File:Loanable funds, money multiplier, money creation (3 types of theories) without almost forgotten Credit Mechanics (table by IMF 2019).png

Size of this preview: 800 × 393 pixels. Other resolutions: 320 × 157 pixels | 904 × 444 pixels.
Original file (904 × 444 pixels, file size: 91 KB, MIME type: image/png)
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
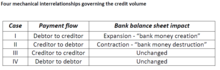
| current | 12:52, 29 August 2023 |  | 904 × 444 (91 KB) | Carlbrandner | {{Information |Description=Table: Three types and views of different [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Money_supply money supply] theories. |Source=International Monetary Fund (IMF), Gross, Siebenbrunner: [https://www.oecd.org/naec/new-economic-policymaking/Money_Creation_and_Liquid_Funding_Needs_%20NAEC_Siebenbrunner.pdf ''Money Creation and Liquid Funding Needs''] (PDF), p. 2. |Date=2019 |Author=Marco Gross (IMF), Christoph Siebenbrunner (Oxford University) |permission= {{PD-shape}}[[Category... |
File usage
The following pages on the English Wikipedia use this file (pages on other projects are not listed):
Global file usage
The following other wikis use this file:
- Usage on de.wikipedia.org