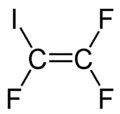
Iodotrifluoroethylene
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,1,2-Trifluoro-2-iodoethene | |
| Other names
1,1,2-Trifluoro-2-iodoethylene, trifluoroiodoethylene, iodotrifluoroethylene
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.028 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2F3I | |
| Molar mass | 207.92 g/mol |
| Density | 2.284 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 30 °C (86 °F; 303 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Irritant (Xi) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Iodotrifluoroethylene is the organofluorine compound with the formula C
2F
3I. It is a volatile colorless liquid.
Preparation and reactions[edit]
It is prepared by iodination of trifluorovinyl lithium.[1]
Iodotrifluoroethylene reacts with cadmium metal to give CdC2F3(I).[2]
It reacts with nitric oxide under UV light, producing a nitroso compound, with iodine as a byproduct:[3]
- 2 C
2F
3I + 2 NO → 2 C
2F
3NO + I
2
References[edit]
- ^ Burdon, James; Coe, Paul L.; Haslock, Iain B.; Powell, Richard L. (1996). "The hydrofluorocarbon 1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane (HFC-134a) as a ready source of trifluorovinyllithium". Chemical Communications: 49. doi:10.1039/CC9960000049.
- ^ Burton, Donald J.; Yang, Zhen-Yu; Morken, Peter A. (1994). "Fluorinated organometallics: Vinyl, Alkynyl, Allyl, Benzyl, Propargyl and Aryl". Tetrahedron. 50 (10): 2993–3063. doi:10.1016/S0040-4020(01)81105-4.
- ^ Griffin, C. E.; Haszeldine, R. N . (1960). "Perfluoroalkyl derivatives of nitrogen. Part VIII. Trifluoronitrosoethylene and its polymers". Journal of the Chemical Society (Resumed): 1398–1406. doi:10.1039/JR9600001398.
