2020 VT4
| Discovery [1][2] | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | ATLAS-MLO |
| Discovery site | Mauna Loa Obs. |
| Discovery date | 14 November 2020 |
| Designations | |
| 2020 VT4 | |
| A10sHcN [3][4] | |
| NEO · Apollo (pre-flyby)[5] Aten (post-flyby)[2] | |
| Orbital characteristics [2] | |
| Epoch 17 December 2020 (JD 2459200.5) (post-flyby as pre-flyby was very different) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 5 | |
| Observation arc | 5 days |
| Aphelion | 1.092 AU |
| Perihelion | 0.724 AU |
| 0.908 AU | |
| Eccentricity | 0.20299 |
| 0.86 yr (315.92 d) | |
| 143.860° | |
| 1° 8m 22.286s / day | |
| Inclination | 10.173° |
| 231.422° | |
| 14 November 2020 12:17 UT (pre-flyby)[5] | |
| 53.678° | |
| Earth MOID | 0.0002 AU |
| Physical characteristics | |
| 5–11 m (assumed)[6] | |
| 20.0 (current)[7] 17.3 (at discovery)[1] | |
| 28.66±0.50[5] 28.7[2] | |
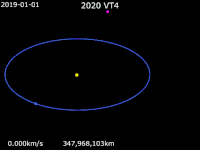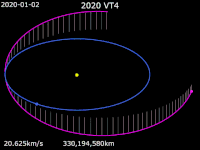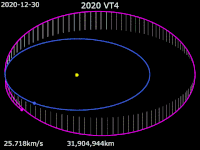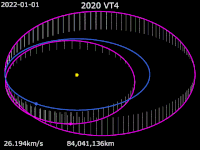
2020 VT4 is a tiny near-Earth asteroid that passed 370 km (230 mi) above Earth's surface on 13 November 2020 at 17:20 UTC.[a] The asteroid was discovered by the Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System (ATLAS) survey at the Mauna Loa Observatory fifteen hours after its closest approach to Earth.[b] The Earth encounter perturbed the asteroid's trajectory from an Earth-crossing Apollo-type orbit to an Aten-type orbit, subsequently reducing the asteroid's heliocentric orbital period from 1.5 years to 0.86 years.[5][2]
2020 VT4 passed closer to Earth than any known asteroid, except for those that became meteors. It passed closer than 2020 QG and 2011 CQ1, which passed about 3,000 km and 5,500 km from Earth's surface, respectively.[6] Given an estimated absolute magnitude of 28.7, 2020 VT4 is estimated to be around 5 to 10 metres in diameter. Had it impacted Earth, it would mostly have disintegrated during atmospheric entry and might have left a common strewn field.[4]
Discovery
[edit]2020 VT4 was discovered on 14 November 2020, by the Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System (ATLAS) survey at the Mauna Loa Observatory in Hawaii. The asteroid was discovered fifteen hours after its closest approach to Earth, moving about 0.28 degrees per hour across the constellation Fornax at an apparent magnitude of 17.3.[1][c] At the time of discovery, 2020 VT4 was about 0.003 astronomical units (450,000 km; 280,000 mi) from Earth and had a solar elongation of 134 degrees.[8]
The discovery was subsequently reported to the Minor Planet Center's Near-Earth Object Confirmation Page (NEOCP) under the internal designation A10sHcN.[3][4] Further refinements to the asteroid's preliminary trajectory were made with additional follow-up observations by the Galhassin Robotic Telescope, iTelescope Observatory, and the Glenlee Observatory. The asteroid was also identified in earlier observations by the Zwicky Transient Facility one hour before its discovery by ATLAS-MLO. The asteroid was then confirmed by the Minor Planet Center and announced with the provisional designation 2020 VT4 on 14 November 2020.[1]
Orbit and classification
[edit]2020 VT4 is currently on an Earth-crossing Aten-type orbit with an orbital semi-major axis of 0.908 AU (136 million km; 84.4 million mi) and an orbital period of 0.86 years or 316 days.[2] With a nominal perihelion distance of 0.724 AU and an aphelion distance of 1.092 AU, 2020 VT4's orbit extends from Venus to Earth, resulting in occasional close passes with these planets. The nominal minimum orbit intersection distances (MOID) with Venus and Earth are approximately 0.0351 AU (5,250,000 km; 3,260,000 mi) and 0.0002 AU (30,000 km; 19,000 mi), respectively.[4] 2020 VT4 has an orbital eccentricity of 0.203 and an inclination of 10.2 degrees to the ecliptic.[2]
Before the Earth encounter on 13 November 2020, 2020 VT4 had an Apollo-type orbit crossing the paths of Earth and Mars. It had a perihelion distance of 0.989 AU and a semi-major axis of 1.31 AU (196 million km; 122 million mi), with an orbital period of 1.5 years or 550 days. The orbit had an orbital eccentricity of 0.246 and an inclination of 12.9 degrees to the ecliptic. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory's Small-Body Database still provides an Apollo-type osculating orbit for 2020 VT4 based on the epoch 31 May 2020 (JD 2459000.5) before the Earth encounter; excluding all gravitational perturbations, the given orbit implies the asteroid would have passed perihelion 19 hours after it passed Earth.[5]
| Parameter | Epoch | Period (p) |
Aphelion (Q) |
Perihelion (q) |
Semi-major axis (a) |
Eccentricity (e) |
Inclination (i) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Units | (days) | AU | (°) | ||||
| Pre-flyby | 2020-May-31[5] | 549.2 | 1.636 | 0.989 | 1.313 | 0.2462 | 12.909° |
| Post-flyby | 2020-Dec-17[2][9] | 315.9 | 1.092 | 0.724 | 0.908 | 0.2028 | 10.161° |
2020 flyby
[edit]On 13 November 2020, 15 hours prior to its discovery, 2020 VT4 passed 373 ± 25 km (232 ± 16 mi) over the South Pacific Ocean at 17:20 UTC.[5][10] At this time of closest approach, 2020 VT4's on-sky position was close to the Sun with a minimum solar elongation of 36 degrees, making it unobservable to Earth-based telescopes.[11][12] 2020 VT4 passed closer to Earth than any known asteroid, except for those that became meteors. It passed closer than 2020 QG and 2011 CQ1, which passed about 3,000 km and 5,500 km from Earth's surface, respectively.[6]
| Asteroid | Date | Distance from surface of Earth |
Uncertainty in approach distance |
Observation arc | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 VT4 | 2020-11-13 17:21 | 368 km | ±11 km | 5 days (34 obs) | data |
| 2020 QG | 2020-08-16 04:09 | 2939 km | ±11 km | 2 days (35 obs) | data |
| 2021 UA1 | 2021-10-25 03:07 | 3049 km | ±10 km | 1 day (22 obs) | data |
| 2023 BU | 2023-01-27 00:29 | 3589 km | ±<1 km | 10 days (231 obs) | data |
| 2011 CQ1 | 2011-02-04 19:39 | 5474 km | ±5 km | 1 day (35 obs) | data |
| 2019 UN13 | 2019-10-31 14:45 | 6235 km | ±189 km | 1 day (16 obs) | data |
| 2008 TS26 | 2008-10-09 03:30 | 6260 km | ±970 km | 1 day (19 obs) | data |
| 2004 FU162 | 2004-03-31 15:35 | 6535 km | ±13000 km | 1 day (4 obs) | data |
See also
[edit]Notes
[edit]- ^ 2020 VT4's nominal closest approach distance from Earth's center is approximately 4.509×10−5 AU (0.01755 LD), or 6,745 km (4,191 mi). The asteroid's altitude from Earth's surface is the difference between the geocentric approach distance and Earth's radius: 6,745 – 6,371 = 374 km.
- ^ 2020 VT4 did not have a solar elongation greater than 90 degrees until about 10 minutes after closest approach.
- ^ The celestial coordinates of 2020 VT4 at the time of discovery were 02h 45m 59.46s −27° 18′ 36.9″.[1] See Fornax for constellation coordinates.
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d e "MPEC 2020-V152 : 2020 VT4". Minor Planet Electronic Circular. Minor Planet Center. 14 November 2020. Archived from the original on 14 November 2020. Retrieved 14 November 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "2020 VT4". Minor Planet Center. International Astronomical Union. Archived from the original on 3 December 2020. Retrieved 14 November 2020.
- ^ a b "2020 VT4". NEO Exchange. Las Cumbres Observatory. 14 November 2020. Archived from the original on 14 November 2020. Retrieved 14 November 2020.
- ^ a b c d ""Pseudo-MPEC" for A10sHcN = 2020 VT4". Project Pluto. 14 November 2020. Archived from the original on 14 November 2020. Retrieved 14 November 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f g "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: 2020 VT4" (2020-11-19 last obs.). Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Archived from the original on 15 November 2020. Retrieved 17 November 2020.
- ^ a b c "NEO Earth Close Approaches". Center for Near Earth Object Studies. Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Archived from the original on 19 October 2017. Retrieved 14 November 2020.
- ^ "2020VT4". Near Earth Objects – Dynamic Site. Department of Mathematics, University of Pisa, Italy. Archived from the original on 22 November 2020. Retrieved 14 November 2020.
- ^ "2020VT4 Ephemerides". Near Earth Objects – Dynamic Site (Ephemerides at discovery (obs. code T08)). Department of Mathematics, University of Pisa, Italy. Archived from the original on 27 November 2020. Retrieved 18 November 2020.
- ^ "Orbital Elements for Asteroid (2020 VT4)". Horizons output. Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Retrieved 14 November 2020. ("Ephemeris Type" select "Orbital Elements" · Set "Time Span" to 2020-Dec-17)
- ^ Irizarry, Eddie (16 November 2020). "This asteroid just skimmed Earth's atmosphere". EarthSky. Archived from the original on 16 November 2020. Retrieved 18 November 2020.
- ^ "2020VT4 Ephemerides". Near Earth Objects – Dynamic Site (Ephemerides at closest approach (geocentric)). Department of Mathematics, University of Pisa, Italy. Archived from the original on 3 December 2020. Retrieved 18 November 2020.
- ^ Dickinson, David (17 November 2020). "A Record Close Shave: Asteroid 2020 VT4 Just Skimmed by Earth". Universe Today. Archived from the original on 17 November 2020. Retrieved 18 November 2020.
External links
[edit]- "Pseudo-MPEC" for A10sHcN Archived 14 November 2020 at the Wayback Machine, Project Pluto, 14 November 2020
- 2020 VT4 at NeoDyS-2, Near Earth Objects—Dynamic Site
- 2020 VT4 at ESA–space situational awareness
- 2020 VT4 at the JPL Small-Body Database