Kanker State
| Kanker State कांकेर रियासत | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Princely State of British India | |||||||
| 14th century–1947 | |||||||
|
Flag | |||||||
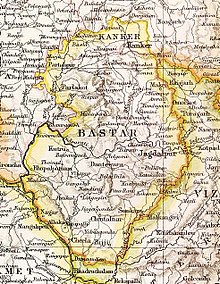 Kanker State in the Imperial Gazetteer of India | |||||||
| Area | |||||||
• 1901 | 3,701.09 km2 (1,429.00 sq mi) | ||||||
| Population | |||||||
• 1901 | 103,536 | ||||||
| History | |||||||
• Established | 14th century | ||||||
| 1947 | |||||||
| |||||||
Kanker State (Hindi: कांकेर) was one of the princely states of India during the period of the British Raj. Its last ruler signed the accession to the Indian Union in 1947.
Kanker State was located north of Bastar State and, except for the valley of the Mahanadi in its eastern part, it consisted mostly of hills covered by forests in which teak (Tectona grandis), sirsā (Dalbergia latifolia), śāl (Shorea robusta) and bījāsāl (Pterocarpus marsupium) predominated. The state had 63,610 inhabitants in 1881 and 103,536 in 1901, more than half of which were Gonds. Kanker town in Kanker District, Chhattisgarh, was the capital of the state and the see of the Raja's residence. The languages spoken in the state were mainly Chhattisgarhi and Gondi.[1]
Origin[edit]
The early history of the state is obscure. According to tradition Kanker was ruled in the early 2nd century by Raja Satkarni of the Satavahana dynasty.[2] As per another source the Kanker family came to this region from Puri of Odisha.[3] The ancestor of the rajas of Kanker, Raja Veer Kanhar Dev, the king of Jagannath Puri, abdicated his throne due to leprosy and moved to Sihawa, from where the Mahanadi River originates. There he spent his time in worship until one night he had a dream that if he took a bath in a tank at Sihawa, his leprosy would be cured. The dream turned out to be true and the people, surprised by this event, elected him the king. Veer Kanhar Dev founded the Chandra dynasty of Kanker and ruled until 1404.[4][5]
History[edit]

During the rule of the Haihaiyavansi dynasty in Chhattisgarh, the raja of Kanker held the Dhamtari region and was in tributary relationship with the Haihaiyavansi king.[1] When the Haihaiyavansi Kingdom fell to the Maratha invasion in 1740, the Kanker kingdom came under the supremacy of Mohan Singh, the vassal Haihaya ruler. On Mohan Singh's death, it came under Bimbaji Bhonsle, the Maratha governor of Chhattisgarh.[6]
Under the Marathas, the Kanker State was held on condition of furnishing a military contingent 500 strong whenever needed.[4] The state was occupied by the Marathas of Nagpur in 1809 and the Raja of Kanker, Bhup Deo was deprived of his power. In 1818, the British resident of Nagpur State, Mr. Richard Jenkins, restored Bhup Deo to his throne on payment of a tribute of Rs 500. The tribute imposed on Kanker State was remitted in 1823.[1]
At the time of the British Raj Kanker was one among the 26 feudatory states of the Chhattisgarh States Agency. The princely rulers had good administrative qualities, were relatively popular with their people, and constructed several temples and schools.[5] The state's accession to the Indian Union was signed by its last ruler Bhanupratap Deo on 15 August 1947.[7]
Rulers[edit]
The Rajas of the princely state were:[7]
- .... – 1729 Ghoor Sai Deo (d. 1729)
- 1729–1775 Harpal Deo (d. 1775)
- 1775 – .... Dhiraj Singh Deo
- .... – .... Ram Raj Singh Deo
- .... – 1802 Shyam Singh Deo
- 1802–1809 Bhup Deo (1st time) (d. 1839)
- 1809–1818 occupied by Nagpur
- 1818–1839 Bhup Deo (2nd time) (s.a.)
- 1839–1853 Padma Deo (d. 1853)
- 5 December 1853 –May 1903 Narhar Deo (b. 1850 – d. 1903)
- 9 May 1903 – 8 January 1925 Lal Kamal Deo (b. 1873 – d. 1925)
- 8 January 1925 – 15 August 1947 Bhanupratap Deo (b. 1922 – d. 1969)
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ a b c Imperial Gazetteer of India, v. 14, p. 402.
- ^ Hunter, Sir William Wilson. The Imperial Gazetteer of India. London: Trübner & co., 1885
- ^ "Central Provinces District Gazetteers: Raipur District, Volume a descriptive". Byculla, British India Press. 1909.
- ^ a b Rathore, Abhinay (27 November 1970). "Kanker (Princely State)". Rajput Provinces of India.
- ^ a b "Kanker History". 164.100.86.30.
- ^ Mishra, Prabhu Lal (1979). The Political History of Chhattisgarh, 1740-1858 A.D. Vishwa Bharati Prakashan.
- ^ a b Princely States of India K-Z
External links[edit]
 Media related to Kanker State at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Kanker State at Wikimedia Commons

