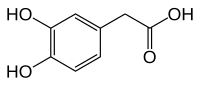
3,4-Dihydroxyphenylacetic acid
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)acetic acid | |
| Other names
2-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)acetic acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.750 |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | 3,4-Dihydroxyphenylacetic+Acid |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H8O4 | |
| Molar mass | 168.148 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
3,4-Dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC) is a metabolite of the neurotransmitter dopamine. Dopamine can be metabolized into one of three substances. One such substance is DOPAC. Another is 3-methoxytyramine (3-MT). Both of these substances are degraded to form homovanillic acid (HVA). Both degradations involve the enzymes monoamine oxidase (MAO) and catechol-O-methyl transferase (COMT), albeit in reverse order: MAO catalyzes dopamine to DOPAC, and COMT catalyzes DOPAC to HVA; whereas COMT catalyzes dopamine to 3-MT and MAO catalyzes 3-MT to HVA. The third metabolic end-product of dopamine is norepinephrine (noradrenaline).

It can also be found in the bark of Eucalyptus globulus.[1]
This product has been synthesized (52% yield) from 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid via aerobic biotransformation using whole cell cultures of Arthrobacter protophormiae.[2][3]
References
[edit]- ^ Santos, Sónia A. O.; Freire, Carmen S. R.; Domingues, M. Rosário M.; Silvestre, Armando J. D.; Neto, Carlos Pascoal (2011). "Characterization of Phenolic Components in Polar Extracts of Eucalyptus globulus Labill. Bark by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 59 (17): 9386–93. doi:10.1021/jf201801q. PMID 21761864.
- ^ Robins, Karen T.; Osorio-Lozada, Antonio; Avi, Manuela; Meyer, Hans-Peter (2009). "Lonza: Biotechnology – A Key Ingredient for Success in the Future". CHIMIA International Journal for Chemistry. 63 (6): 327–330. doi:10.2533/chimia.2009.327.
- ^ Sutton, Peter; Whittall, John (2012). Practical Methods for Biocatalysis and Biotransformations 2. Chichester, West Sussex: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. pp. 150–153. ISBN 9781119991397.
