Aralosaurini
| Aralosaurini Temporal range: Late Cretaceous,
| |
|---|---|
| |
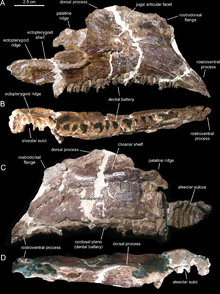
| Right maxilla (Holotype) of Canardia garonnensis from the basal part of the Marnes d'Auzas Formation.[1] | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Dinosauria |
| Clade: | †Ornithischia |
| Clade: | †Ornithopoda |
| Family: | †Hadrosauridae |
| Subfamily: | †Lambeosaurinae |
| Tribe: | †Aralosaurini Prieto-Márquez et al., 2013 |
| Type species | |
| †Aralosaurus tuberiferus Rozhdestvensky, 1968
| |
| Genera | |
Aralosaurini is a proposed tribe of hadrosaurid dinosaurs belonging to the subfamily Lambeosaurinae. The members of this group lived in Asia and Europe during the end of the Late Cretaceous about 83.6 to 66.0 million years ago. The clade may not be monophyletic, with Canardia and Aralosaurus potentially instead being unrelated primitive members of the subfamily.
Description[edit]
The Aralosaurini are distinguished by their maxilla whose anterior part is elevated dorsally. More precisely, the rostrodorsal region of the bone widens to form a prominent subrectangular flange, which rises vertically above the rostroventral process.[1]
Aralosaurus was previously reconstituted with a nasal boss similar to that of Gryposaurus and classified as a member of Hadrosaurinae.[2] A new study of the incomplete skull of the animal showed that the fragmentary nasal was in fact a portion of a hollow structure that communicated with the respiratory system. Which is a typical lambeosaurine feature.[3] Given the fragmentary nature of the nasal, the size and shape of the hollow structure of Aralosaurus are still unknown, but it was located far in front of the orbits, which is a primitive position in lambeosaurine.[3] In Canardia, the too fragmentary state of the skull does not say anything about the presence of a crest.[1]
Phylogeny[edit]

This clade was found by the study first naming it to contain only Aralosaurus from the Late Santonian-Early Campanian of Kazakhstan and Canardia from the Late Maastrichtian of France.[1]
The following cladogram was produced by Xing Hai and his colleagues in 2022 and shows the phylogeny of Lambeosaurinae. Aralosaurus and its close relative Canardia are included in the tribe of Aralosaurini, which are identified as the most basal members of Lambeosaurinae.[4]
Other recent phylogenetic analyses have failed to recover Canardia and Aralosaurus forming a monophyletic clade.[5][6][7]
Palaeoecology[edit]
The Aralosaurini appear to have preferred coastal wetland habitats. Aralosaurus lived on the west coast of the Asian continent bordering the Turgai Sea,[8] while Canardia lived on the west coast of the Ibero-Armorican island bordering the Atlantic Gulf.[9]
References[edit]
- ^ a b c d Prieto-Márquez, A.; Dalla Vecchia, F.M.; Gaete, R.; Galobart, À. (2013). "Diversity, Relationships, and Biogeography of the Lambeosaurine Dinosaurs from the European Archipelago, with Description of the New Aralosaurin Canardia garonnensis". PLOS ONE. 8 (7): 1–44. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...869835P. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0069835. PMC 3724916. PMID 23922815.
- ^ Rozhdestvensky, A.K. (1968). "Gadrozavry Kazakhstana [Hadrosaurs of Kazakhstan]. [Upper Paleozoic and Mesozoic Amphibians and Reptiles]" (PDF). Akademia Nauk SSSR, Moscow: 97–141.
- ^ a b c Godefroit, P.; Alifanov, V.; Boltsky, Y. (2004). "A re-appraisal of "Aralosaurus tuberiferus" (Dinosauria, Hadrosauridae) from the Late Cretaceous of Kazakhstan". Bulletin de l'Institut Royal des Sciences Naturelles de Belgique, Sciences de la Terre. 74 (Suppl): 139–154.
- ^ Xing, Hai; Gu, Wei; Hai, Shulin; Yu, Tingxiang; Han, Dong; Zhang, Yuguang; Zhang, Shujun (2022). "Osteological and taxonomic reassessments of Sahaliyania elunchunorum (Dinosauria, Hadrosauridae) from the Upper Cretaceous Yuliangzi Formation, northeast China". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 41 (6): e2085111. doi:10.1080/02724634.2021.2085111. S2CID 250463301.
- ^ Gates, Terry A.; Evans, David C.; Sertich, Joseph J. W. (2021). "Description and rediagnosis of the crested hadrosaurid (Ornithopoda) dinosaur Parasaurolophus cyrtocristatus on the basis of new cranial remains". PeerJ. 9: e10669. doi:10.7717/peerj.10669. PMC 7842145. PMID 33552721.
- ^ Longrich, Nicholas R.; Suberbiola, Xabier Pereda; Pyron, R. Alexander; Jalil, Nour-Eddine (2020). "The first duckbill dinosaur (Hadrosauridae: Lambeosaurinae) from Africa and the role of oceanic dispersal in dinosaur biogeography". Cretaceous Research. 120: 104678. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2020.104678. S2CID 228807024.
- ^ Serrano-Brañas, Claudia Inés; Prieto-Márquezc, Albert (2022). "Taphonomic attributes of the holotype of the lambeosaurine dinosaur Latirhinus uitstlani from the late Campanian of Mexico: Implications for its phylogenetic systematics". Journal of South American Earth Sciences. 114: 103689. Bibcode:2022JSAES.11403689S. doi:10.1016/j.jsames.2021.103689.
- ^ Averianov, A.; Dyke, G.; Danilov, I.; Skutschas, P. (2015). "The paleoenvironments of azhdarchid pterosaurs localities in the Late Cretaceous of Kazakhstan". ZooKeys (483): 59–80. doi:10.3897/zookeys.483.9058. PMC 4351447. PMID 25755624.
- ^ Csiki-Sava, Z.; Buffetaut, E.; Ősi, A.; Pereda-Suberbiola, X.; Brusatte, S.L. (2015). "Island life in the Cretaceous-faunal composition, biostratigraphy, evolution, and extinction of land-living vertebrates on the Late Cretaceous European archipelago". ZooKeys (469): 1–161. doi:10.3897/zookeys.469.8439. PMC 4296572. PMID 25610343.








