Drepanosaur
| Drepanosaurs Temporal range: Late Triassic,
| |
|---|---|

| |
| Fossil specimen of Drepanosaurus unguicaudatus | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Clade: | Neodiapsida |
| Clade: | †Drepanosauromorpha Renesto et al., 2010 |
| Subgroups | |
| |
Drepanosaurs (members of the clade Drepanosauromorpha) are a group of extinct reptiles that lived between the Carnian and Rhaetian stages of the late Triassic Period, approximately between 230 and 210 million years ago.[1] The various species of drepanosaurs were characterized by a bird-like skull, a barrell shaped body, and a horizontally narrow tail. A number of drepanosaurs had specialized grasping limbs and often prehensile tails similar to those of chameleons. Drepanosaurs are generally thought to have been arboreal (tree-dwelling),[2] and probably insectivores.[3] Some studies have alternately suggested fossorial (digging) and aquatic lifestyles for some members.[4] Fossils of drepanosaurs have been found in North America (Arizona, New Mexico, New Jersey, Utah) and Europe (England and northern Italy). The name is taken from the family's namesake genus Drepanosaurus, which means "sickle lizard," a reference to their strongly curved claws.
Some studies have included Drepanosaurs within the group Avicephala, which also includes the gliding Weigeltisauridae, but the close relationship between the two groups has been doubted by other authors. Their phylogenetic position has been disputed, with some studies considering them to be members of Archosauromorpha (and thus more closely related to modern birds and crocodilians than to lizards), while other studies have considered them to be basal neodiapsids that are not related to any modern reptiles.[2]
Description
[edit]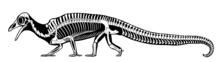
Drepanosaurs are notable for their distinctive, triangular skulls, which resemble the skulls of birds. Some drepanosaurs, such as Avicranium, had pointed, toothless, bird-like beaks. This similarity to birds may have led to the misattribution of what may be a drepanosaur skull to the would-be "first bird," Protoavis.[5]

Drepanosaurs featured a suite of bizarre, almost chameleon-like skeletal features. Above the shoulders of most species was a specialized "hump" formed from fusion of the vertebrae, possibly used for advanced muscle attachments to the neck, and allowing for quick forward-striking movement of the head (perhaps to catch insects). Many had derived hands with two fingers opposed to the remaining three, an adaptation for grasping branches. Some individuals of Megalancosaurus (possibly exclusive to either males or females) had a primate-like opposable toe on each foot, perhaps used by one sex for extra grip during mating. Most species had broad, prehensile tails, sometimes tipped with a large "claw," again to aid in climbing. These tails, tall and flat like those of newts and crocodiles, have led some researches to conclude that they were aquatic rather than arboreal. In 2004, Senter dismissed this idea, while Colbert and Olsen, in their description of Hypuronector, state that while other drepanosaurs were probably arboreal, Hypuronector was uniquely adapted to aquatic life.[6] The tail of this genus was extremely deep and non-prehensile: much more fin-like than members of the more exclusive group Drepanosauridae.[7] Aerial locomotion has been attributed to at least two drepanosaur genera: Megalancosaurus and Hypuronector. The first was originally suggested by Ruben et al. 1998 on the basis of bird-like characters and limb proportions.[8] While the suggestion has not been ruled out entirely, it has since been largely dismissed, due to Megalancosaurus' clunky, chameleon-like anatomy.[5] Hypuronector, however, is much more likely to be a glider or flyer due to the elongated forelimbs.[9] Fossorial or digging-related adaptations have been recognized in three drepanosaur genera: Skybalonyx, Ancistronychus, and Drepanosaurus. In particular, Drepanosaurus may have been adapted to hook-and-pull digging, similar to modern-day anteaters. Skybalonyx possessed claws similar in shape to modern-day moles and echidna, both of which are humeral-rotation diggers.[4]

The phylogenetic position of drepanosaurs is highly disputed. Various studies have proposed that drepanosaurs are protorosaurian archosauromorphs,[10] lepidosauromorphs related to kuehneosaurids,[11] non-saurian diapsids related to weigeltisaurids,[6] or (most recently) basal neodiapsids.[12]
Early studies
[edit]When Drepanosaurus and Dolabrosaurus were first discovered (in 1980 and 1992, respectively), they were each considered early lepidosaurians, ancestral to modern lizards. Megalancosaurus was first believed to be a thecodont (i.e. an archosauriform) upon its discovery in 1980, but later studies placed it as a prolacertiform, and perhaps even an ancestor to birds, although this latter hypothesis has not been supported by subsequent studies.[12]
Drepanosaurs outside Neodiapsida: Avicephala and Simiosauria
[edit]A 2004 study by Senter placed drepanosaurs with the coelurosauravids (weigeltisaurids) and Longisquama in a clade called which he called Avicephala. Senter's analysis placed Avicephala within Diapsida but outside Neodiapsida, defined by Senter as the clade containing "all taxa phylogenetically bracketed by Younginiformes and living diapsids."[6][13]
Within Avicephala, Senter named the group Simiosauria ("monkey lizards") for the extremely derived tree-dwelling forms. Simiosauria was defined as "all taxa more closely related to Drepanosauridae than to Coelurosauravus or Sauria." However, Renesto and colleagues (see below) found drepanosaurids to lie within Sauria, which would make the clade Simiosauria obsolete. Senter found that Hypuronector, originally described as a drepanosaurid, actually lies just outside that clade, along with the primitive drepanosaur Vallesaurus. He also recovered a close relationship between the drepanosaurids Dolabrosaurus and Megalancosaurus.[6]
The following cladogram was proposed by Senter in his 2004 analysis:[6]
| Simiosauria |
| ||||||||||||
A clade containing drepanosaurids, Longisquama, and Coelurosauravus (as well as Wapitisaurus) was also recovered in a 2003 analysis conducted by John Merck; however, in Merck's analysis this clade was nested within Neodiapsida as the sister taxon of Sauria.[14]

In a 2006 study, Renesto and Binelli found that when pterosaur Eudimorphodon was added to Senter's original matrix, it was found to be a member of Avicephala.[15] The authors also conducted a second analysis, this time based on a character set and matrix updated by scoring additional characters previously reported as unknown and by adding a few relevant characters. This analysis recovered drepanosaurids as the sister taxon of Eudimorphodon; the clade containing pterosaurs and drepanosaurids was recovered as the sister taxon of Archosauriformes. Longisquama and Coelurosauravus were not found to be closely related to drepanosaurids, but instead were recovered as non-neodiapsid diapsids as in Senter's analysis. However, it is feasible that this arrangement might be a result of poor knowledge of Longisquama rather than a reflection of its true phylogenetic position. The authors did note that there are similarities in the structure of the forelimb and shoulder regions of Longisquama and all or some drepanosaurids (e.g. the humerus of both Longisquama and Vallesaurus is as long as the fourth digit of the manus). They stressed that they could not rule out the possibility that at least some of the similarities are convergent due to a similar behaviors, and that they did not examine Longisquama firsthand. Therefore, further studies of drepanosaurids should take the hypothesis that Longisquama might be a drepanosaurid into consideration.[15]
Drepanosaurs as relatives of kuehneosaurids
[edit]Drepanosaurids were also found to be non-saurian neodiapsids in a 2004 analysis conducted by Johannes Müller; however, in this analysis Drepanosauridae were not found to be closely related to Coelurosauravus, but rather were recovered as the sister taxon of Kuehneosauridae.[16] In a 2009 study, Susan E. Evans conducted a phylogenetic analysis using a modified version of Müller's matrix. Evans also recovered Drepanosauridae as the sister taxon of the clade containing basal kuehneosaurid Pamelina and the rest of Kuehneosauridae; however, unlike Müller's analysis, drepanosaurids and kuehneosaurids were recovered as non-lepidosaurian lepidosauromorphs. Evans did note that the two families share few synapomorphies, with Müller citing only two. One of them is the increased angulation of the zygapophyses in the posterior dorsal vertebrae; Evans noted that this character is also present in the skeletons of lizards belonging to the modern genus Draco "and is likely to be functional (and thus potentially convergent)." The other synapomorphy, the enclosed thyroid fenestra in the pelvis, "may be variable in the British kuehneosaurs and remains unknown in Pamelina," according to Evans. The author also noted that there are many differences between the skulls of drepanosaurids and kuehneosaurids, and that the only skull characters shared by members of both families are primitive neodiapsid characters and thus cannot be used to support a close relationship between the two clades.[11]
Drepanosaurs as archosauromorphs and the abandonment of Avicephala
[edit]In 1998, Dilkes argued that drepanosaurs were close relatives of tanystropheids, and his phylogenetic analysis has been used by many other authors.[10] Gottmann-Quesada and Sander (2009) included one member of Drepanosauridae, Megalancosaurus, in their analysis of archosauromorph relationships; it was found to be one of the most basal known members of Archosauromorpha and the sister taxon of Protorosaurus.[17]
In a later study, Renesto et al.[1] demonstrated that Senter's 2004 cladogram was based on poorly defined characters and data. The resulting phylogeny was therefore very unusual compared to any other previous study on drepanosaurs or related taxa. The new cladogram proposed in this last study abandoned both Avicephala (because it was polyphyletic) and Simiosauria. Senter's definition of Simiosauria included Sauria as an external specifier, causing the clade to become obsolete in Renesto et al.'s study (where drepanosaurs nested within Sauria). Renesto and colleagues instead defined a new clade, Drepanosauromorpha, as the least inclusive clade containing Hypuronector limnaios and Megalancosaurus preonensis. A more inclusive taxon, Elyurosauria ("lizard with coiled tail"), was erected in order to include all the drepanosaurs with coiled tails. Vallesaurus is thus more derived than Hypuronector (as shown by its morphology). Drepanosaurus and Megalancosaurus were also placed in a new taxon named Megalancosaurinae.
The alternative cladogram presented in Renesto et al. (2010).[1]
| Drepanosauromorpha |
| ||||||||||||||||||
Renesto et al. (2010) used modified versions of the matrices from the earlier analyses of Laurin (1991)[18] and Dilkes (1998)[10] in order to determine the phylogenetic position of Drepanosauromorpha within Diapsida. The analyses using Laurin's matrix recovered drepanosaurs either as the sister group of the clade containing Prolacerta, Trilophosaurus and Hyperodapedon, (Archosauromorpha), or in unresolved polytomy with Archosauromorpha and Lepidosauromorpha. The analyses using Dilkes' matrix recovered drepanosaurs either as "protorosaur" archosauromorphs and the sister taxon to the clade containing Tanystropheus, Langobardisaurus and Macrocnemus, or in unresolved polytomy with Lepidosauromorpha, Choristodera and several archosauromorph clades. Renesto et al. (2010) concluded that avicephalan synapomorphies proposed by Senter (2004) are merely evolutionary convergences caused by common lifestyle shared by drepanosaurids, coelurosauravids and Longisquama. The authors did not rule out the possibility that drepanosaurs and Longisquama might really be close relatives.[1]
The phylogenetic study published by Buffa et al. (2024) did not recover "avicephalans" as closely related. The authors' phylogenetic analysis recovered Drepanosauromorpha as allokotosaurian archosauromorphs, specifically as the sister group of trilophosaurids.[2]
Drepanosaurs as basal diapsids
[edit]In 2017, Pritchard and Nesbitt employed a phylogenetic analysis in their description of Avicranium, a new genus of drepanosaur. This study found that Drepanosauromorpha was one of the earliest diverging groups of diapsids in the analysis, even more basal than weigeltisaurids (such as Coelurosauravus), tangasaurids (such as Hovasaurus), and younginids (such as Youngina). However, they were not found to be as basal as Petrolacosaurus, one of the earliest and most primitive diapsids known. Although drepanosaurs are only known from the late Triassic, this new finding suggests that the first members of the drepanosauromorph lineage may have evolved much earlier, in the Permian (about 260 million years ago).[12]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d Renesto, S.C.; Spielmann, J.A.; Lucas, S.G. (2009-05-29). "The oldest record of drepanosaurids (Reptilia, Diapsida) from the Late Triassic (Adamanian Placerias Quarry, Arizona, USA) and the stratigraphic range of the Drepanosauridae". Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie - Abhandlungen. 252 (3): 315–325. doi:10.1127/0077-7749/2009/0252-0315. ISSN 0077-7749.
- ^ a b c Buffa, Valentin; Frey, Eberhard; Steyer, J-Sébastien; Laurin, Michel (2024-05-11). "'Birds' of two feathers: Avicranium renestoi and the paraphyly of bird-headed reptiles (Diapsida: 'Avicephala')". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. doi:10.1093/zoolinnean/zlae050. ISSN 0024-4082.
- ^ Castiello, Marco; Renesto, Silvio; Bennett, S. Christopher (2016-11-16). "The role of the forelimb in prey capture in the Late Triassic reptile Megalancosaurus (Diapsida, Drepanosauromorpha)". Historical Biology. 28 (8): 1090–1100. doi:10.1080/08912963.2015.1107552. ISSN 0891-2963.
- ^ a b Jenkins, X.A.; Pritchard, A.C.; Marsh, A.D.; Kligman, B.T.; Sidor, C.A.; Reed, K.E. (2020-10-08). "Using manual ungual morphology to predict substrate use in the Drepanosauromorpha and the description of a new species". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 40 (5): e1810058. doi:10.1080/02724634.2020.1810058. ISSN 0272-4634. S2CID 225136171.
- ^ a b Renesto, S. (2000-07-31). "Bird-like head on a chameleon body: New specimens of the enigmatic diapsid reptile Megalancosaurus from the Late Triassic of Northern Italy". Rivista italiana di Paleontologia e Stratigrafia. 106 (2): 157–179. doi:10.13130/2039-4942/5396.
- ^ a b c d e Senter, P. (2004). "Phylogeny of Drepanosauridae (Reptilia: Diapsida)". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 2 (3): 257–268. doi:10.1017/s1477201904001427. ISSN 1477-2019. S2CID 83840423.
- ^ Colbert, E.H.; Olsen, P.E. (2001-06-22). "A New and Unusual Aquatic Reptile from the Lockatong Formation of New Jersey (Late Triassic, Newark Supergroup)". American Museum Novitates (3334): 1–24. doi:10.1206/0003-0082(2001)334<0001:anauar>2.0.co;2. ISSN 0003-0082. S2CID 17294610.
- ^ Schoch, R.R. (2007-11-29). "Osteology of the small archosaur Aetosaurus from the Upper Triassic of Germany". Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie - Abhandlungen. 246 (1): 1–35. doi:10.1127/0077-7749/2007/0246-0001. ISSN 0077-7749.
- ^ Renesto, S.; Spielmann, J.A.; Lucas, S.G.; Spagnoli, G.T. (2010). The taxonomy and paleobiology of the Late Triassic (Carnian-Norian: Adamanian-Apachean) drepanosaurs (Diapsida: Archosauromorpha: Drepanosauromorpha). Albuquerque, NM, US: New Mexico Museum of Natural History and Science. OCLC 550640808.
- ^ a b c Dilkes, D.M. (1998). "The Early Triassic rhynchosaur Mesosuchus browni and the interrelationships of basal archosauromorph reptiles". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, Series B. 353 (1368): 501–541. doi:10.1098/rstb.1998.0225. PMC 1692244.
- ^ a b Evans, S.E. (2009). "An early kuehneosaurid reptile from the Early Triassic of Poland" (PDF). Palaeontologia Polonica. 65: 145–178.
- ^ a b c Pritchard, A.C.; Nesbitt, S.J. (2017-10-01). "A bird-like skull in a Triassic diapsid reptile increases heterogeneity of the morphological and phylogenetic radiation of Diapsida". Royal Society Open Science. 4 (10): 170499. Bibcode:2017RSOS....470499P. doi:10.1098/rsos.170499. ISSN 2054-5703. PMC 5666248. PMID 29134065.
- ^ Renesto, S. (1994-03-31). "Megalancosaurus, a possibly arboreal archosauromorph (Reptilia) from the Upper Triassic of northern Italy". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 14 (1): 38–52. doi:10.1080/02724634.1994.10011537. ISSN 0272-4634.
- ^ Merck, J. (2003). "An arboreal radiation of non-saurian diapsids". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 23 (Supplement to 3): 78A. doi:10.1080/02724634.2003.10010538. S2CID 220410105.
- ^ a b Renesto, S.; Binelli, G. (2006-03-31). "Vallesaurus cenensis WILD, 1991, a drepanosaurid (Reptilia, Diapsida) from the Late Triassic of northern Italy". Rivista italiana di Paleontologia e Stratigrafia. 112 (1): 77–94. doi:10.13130/2039-4942/5851.
- ^ Müller, J. (2004). "The relationships among diapsid reptiles and the influence of taxon selection". In Arratia, G.; Wilson, M.V.H.; Cloutier, R. (eds.). Recent Advances in the Origin and Early Radiation of Vertebrates. Verlag Dr. Friedrich Pfeil. pp. 379–408. ISBN 978-3-89937-052-2.
- ^ Gottmann-Quesada, A.; Sander, P.M. (2009-03-19). "A redescription of the early archosauromorph Protorosaurus speneri MEYER, 1832, and its phylogenetic relationships". Palaeontographica Abteilung A. 287 (4–6): 123–220. doi:10.1127/pala/287/2009/123.
- ^ Laurin, M. (1991). "The osteology of a Lower Permian eosuchian from Texas and a review of diapsid phylogeny". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 101 (1): 59–95. doi:10.1111/j.1096-3642.1991.tb00886.x.
External links
[edit]- Monkey Lizards of the Triassic - An illustrated article on drepanosaurs from HMNH.
- Prof. Silvio Renesto—Vertebrate Paleontology at Insubria University: Research - Images and discussion of Drepanosaurus.
- Prof. Silvio Renesto—Vertebrate Paleontology at Insubria University: Research - Images and discussion of Megalancosaurus.





