Ramban district
Ramban district | |
|---|---|
 View of Ramban | |
 Interactive map of Ramban district | |
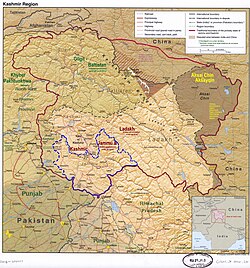 Ramban district is in the Jammu division (shown with neon blue boundary) of Indian-administered Jammu and Kashmir (shaded in tan in the Kashmir region of India | |
| Coordinates (Ramban): 33°14′N 75°14′E / 33.24°N 75.24°E | |
| Administering country | India |
| Union Territory | Jammu and Kashmir |
| Division | Jammu Division |
| Region | Chenab Valley |
| Headquarters | Ramban |
| Tehsils |
|
| Area | |
• Total | 1,329 km2 (513 sq mi) |
| Population (2011) | |
• Total | 283,713 |
| • Density | 210/km2 (550/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 4.16% [2] |
| Demographics | |
| • Literacy | 54.27% [3] |
| • Sex ratio | 902 |
| Languages | |
| • Spoken | Kashmiri, Pogali, Urdu & Gojri |
| • Official | Kashmiri, Dogri, English & Urdu [4][5] |
| Time zone | UTC+05:30 (IST) |
| Vehicle registration | JK-19 |
| Major highways | NH-44 |
| Website | http://ramban.gov.in |
Ramban district is an administrative district in the Jammu division of Indian-administered Jammu and Kashmir in the disputed Kashmir region.[1] It is located in a valley surrounded the Pir Panjal range. It was carved out as a separate district from erstwhile Doda district in 2007.[6] It is located in the Jammu division. The district headquarters are at Ramban town, which is located midway between Jammu and Srinagar along the Chenab river in the Chenab valley on National Highway-44, approximately 151 km from Jammu and Srinagar.[7]
Administration
[edit]Ramban District is divided into eight tehsils: Banihal, Ramban, Khari, Rajgarh, Batote, Gool, Pogal Paristan (Ukhral) and Ramsoo.[8]
Each tehsil has its tehsildar, who is the administrative head. The district consisted of 116 census villages and 127 revenue villages in 2001. The total number of panchayat Halqas in the district was 124.
District Development Council Ramban
[edit]In the elections for Ramban's District Development Council, Shamshad Begum was elected chairman and Rabiya Beigh was elected vice-chairman.[9]
Geography
[edit]Ramban district is 1,156 metres (3,792 feet) above sea level (on average). The boundary lines of Ramban district encompass hill station Patnitop as its southernmost point, Assar on its eastern edge, Gool to the west, and Banihal to the north. The terrain of district Ramban is tough and hilly. District Ramban shares its boundary with Reasi, Udhampur, Doda, Anantnag and Kulgam districts.[6]
Climate
[edit]The climate of the district varies according to altitude. The temperature rises as high as 42 °C in the low-lying areas like Ramban town located in between steep mountains on the banks of Chenab River and drops to sub-zero in high-altitude areas like Sangaldan, Gool, Dhagantop, Asthanmarg, Lalagundi, Budhan, Pogal, Paristan, Neel. The working season in most of the district is about eight months because of weather conditions in the district.
Politics
[edit]Ramban district has two assembly constituencies: Ramban and Banihal.[10]
On 21 January 2021, Ramban district was declared a 'terrorist free' district in Jammu and Kashmir.[11]
Demographics
[edit]| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1901 | 46,580 | — |
| 1911 | 50,305 | +8.0% |
| 1921 | 51,062 | +1.5% |
| 1931 | 57,361 | +12.3% |
| 1941 | 61,720 | +7.6% |
| 1951 | 71,242 | +15.4% |
| 1961 | 80,764 | +13.4% |
| 1971 | 105,767 | +31.0% |
| 1981 | 130,569 | +23.4% |
| 1991 | 168,962 | +29.4% |
| 2001 | 214,944 | +27.2% |
| 2011 | 283,713 | +32.0% |
| source:[12] † 1951 and 1991 populations are estimated | ||
According to the 2011 census, Ramban district has a population of 283,713.[13] roughly equal to the nation of Barbados.[14] This gives it a ranking of 573rd in India (out of a total of 640).[13] The district has a population density of 213 inhabitants per square kilometre (550/sq mi) .[13] Its population growth rate over the decade 2001-2011 was 31.81%.[13] Ramban has a sex ratio of 902 females for every 1000 males,[13] and a literacy rate of 54.27%.[13]
| Ramban district: religion, gender ratio, and % urban of population, according to the 2011 Census.[15] | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hindu | Muslim | Christian | Sikh | Buddhist | Jain | Other | Not stated | Total | |
| Total | 81,026 | 200,516 | 414 | 753 | 43 | 3 | 252 | 706 | 283,713 |
| 28.56% | 70.68% | 0.15% | 0.27% | 0.02% | 0.00% | 0.09% | 0.25% | 100.00% | |
| Male | 43,844 | 104,078 | 253 | 427 | 24 | 2 | 132 | 372 | 149,132 |
| Female | 37,182 | 96,438 | 161 | 326 | 19 | 1 | 120 | 334 | 134,581 |
| Gender ratio (% female) | 45.9% | 48.1% | 38.9% | 43.3% | 44.2% | 33.3% | 47.6% | 47.3% | 47.4% |
| Sex ratio (no. of females per 1,000 males) |
848 | 927 | – | 763 | – | – | – | 898 | 902 |
| Urban | 5,087 | 6,224 | 70 | 405 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 22 | 11,811 |
| Rural | 75,939 | 194,292 | 344 | 348 | 42 | 2 | 251 | 684 | 271,902 |
| % Urban | 6.3% | 3.1% | 16.9% | 53.8% | 2.3% | 33.3% | 0.4% | 3.1% | 4.2% |
Tourist attractions
[edit]Sanasar
[edit]
Tourist activities Sanasar include paragliding, hot air ballooning, trekking, camping, golf, rock climbing and abseiling.[17]
Major projects
[edit]- Baglihar Dam
- Pir Panjal Railway Tunnel
- Banihal Qazigund Road Tunnel
- Dr. Syama Prasad Mookerjee Tunnel
- Sangaldan Railway Station
- Sangaldan Tunnel
See also
[edit]- Adhwa
- Baglihar Dam
- Banihal
- Banihal Pass
- Chanderkot
- Chenab Valley
- Doda District
- Jammu and Kashmir
- Badshah Khan (wrestler)
- Maitra
- Pir Panjal Range
- Ramban
- Sangaldan
References
[edit]- ^ a b The application of the term "administered" to the various regions of Kashmir and a mention of the Kashmir dispute is supported by the tertiary sources (a) through (d), reflecting due weight in the coverage. Although "controlled" and "held" are also applied neutrally to the names of the disputants or to the regions administered by them, as evidenced in sources (f) through (h) below, "held" is also considered politicized usage, as is the term "occupied," (see (i) below).
(a) Kashmir, region Indian subcontinent, Encyclopaedia Britannica, retrieved 15 August 2019 (subscription required) Quote: "Kashmir, region of the northwestern Indian subcontinent ... has been the subject of dispute between India and Pakistan since the partition of the Indian subcontinent in 1947. The northern and western portions are administered by Pakistan and comprise three areas: Azad Kashmir, Gilgit, and Baltistan, the last two being part of a territory called the Northern Areas. Administered by India are the southern and southeastern portions, which constitute the state of Jammu and Kashmir but are slated to be split into two union territories.";
(b) Pletcher, Kenneth, Aksai Chin, Plateau Region, Asia, Encyclopaedia Britannica, retrieved 16 August 2019 (subscription required) Quote: "Aksai Chin, Chinese (Pinyin) Aksayqin, portion of the Kashmir region, at the northernmost extent of the Indian subcontinent in south-central Asia. It constitutes nearly all the territory of the Chinese-administered sector of Kashmir that is claimed by India to be part of the Ladakh area of Jammu and Kashmir state.";
(c) "Kashmir", Encyclopedia Americana, Scholastic Library Publishing, 2006, p. 328, ISBN 978-0-7172-0139-6 C. E Bosworth, University of Manchester Quote: "KASHMIR, kash'mer, the northernmost region of the Indian subcontinent, administered partlv by India, partly by Pakistan, and partly by China. The region has been the subject of a bitter dispute between India and Pakistan since they became independent in 1947";
(d) Osmańczyk, Edmund Jan (2003), Encyclopedia of the United Nations and International Agreements: G to M, Taylor & Francis, pp. 1191–, ISBN 978-0-415-93922-5 Quote: "Jammu and Kashmir: Territory in northwestern India, subject to a dispute betw een India and Pakistan. It has borders with Pakistan and China."
(e) Talbot, Ian (2016), A History of Modern South Asia: Politics, States, Diasporas, Yale University Press, pp. 28–29, ISBN 978-0-300-19694-8 Quote: "We move from a disputed international border to a dotted line on the map that represents a military border not recognized in international law. The line of control separates the Indian and Pakistani administered areas of the former Princely State of Jammu and Kashmir.";
(f) Kashmir, region Indian subcontinent, Encyclopaedia Britannica, retrieved 15 August 2019 (subscription required) Quote: "... China became active in the eastern area of Kashmir in the 1950s and has controlled the northeastern part of Ladakh (the easternmost portion of the region) since 1962.";
(g) Bose, Sumantra (2009), Kashmir: Roots of Conflict, Paths to Peace, Harvard University Press, pp. 294, 291, 293, ISBN 978-0-674-02855-5 Quote: "J&K: Jammu and Kashmir. The former princely state that is the subject of the Kashmir dispute. Besides IJK (Indian-controlled Jammu and Kashmir. The larger and more populous part of the former princely state. It has a population of slightly over 10 million, and comprises three regions: Kashmir Valley, Jammu, and Ladakh.) and AJK ('Azad" (Free) Jammu and Kashmir. The more populous part of Pakistani-controlled J&K, with a population of approximately 2.5 million. AJK has six districts: Muzaffarabad, Mirpur, Bagh, Kodi, Rawalakot, and Poonch. Its capital is the town of Muzaffarabad. AJK has its own institutions, but its political life is heavily controlled by Pakistani authorities, especially the military), it includes the sparsely populated "Northern Areas" of Gilgit and Baltistan, remote mountainous regions which are directly administered, unlike AJK, by the Pakistani central authorities, and some high-altitude uninhabitable tracts under Chinese control."
(h) Fisher, Michael H. (2018), An Environmental History of India: From Earliest Times to the Twenty-First Century, Cambridge University Press, p. 166, ISBN 978-1-107-11162-2 Quote: "Kashmir’s identity remains hotly disputed with a UN-supervised “Line of Control” still separating Pakistani-held Azad (“Free”) Kashmir from Indian-held Kashmir.";
(i) Snedden, Christopher (2015), Understanding Kashmir and Kashmiris, Oxford University Press, p. 10, ISBN 978-1-84904-621-3 Quote:"Some politicised terms also are used to describe parts of J&K. These terms include the words 'occupied' and 'held'." - ^ Census of India 2011
- ^ "Ramban District Population, Caste, Religion Data (Jammu and Kashmir) - Census 2011".
- ^ "The Jammu and Kashmir Official Languages Act, 2020" (PDF). The Gazette of India. 27 September 2020. Retrieved 27 September 2020.
- ^ "Parliament passes JK Official Languages Bill, 2020". Rising Kashmir. 23 September 2020. Retrieved 30 May 2021.
- ^ a b - About Ramban
- ^ Statement showing the number of blocks in respect of 22 Districts of Jammu and Kashmir State including newly Created Districts Archived 2008-09-10 at the Wayback Machine dated 2008-03-13, accessed 2008-08-30
- ^ "District Profile". District Administration, Ramban. Indian Government. Retrieved 15 September 2017.
- ^ "DDC election for chairperson: NC bags Chairman posts in Kishtwar, Ramban". Daily Excelsior. 18 February 2021. Retrieved 19 February 2021.
- ^ "ERO's and AERO's". Chief Electoral Officer, Jammu and Kashmir. Archived from the original on 22 October 2008. Retrieved 28 August 2008.
- ^ "J-K: Doda, Ramban districts now 'terrorism-free', say police". ANI. 21 January 2021.
- ^ "A-2 Decadal Variation In Population Since 1901". Censusindia.gov.in. Retrieved 9 August 2019.
- ^ a b c d e f "District Census 2011". Census2011.co.in. 2011. Retrieved 30 September 2011.
- ^ US Directorate of Intelligence. "Country Comparison:Population". Archived from the original on 13 June 2007. Retrieved 1 October 2011.
Barbados 286,705 July 2011 est.
- ^ a b C-1 Population By Religious Community – Jammu & Kashmir (Report). Office of the Registrar General & Census Commissioner, India. Retrieved 28 July 2020.
- ^ C-16 Population By Mother Tongue – Jammu & Kashmir (Report). Office of the Registrar General & Census Commissioner, India. Retrieved 18 July 2020.
- ^ "Sanasar Sightseeing, Places To Visit In Sanasar, Things To Do In Sanasar". www.holidify.com. Retrieved 18 January 2017.
