EnRUPT
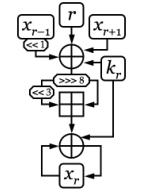 One round of EnRUPT[1] | |
| General | |
|---|---|
| First published | 2008 |
| Derived from | Corrected Block TEA |
| Cipher detail | |
| Key sizes | variable |
| Block sizes | arbitrary, at least two words (64 bits) |
| Structure | Unbalanced Feistel Network |
| Rounds | 8 * (plaintext words) + 4 * (key words) |
| Best public cryptanalysis | |
| 2480 complexity meet-in-the-middle preimage attack against EnRUPT hash,[2]
collision attack with 240 time complexity[3] | |
EnRUPT is a block cipher and a family of cryptographic algorithms based on XXTEA.[1][5] EnRUPT hash function was submitted to SHA-3 competition but it wasn't selected to the second round.
References[edit]
- ^ a b Sean O'Neil (2008). "EnRUPT: First all-in-one symmetric cryptographic primitive" (ZIP). Workshop Record. SASC 2008 workshop.
- ^ Khovratovich, Dmitry; Nikolić, Ivica (2008). "Cryptanalysis of EnRUPT" (PDF).
- ^ Sebastiaan Indesteege; Bart Preneel (2009). "Practical Collisions for EnRUPT" (PDF). In Orr Dunkelman (ed.). Fast Software Encryption. FSE 2009. pp. 246–259. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-03317-9_15.
- ^ Yarrkov, Elias (2010). "Cryptanalysis of block EnRUPT" (PDF).
- ^ Sean O'Neil; Karsten Nohl; Luca Henzen. "EnRUPT Hash Function Specification" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 July 2010.
