1952 Pacific hurricane season
| 1952 Pacific hurricane season | |
|---|---|
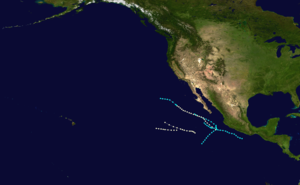 Season summary map | |
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | May 29, 1952 |
| Last system dissipated | October 15, 1952 |
| Strongest storm | |
| Name | Seven, Five |
| • Maximum winds | 85 mph (140 km/h) (1-minute sustained) |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Total storms | 7 |
| Hurricanes | 3 |
| Major hurricanes (Cat. 3+) | 0 |
| Total fatalities | 0 |
| Total damage | Unknown |
| Related articles | |
The 1952 Pacific hurricane season ran through the summer and fall of 1952. Of the seven known tropical cyclones, all remained at sea.
Systems[edit]
Tropical Storm One[edit]
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | May 29 – May 31 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 50 mph (85 km/h) (1-min); |
Tropical Storm One existed from May 29 to May 31.
Tropical Storm Two[edit]
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | June 12 – June 16 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 50 mph (85 km/h) (1-min); |
Tropical Storm Two existed from June 12 to June 16.
Tropical Storm Three[edit]
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | July 19 – July 21 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 50 mph (85 km/h) (1-min); |
Tropical Storm Three existed from July 19 to July 21.
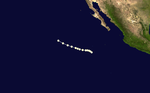
Hurricane Four[edit]
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | July 24 – July 27 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 80 mph (130 km/h) (1-min); |
Hurricane Four remained at sea.[1]
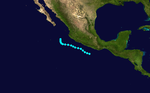
Hurricane Five[edit]
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 15 – September 22 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 85 mph (140 km/h) (1-min); |
A hurricane developed on September 15 southwest of Baja California and dissipated seven days later.[1] Moisture from Five produced 2 in (51 mm) of rainfall in the deserts and mountains of central and southern California.[2]
Tropical Storm Six[edit]
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 26 – September 28 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 50 mph (85 km/h) (1-min); |
Tropical Storm Six existed from September 26 to September 28.
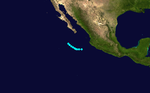
Hurricane Seven[edit]
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | October 13 – October 15 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 85 mph (140 km/h) (1-min); |
Hurricane Seven existed from October 13 to October 15.
See also[edit]
- List of Pacific hurricanes
- Pacific hurricane season
- 1952 Atlantic hurricane season
- 1952 Pacific typhoon season
- Australian region cyclone seasons: 1952–53 1953–54
- South Pacific cyclone seasons: 1952–53 1953–54
- South-West Indian Ocean cyclone seasons: 1952–53 1953–54
References[edit]
- ^ a b National Hurricane Center; Hurricane Research Division; Central Pacific Hurricane Center (April 4, 2023). "The Northeast and North Central Pacific hurricane database 1949–2022". United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's National Weather Service. A guide on how to read the database is available here.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Jack Williams (May 5, 2005). "California's Tropical Cyclones". USA Today. Retrieved July 19, 2012.