially only a few samples are taken within each pixel. If these values are very similar, only these samples are used to determine the color. If not, more are used. The result of this method is that a higher number of samples are calculated only where necessary, thus improving performance.
Supersampling patterns[edit]
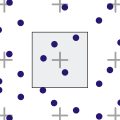
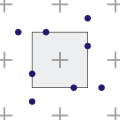
When taking samples within a pixel, the sample positions have to be determined in some way. Although the number of ways in which this can be done is infinite, there are a few ways which are commonly used.[1][2]
-
Grid algorithm in uniform distribution
-
Rotated grid algorithm (with 2x times the sample density)
-
Random algorithm
-
Jitter algorithm
-
Poisson disc algorithm
-
Quasi-Monte Carlo method algorithm
-
N-Rooks
-
RGSS
-
High-resolution antialiasing (HRAA), Quincunx
-
Flipquad
-
Fliptri
Grid[edit]
The simplest algorithm. The pixel is split into several sub-pixels, and a sample is taken from the center of each. It is fast and easy to implement. Although, due to the regular nature of sampling, aliasing can still occur if a low number of sub-pixels is used.
Random[edit]
Also known as stochastic sampling, it avoids the regularity of grid supersampling. However, due to the irregularity of the pattern, samples end up being unnecessary in some areas of the pixel and lacking in others.[3]
Poisson disk[edit]

The Poisson disk sampling algorithm [4] places the samples randomly, but then checks that any two are not too close. The end result is an even but random distribution of samples. The naive "dart throwing" algorithm is extremely slow for large data sets, which once limited its applications for real-time rendering.[3] However, many fast algorithms now exist to generate Poisson disk noise, even those with variable density.[5][6][7] The Delone set provides a mathematical description of such sampling.
Jittered[edit]
A modification of the grid algorithm to approximate the Poisson disk. A pixel is split into several sub-pixels, but a sample is not taken from the center of each, but from a random point within the sub-pixel. Congregation can still occur, but to a lesser degree.[3]
Rotated grid[edit]
A 2×2 grid layout is used but the sample pattern is rotated to avoid samples aligning on the horizontal or vertical axis, greatly improving antialiasing quality for the most commonly encountered cases. For an optimal pattern, the rotation angle is arctan (1/2) (about 26.6°) and the square is stretched by a factor of √5/2[8][citation needed], making it also a 4-queens solution.
See also[edit]
- Oversampling
- Multisample anti-aliasing
- Quincunx
- Graphics card
- Graphics processing unit
- Ray tracing (graphics)
- Framebuffer
- Game engine
- Image scaling
- 2×SaI
- Deep Learning Super Sampling
References[edit]
- ^ a b "Anti-aliasing techniques comparison". sapphirenation.net. 2016-11-29. Retrieved 2020-04-19.
Generally speaking, SSAA provides exceptional image quality, but the performance hit is major here because the scene is rendered at a very high resolution.
- ^ "What is supersampling?". everything2.com. 2004-05-20. Retrieved 2020-04-19.
- ^ a b c Allen Sherrod (2008). Game Graphic Programming. Charles River Media. p. 336. ISBN 978-1584505167.
- ^ Cook, R. L. (1986). "Stochastic sampling in computer graphics". ACM Transactions on Graphics. 5 (1): 51–72. doi:10.1145/7529.8927. S2CID 8551941.
- ^ Dunbar, Daniel; Humphreys, Greg (2006). "A spatial data structure for fast Poisson-disk sample generation". ACM SIGGRAPH 2006 Papers on - SIGGRAPH '06. p. 503. doi:10.1145/1179352.1141915. ISBN 1595933646. S2CID 13954223. Retrieved 7 January 2023.
- ^ Bridson, Robert (2007). "Fast Poisson disk sampling in arbitrary dimensions" (PDF). ACM SIGGRAPH 2007 sketches. p. 22. doi:10.1145/1278780.1278807. ISBN 9781450347266. S2CID 3129455. Retrieved 7 January 2023.
- ^ Dwork, N; Baron, CA; Johnson, EMI; O'Connor, D; Pauly, JM; Larson, PEZ (April 2021). "Fast variable density Poisson-disc sample generation with directional variation for compressed sensing in MRI". Magnetic Resonance Imaging. 77: 186–193. doi:10.1016/j.mri.2020.11.012. PMC 7878411. PMID 33232767.
- ^ "Super-sampling Anti-aliasing Analyzed" (PDF). Beyond3D.com. Retrieved 2020-04-19.
External links[edit]
- "High-Resolution Antialiasing (HRAA)". Technical Brief: High-Resolution Antialiasing through Multisampling. Retrieved 22 April 2017.
- "What is supersampling (antialiasing technique)?". Hardware Knowledgebase. Archived from the original on 2006-03-25. Retrieved 1 May 2006.
- Getreuer, Pascal (2011). "Image Interpolation with Contour Stencils". Image Processing on Line. 1: 70–82. doi:10.5201/ipol.2011.g_iics. Retrieved 21 October 2010.