Octamethylenediamine
Structural formula of octamethylenediamine
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Octane-1,8-diamine
| |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| Abbreviations | OMDA |
| 3-04-00-00612 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.150 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H20N2 | |
| Molar mass | 144.26 g mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless solid with an amine-like odor[1] |
| Density | 0.83 g cm−3 (60 °C)[1] |
| Melting point | 52 °C[3] |
| Boiling point | 225-226 °C[1][2] |
| Easily soluble in water (575 g l−1 at 20°C)[1] | |
| Vapor pressure | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling:[1] | |
 
| |
| Danger | |
| H302, H314, H317 | |
| P260, P280, P301+P312+P330, P303+P361+P353, P305+P351+P338+P310 | |
| Flash point | 113 °C |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | "1,8-Diaminooctane". GESTIS-Stoffdatenbank. Retrieved 2022-08-05. |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Octamethylenediamine (OMDA) is an organic chemical compound from the substance group of aliphatic diamines. It is used as a versatile reaction intermediate in the manufacture of pesticides, especially fungicides.
Manufacture[edit]
The industrial production of octamethylene diamine is carried out by the catalytic hydrogenation of suberonitrile at temperatures of 150 to 180 °C and a pressure of 50 to 180 bar in the presence of ammonia over heterogeneous cobalt unsupported catalysts:
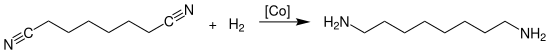
The reaction is carried out in the liquid phase and is carried out continuously or batchwise. The catalyst is arranged as a fixed bed in a shaft, tube, or tube bundle reactor.
Characteristics[edit]
Octamethylenediamine is a combustible but difficult to ignite. It is a solid that is easily soluble in water. The aqueous solutions are strongly alkaline (pH value of 12.1 at a concentration of 10 g/L).[4]
Use[edit]
Octamethylenediamine is used as a versatile intermediate in manufacturing pesticides, especially fungicides.[5]
Safety instructions[edit]
While octamethylenediamine is combustible, it is difficult to ignite because it is solid at moderate temperatures. It has a lower explosive limit (LEL) of 1.1 % by volume and an upper explosive limit (UEL) of 6.8 % by volume. The ignition temperature is 280 °C The substance therefore falls into temperature class T3. With a flash point of 113 °C, the liquid is considered difficult to ignite.[4]
References[edit]
- ^ a b c d e f g h Record of Octamethylenediamine in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, accessed on 2022-01-20.
- ^ "373-44-4 - 1,8-Diaminooctane, 98% - 1,8-Octanediamine - B23885". Alfa Aesar. 2017-10-22. Retrieved 2022-08-06.
- ^ "1,8-Octanediamine". CAS Common Chemistry. Retrieved 2022-08-05.
- ^ a b "WO2018050555A1 Method for the Preparation of Polyamines from Dinitriles and/or Amino Nitrile". Espacenet – patent search. 2021-03-20. Retrieved 2022-08-05.
- ^ Peter Roose, Karsten Eller, Erhard Henkes, Roland Rossbacher, Hartmut Höke: Amines, Aliphatic. In: Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Wiley‐VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA., 30. September 2015, doi:10.1002/14356007.a02_001.pub2.
External links[edit]
- "1,8-diaminooctane". MetaCyc. 2022-08-05. Retrieved 2022-08-06.
- Thalladi, V.R.; Boese, R.; Weiss, H.-C. (2001), CCDC 132875: Experimental Crystal Structure Determination, Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre, doi:10.5517/CC4G894, retrieved 2022-08-06
