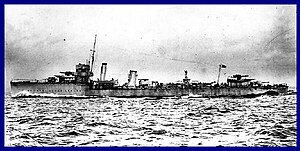
HMS Vehement (1917)
| |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Name | HMS Vehement |
| Namesake | Vehement |
| Ordered | July 1916[1] |
| Builder | William Denny and Brothers, Dumbarton[1] |
| Laid down | 25 September 1916[3] |
| Launched | 6 July 1917[1] |
| Completed | October 1917[2] |
| Commissioned | October 1917 |
| Identification |
|
| Fate | Sunk 2 August 1918 |
| General characteristics | |
| Class and type | Admiralty V-class destroyer |
| Displacement | 1,272–1,339 tons |
| Length | 300 ft (91.4 m) o/a, 312 ft (95.1 m) p/p |
| Beam | 26 ft 9 in (8.2 m) |
| Draught | 9 ft (2.7 m) standard, 11 ft 3 in (3.4 m) deep |
| Propulsion |
|
| Speed | 34 kt |
| Range | 320–370 tons oil, 3,500 nmi at 15 kt, 900 nmi at 32 kt |
| Complement | 110 |
| Armament |
|
The first HMS Vehement was a V-class destroyer of the British Royal Navy that saw service in World War I. She spent her short career in minelaying operations in the North Sea before striking a mine and sinking in 1918.
Construction and commissioning[edit]
Vehement was ordered in July 1916. She was laid down on 25 September 1916[3] by William Denny and Brothers at Dumbarton, Scotland, and, per a British Admiralty order of 12 January 1917, was fitted to carry 60 naval mines.[1] She was launched on 6 July 1917[1] and was completed in October 1917,[2] and she was commissioned into service that month. Her original pennant number, F1A, was changed to F12 in January 1918 and to H2A in June 1918.[1]
Service history[edit]
In October 1917, Vehement was assigned to the 13th Destroyer Flotilla[4] in the Grand Fleet.[5]
Vehement collided with the British destroyer HMS Murray on 14 January 1918.[6] An investigation attributed the accident to an error in judgment by her lieutenant in command.[6]
In February 1918, Vehement was reassigned to the 20th Destroyer Flotilla,[7] based at the Humber.[8] The 20th Destroyer Flotilla was engaged in a major British effort to lay minefields in the North Sea to close the Heligoland Bight to passage by German ships and submarines. On 31 May 1918, Vehement put to sea from Immingham with the flotilla to lay mines in the Dogger Bank area.[9] On the night of 4–5 June 1918, the flotilla again deployed from the Humber estuary to mine the same area, bringing the total number of mines laid in the two expeditions to 330.[10]
Vehement′s next sortie from Immingham on 21 June 1918 ended almost as soon as it began when her propellers suffered damage after striking a cable while she was leaving the harbour, forcing her to remain in port for repairs. She was back in service in time to join her flotilla in laying a North Sea minefield on 27 June 1918. On the night of 5–6 July and again on the night of 8–9 July 1918, she joined her flotilla in laying a field of 384 mines in 18 rows in the North Sea.[11]
On the night of 13–14 July 1918, Vehement and the destroyers HMS Telemachus, HMS Vanquisher, and HMS Venturous laid a field of 224 mines in the North Sea. On the night of 17–18 July 1918, her flotilla laid another North Sea minefield of 424 mines with cover for the operation provided by the 7th Cruiser Squadron, but German forces did not interfere.[12]
Vehement′s next minelaying operation on 24 July 1918 involved the entire flotilla laying 496 mines in the North Sea in 22 rows; during the operation, Vehement detected two periscopes. The flotilla sortied from the Humber again at 13:00 hours on 28 July 1918 and during the night of 28–29 July laid a North Sea field of 416 mines in 18 rows.[13]
On 1 August 1918, the 20th Destroyer Flotilla departed the Humber to lay a minefield in the North Sea at the seaward end of one of the German-swept channels through the German minefield in the Heligoland Bight. At 23:47 hours the force was within 20 nautical miles (37 km; 23 mi) of the area it was to mine when Vehement struck a mine at 55°33′00″N 005°24′00″E / 55.55000°N 5.40000°E. Its explosion caused her forward ammunition magazine to detonate, blowing off the entire forward section of the ship forward of the forward funnel, killing one officer and 47 ratings.[14][15] The explosion blew her commanding officer overboard; he landed 400 yards (370 m) from the ship, but survived with moderate injuries.[16] As the force manoeuvered to clear the German minefield it had entered, the destroyer HMS Ariel also struck a mine at 00:10 hours on 2 August and, in a repeat of what had happened to Vehement, suffered a magazine detonation that blew off the entire section of the ship forward of the whaleboat′s davit. Ariel sank at about 01:00 hours, with the loss of four officers and 45 ratings,[17] but Vehement remained afloat, and by about an hour after she struck the mine her crew had put out all of her fires. She was taken in tow by the destroyer HMS Abdiel in the hope of saving her, but at 04:00 hours on 2 August Vehement′s stern rose into the air, making further towing impossible. Vehement′s surviving crew opened all of her hull valves to speed her sinking and abandoned ship. Telemachus and Vanquisher then sank Vehement with gunfire.[14]
References[edit]
- ^ a b Friedman, p. 312.
- ^ a b "Clyde Maritime HMS Vehement". Archived from the original on 5 March 2016. Retrieved 9 May 2013.
- ^ Supplement to the Monthly Navy List, October 1917, p. 12.
- ^ Watson, Graham. "Royal Navy Organisation and Ship Deployment, Inter-War Years 1914-1918". www.naval-history.net. Gordon Smith, 27 October 2015. Retrieved 17 July 2018.
- ^ a b Service Record of Hugh Bourchier Wrey, The National Archives. ADM 196/52/62. f. 420.
- ^ Smith, p. 39.
- ^ Supplement to the Monthly Navy List, June 1918, p. 15.
- ^ Smith, p. 66.
- ^ Smith, pp. 66–67.
- ^ Smith, pp. 68, 70.
- ^ Smith, p. 70.
- ^ Smith, pp. 73–74.
- ^ a b LITHERLAND AT WAR 1914–1918 Petty Officer Stoker PETER CULSHAW 1877–1918
- ^ Smith, pp. 74–85.
- ^ Preston, p. 26.
- ^ Smith, pp. 79–81.
Bibliography[edit]
- Campbell, John (1985). Naval Weapons of World War II. Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 0-87021-459-4.
- Colledge, J. J.; Warlow, Ben (2006) [1969]. Ships of the Royal Navy: The Complete Record of all Fighting Ships of the Royal Navy (Rev. ed.). London: Chatham Publishing. ISBN 978-1-86176-281-8.
- Cocker, Maurice (1981). Destroyers of the Royal Navy, 1893–1981. Ian Allan. ISBN 0-7110-1075-7.
- Friedman, Norman (2009). British Destroyers From Earliest Days to the Second World War. Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 978-1-59114-081-8.
- Gardiner, Robert & Gray, Randal, eds. (1985). Conway's All the World's Fighting Ships 1906–1921. Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 0-85177-245-5.
- March, Edgar J. (1966). British Destroyers: A History of Development, 1892–1953; Drawn by Admiralty Permission From Official Records & Returns, Ships' Covers & Building Plans. London: Seeley Service. OCLC 164893555.
- Preston, Antony (1971). 'V & W' Class Destroyers 1917–1945. London: Macdonald. OCLC 464542895.
- Raven, Alan & Roberts, John (1979). 'V' and 'W' Class Destroyers. Man o'War. Vol. 2. London: Arms & Armour. ISBN 0-85368-233-X.
- Smith, Peter C. (2005). Into the Minefields: British Destroyer Minelaying 1916–1960. Barnsley: Pen and Sword Maritime. ISBN 1-84415-271-5.
