Timeline of the 2007 Atlantic hurricane season
| Timeline of the 2007 Atlantic hurricane season | |
|---|---|
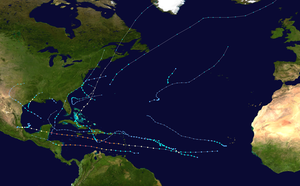 Season summary map | |
| Season boundaries | |
| First system formed | May 9, 2007 |
| Last system dissipated | December 14, 2007 |
| Strongest system | |
| Name | Dean |
| Maximum winds | 175 mph (280 km/h) (1-minute sustained) |
| Lowest pressure | 905 mbar (hPa; 26.72 inHg) |
| Longest lasting system | |
| Name | Dean |
| Duration | 10 days |
The 2007 Atlantic hurricane season was an event in the annual tropical cyclone season in the north Atlantic Ocean. A near average Atlantic hurricane season,[nb 1] September had a record-tying eight storms, although the strength and duration of most of the storms was low.[2] Also, for only the second time in recorded history, an Atlantic hurricane, Felix, and an eastern Pacific hurricane, Henriette, made landfall on the same day.
The season officially began on June 1, 2007, and ended on November 30, 2007, dates that conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones develop in the Atlantic basin.[3] The season's first storm, Subtropical Storm Andrea, developed from an extratropical cyclone that formed on May 6, and the last, Tropical Storm Olga, dissipated on December 11. Altogether, there were 15 named tropical storms during the 2007 season. Six storms attained hurricane strength with two intensifying further into major hurricanes.[nb 2]
This timeline includes information that was not operationally released, meaning that data from post-storm reviews by the National Hurricane Center, such as a storm that was not operationally warned upon, has been included. This timeline documents tropical cyclone formations, strengthening, weakening, landfalls, extratropical transitions, and dissipations during the season.
By convention, meteorologists use one time zone when issuing forecasts and making observations: Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), and also use the 24-hour clock (where 00:00 = midnight UTC).[5] The National Hurricane Center uses both UTC and the time zone where the center of the tropical cyclone is currently located. The time zones utilized (east to west) prior to 2020 were: Atlantic, Eastern, and Central.[6] In this timeline, all information is listed by UTC first with the respective regional time included in parentheses. Additionally, figures for maximum sustained winds and position estimates are rounded to the nearest 5 units (knots, miles, or kilometers), following the convention used in the National Hurricane Center's products. Direct wind observations are rounded to the nearest whole number. Atmospheric pressures are listed to the nearest millibar and nearest hundredth of an inch of mercury.
Timeline[edit]

May[edit]
- May 9

- 2 a.m. EDT (0600 UTC) – Subtropical Storm Andrea forms 150 nautical miles (280 kilometres; 170 miles) east of Jacksonville, Florida.[7]
- May 10
-
- 8 a.m. EDT (1200 UTC) – Subtropical Storm Andrea weakens into a subtropical depression.[7]
- May 11
June[edit]
- June 1
-
- 12 a.m. EDT (0400 UTC) – The 2007 Atlantic hurricane season officially begins.[8]
- 8 a.m. EDT (1200 UTC) – A tropical depression forms just northwest of the western tip of Cuba.[9]
- 2 p.m. EDT (1800 UTC) – The tropical depression near Cuba strengthens into Tropical Storm Barry.[9]
- June 2
July[edit]
- July 30
- July 31
-
- 2 a.m. EDT (0600 UTC) – Tropical Depression Three is upgraded to Tropical Storm Chantal.[10]
August[edit]
- August 1
-
- 2 a.m. EDT (0600 UTC) – Tropical Storm Chantal becomes extratropical.[10]
- August 13
-
- 2 a.m. EDT (0600 UTC) – Tropical Depression Four forms 520 miles (840 km) west-southwest of the southernmost Cape Verde islands.[11]
- August 14
-
- 8 a.m. AST (1200 UTC) – Tropical Depression Four is upgraded to Tropical Storm Dean.[11]
- 7 p.m. CDT (0000 UTC August 15) – Tropical Depression Five forms in Central Gulf of Mexico.[12]
- August 15
-
- 1 p.m. CDT (1800 UTC) – Tropical Depression Five is upgraded to Tropical Storm Erin.[12]
- August 16
-
- 2 a.m. AST (0600 UTC) – Tropical Storm Dean is upgraded to Hurricane Dean.[11]
- 5:30 a.m. CDT (1030 UTC) – Tropical Storm Erin makes landfall near San José Island, Texas with 35 mph (56 km/h).[12]
- 7 a.m. CDT (1200 UTC) – Tropical Storm Erin is downgraded to a tropical depression.[12]
- 8 a.m. AST (1200 UTC) – Hurricane Dean is upgraded to a Category 2 hurricane.[11]
- August 17
-
- 7 a.m. CDT (1200 UTC) – Tropical Depression Erin is downgraded to a remnant low about 50 nautical miles south of San Angelo, Texas.[12]
- 2 p.m. EDT (1800 UTC) – Hurricane Dean is upgraded to a Category 3 hurricane, becoming the first major hurricane of the season.[11]
- 8 p.m. EDT (0000 UTC August 18) – Hurricane Dean is upgraded to a Category 4 hurricane.[11]
- August 18
- August 20

- 8 p.m. EDT (0000 UTC August 21) – Hurricane Dean is re-upgraded to a Category 5 hurricane.[11]
- August 21
- August 22
-
- c. 11:30 a.m. CDT (1630 UTC) – Hurricane Dean is again upgraded to a Category 2 hurricane.[11]
- 11:30 a.m. CDT (1630 UTC) – Hurricane Dean makes its second landfall, near Tecolutla, Veracruz with 100 mph (160 km/h) winds.[11]
- 7 p.m. CDT (0000 UTC August 23) – Hurricane Dean is downgraded to a tropical depression inland over Mexico.[11]
- August 23
-
- 1 a.m. CDT (0600 UTC) – Tropical Depression Dean dissipates inland over Mexico.[11]
- August 31
-
- 8 a.m. AST (1200 UTC) – Tropical Depression Six forms east of the Windward Islands.[13]
- 8 p.m. AST (0000 UTC September 1) – Tropical Depression Six is upgraded to Tropical Storm Felix.[13]
September[edit]
- September 1
-
- 4:45 a.m. AST (0845 UTC) – Tropical Storm Felix makes landfall on Grenada with 50 mph (80 km/h) winds.[13]
- 8 p.m. AST (0000 UTC September 2) – Tropical Storm Felix is upgraded to Hurricane Felix.[13]
- September 2

- September 3
-
- 2 a.m. AST (0600 UTC) – Hurricane Felix is upgraded to the second Category 5 hurricane of the season.[13]
- September 4
- September 5
- September 7
-
- 8 p.m. EDT (0000 UTC September 8) – Subtropical Storm Gabrielle forms 385 mi (620 km) South-East of Cape Lookout, North Carolina.[14]
- September 8
-
- 2 p.m. EDT (1800 UTC) – Subtropical Storm Gabrielle becomes Tropical Storm Gabrielle.[14]
- September 9
-
- 11:30 a.m. EDT (1530 UTC) – Tropical Storm Gabrielle makes landfall near the Cape Lookout National Seashore with 60 mph (97 km/h) winds.[14]
- September 10
-
- 2 a.m. EDT (0600 UTC) – Tropical Storm Gabrielle is downgraded to a tropical depression.[14]
- September 11
-
- 8 a.m. EDT (1200 UTC) – Tropical Depression Gabrielle dissipates.[14]
- September 12
-
- 8 a.m. EDT (1200 UTC) – Tropical Depression Eight forms east of the Lesser Antilles.[15]
- 8 a.m. EDT (1200 UTC) – Tropical Storm Humberto forms in the Gulf of Mexico, southeast of Houston, Texas.[16]
- September 13
-
- 1 a.m. CDT (0600 UTC) – Tropical Storm Humberto is upgraded to Hurricane Humberto.[16]
- 2 a.m. AST (0600 UTC) – Tropical Depression Eight is upgraded to Tropical Storm Ingrid.[15]
- 2 a.m. CDT (0700 UTC) – Hurricane Humberto makes landfall just east of High Island, Texas with 90 mph (140 km/h) winds.[16]
- 1 a.m. CDT (1800 UTC) – Hurricane Humberto is downgraded to a tropical storm.[16]
- 7 p.m. CDT (0000 UTC September 14) – Tropical Storm Humberto is downgraded to a tropical depression.[16]
- September 14
-
- 7 p.m. CDT (0600 UTC) – Tropical Depression Humberto is downgraded to a low.[16]
- September 15
-
- 2 p.m. AST (1800 UTC) – Tropical Storm Ingrid is downgraded to a tropical depression.[15]
- September 17
-
- 2 a.m. AST (0600 UTC) – Tropical Depression Ingrid is downgraded to a remnant low.[15]
- September 21

- 7 a.m. CDT (1200 UTC) – Subtropical Depression Ten forms in the Gulf of Mexico, south of the Florida Panhandle.[17]
- 1 p.m. CDT (1800 UTC) – Subtropical Depression Ten is reclassified as Tropical Depression Ten.[17]
- 7 p.m. CDT (0000 UTC September 22) – Tropical Depression Ten makes landfall near Fort Walton Beach, Florida with 30 mph (48 km/h) winds.[17]
- September 22
- September 23
- September 24
-
- 2 p.m. AST (1800 UTC) – Tropical Storm Jerry is downgraded to a tropical depression.[18]
- 8 p.m. AST (0000 UTC September 25) – Tropical Depression Jerry dissipates.[18]
- 8 p.m. AST (0000 UTC September 25) – Tropical Depression Twelve forms east of the southern Windward Islands.[19]
- September 25
- September 26
- September 27
- September 28
-
- 12 a.m. CDT (0500 UTC) – Hurricane Lorenzo makes landfall Tecolutla, Veracruz, Mexico with 75 mph (121 km/h) winds.[20]
- 2 a.m. AST (0600 UTC) – Tropical Depression Fourteen forms southwest of Cape Verde.[21]
- 7 a.m. CDT (1200 UTC) – Hurricane Lorenzo is downgraded to a tropical depression.[20]
- 7 p.m. CDT (0000 UTC September 29) – Tropical Depression Lorenzo dissipates inland Mexico.[20]
- September 29
-
- 2 a.m. AST (0600 UTC) – Tropical Depression Fourteen is upgraded to Tropical Storm Melissa.[21]
- 2 a.m. EDT (0600 UTC) – Tropical Storm Karen is downgraded to a tropical depression.[19]
- 8 a.m. AST (1200 UTC) – Tropical Depression Karen is downgraded to a low just to the east of the Leeward Islands.[19]
- September 30
October[edit]
- October 11
-
- 8 a.m. AST (1200 UTC) – Tropical Depression Fifteen forms east of Bermuda.[22]
- October 12
-
- 8 p.m. AST (0000 UTC October 13) – Tropical Depression Fifteen degenerates into a remnant low.[22]
- October 27
-
- 8 p.m. EDT (0000 UTC October 28) – Tropical Depression Sixteen forms in the central Caribbean Sea.[23]
- October 28
-
- 8 a.m. EDT (1200 UTC) – Tropical Depression Sixteen strengthens into Tropical Storm Noel.[23]
- October 29
- October 30
-
- 2 a.m. EDT (0600 UTC) – Tropical Storm Noel makes its second landfall near Guardalavaca, Cuba with 60 mph (97 km/h) winds.[23]
November[edit]

- November 1
-
- 9:15 a.m. EDT (1315 UTC) – Tropical Storm Noel makes its third landfall on Andros, Bahamas, with winds of 60 mph (97 km/h).[23]
- 1:15 a.m. EDT (1745 UTC) – Tropical Storm Noel makes its fourth landfall on New Providence, Nassau, Bahamas, with winds of 65 mph (105 km/h).[23]
- 8 p.m. EDT (0000 UTC November 2) – Tropical Storm Noel strengthens into Hurricane Noel.[23]
- November 2
-
- 8 p.m EDT (0000 UTC November 3) – Hurricane Noel becomes extratropical.[23]
- November 30
-
- 11:59 p.m EST (0459 UTC December 1) – The 2007 hurricane season officially ends.[8]
December[edit]
- December 10
-
- 9:45 p.m. AST (0045 UTC December 11) – Subtropical Storm Olga forms north of Puerto Rico.[24]
- December 11
-
- 2 p.m. AST (1800 UTC) – Subtropical Storm Olga makes landfall in north central Puerto Rico, just west of Vega Baja, with 45 mph (72 km/h) winds.[24]
- 2 p.m. AST (1800 UTC) – Subtropical Storm Olga is reclassified as Tropical Storm Olga.[24]
- 2 p.m. AST (1800 UTC) – Tropical Storm Olga makes landfall just south of Punta Cana, Dominican Republic with 60 mph (97 km/h) winds.[24]
- December 12
See also[edit]
- Timeline of the 2007 Pacific hurricane season
- Timeline of the 2007 Pacific typhoon season
- Timeline of the 2007 North Indian Ocean cyclone season
- Timeline of the 2007–08 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season
- Timeline of the 2007–08 South Pacific cyclone season
- Timeline of the 2007–08 Australian region cyclone season
- Timeline of the 2008–09 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season
- Timeline of the 2008–09 South Pacific cyclone season
- Timeline of the 2008–09 Australian region cyclone season
Notes[edit]
- ^ An average season, as defined by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, has twelve tropical storms, six hurricanes and two major hurricanes.[1]
- ^ Hurricanes reaching Category 3 (wind speeds of 111 miles per hour (179 km/h)) or higher on the 5-level Saffir–Simpson wind speed scale are considered major hurricanes.[4]
References[edit]
- ^ Climate Prediction Center Internet Team (August 4, 2011). "Background Information: The North Atlantic Hurricane Season". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Climate Prediction Center. Retrieved January 5, 2013.
- ^ NHC Hurricane Research Division. "Atlantic Hurricane Best Track (1950-present)". NOAA. Archived from the original on 2008-09-16. Retrieved 2008-08-22.
- ^ Dorst, Neal (June 1, 2018). "Hurricane Season Information". Frequently Asked Questions About Hurricanes. Miami, Florida: NOAA Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory. Retrieved June 29, 2020.
- ^ "Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale". Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 29, 2020.
- ^ "Understanding the Date/Time Stamps". Miami, Florida: NOAA National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 10, 2020.
- ^ "Update on National Hurricane Center Products and Services for 2020" (PDF). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. April 20, 2020. Retrieved May 17, 2020.
- ^ a b c Jamie R. Rhome; Jack Beven; Mark Willis (2007-07-01). "Tropical Cyclone Report: Subtropical Storm Andrea (AL012007)" (PDF). National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2007-07-02.
- ^ a b Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory, Hurricane Research Division. "Frequently Asked Questions: When is hurricane season?". NOAA. Archived from the original on 2006-07-18. Retrieved 2008-08-21.
- ^ a b c d Lixion Avila (2007-06-22). "Tropical Cyclone Report: Tropical Storm Barry (AL022007)" (PDF). National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2007-06-23.
- ^ a b c Richard J. Pasch (2007-10-18). "Tropical Cyclone Report: Tropical Storm Chantal" (PDF). National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2008-02-22.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n James L. Franklin (2008-02-19). "Tropical Cyclone Report: Hurricane Dean" (PDF). National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2008-02-22.
- ^ a b c d e Richard D. Knabb (2008-04-07). "Tropical Cyclone Report: Tropical Storm Erin" (PDF). National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2008-04-11.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Jack Beven (2008-01-16). "Tropical Cyclone Report: Hurricane Felix" (PDF). National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2008-02-22.
- ^ a b c d e Daniel P. Brown (2007-10-29). "Tropical Cyclone Report: Tropical Storm Gabrielle" (PDF). National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2008-02-22.
- ^ a b c d Michelle Mainelli (2007-10-17). "Tropical Cyclone Report: Tropical Storm Ingrid" (PDF). National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2008-02-22.
- ^ a b c d e f Eric S. Blake (2007-11-28). "Tropical Cyclone Report: Hurricane Humberto" (PDF). National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2008-02-22.
- ^ a b c d Jamie R. Rhome (2007-10-15). "Tropical Cyclone Report: Tropical Depression Ten" (PDF). National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2008-02-22.
- ^ a b c d e Lixion A. Avila (2007-10-24). "Tropical Cyclone Report: Tropical Storm Jerry" (PDF). National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2008-02-22.
- ^ a b c d e f Richard J. Pasch (2007-11-27). "Tropical Cyclone Report: Hurricane Karen" (PDF). National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2008-02-22.
- ^ a b c d e f James L. Franklin (2007-10-18). "Tropical Cyclone Report: Hurricane Lorenzo" (PDF). National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2008-02-22.
- ^ a b c d Richard D. Knabb (2007-10-13). "Tropical Cyclone Report: Tropical Storm Melissa" (PDF). National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2008-02-22.
- ^ a b Jack Beven (2007-11-22). "Tropical Cyclone Report: Tropical Depression Fifteen" (PDF). National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2008-02-22.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Daniel P. Brown (2007-12-17). "Tropical Cyclone Report: Hurricane Noel" (PDF). National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2008-02-22.
- ^ a b c d e f Michelle Mainelli (2008-01-24). "Tropical Cyclone Report: Tropical Storm Olga" (PDF). National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2008-02-22.
