Portal:Psychiatry/Selected article/12
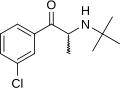
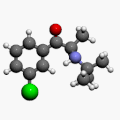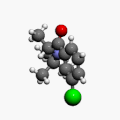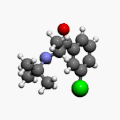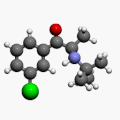
Bupropion (/bjuːˈproʊpi.ɒn/, bew-PROH-pee-on) is a drug primarily used as an antidepressant and smoking cessation aid. Marketed as Wellbutrin and Zyban among other trade names, it is one of the most frequently prescribed antidepressants in the United States, although in many English-speaking countries, including the United Kingdom, Australia and New Zealand, this is an off-label use. It is also widely used to aid people who are trying to quit smoking. It is taken in the form of tablets, and in the United States and most other countries it is available only with a prescription.
Clinically, bupropion serves as an atypical antidepressant fundamentally different from most commonly prescribed antidepressants such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). It is an effective antidepressant on its own, but is also popular as an add-on medication in cases of incomplete response to first-line SSRI antidepressants. In contrast to many other antidepressants, it does not cause weight gain or sexual dysfunction. The most important side effect is an increase in risk for epileptic seizures, which caused the drug to be withdrawn from the market for some time and then caused the recommended dosage to be reduced. (Full article...)
