Sulfine
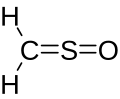
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Methylidene-λ4-sulfanone | |
| Other names
sulfine
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| CH2OS | |
| Molar mass | 62.09 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Sulfinylmethane or sulfine is an organic compound with molecular formula H2CSO. It is the simplest sulfine. Sulfines are chemical compounds with the general structure XY=SO.[1] IUPAC considers the term 'sulfine' obsolete,[2] preferring instead thiocarbonyl S-oxide; despite this, the use of the term sulfine still predominates in the chemical literature.
Substituted sulfines[edit]
The parent sulfine H2CSO is very labile, whereas substituted derivatives are more conveniently isolated.
One route is a variant of ketene synthesis, in which a sulfinyl halide reacts with a hindered base. For example, syn-propanethial-S-oxide, responsible for eye-watering effects of cutting onions, is produced so from allicin.[3]
Another route is oxidation, as with thiobenzophenone from diphenylsulfine:[4]
- (C6H5)2C=S + [O] → (C6H5)2C=S=O

See also[edit]
- Sulfene - related functional group with the formula H2C=SO2
- Ethenone
- Heterocumulene
References[edit]
- ^ Binne Zwanenburg (1989). "Sulfine Chemistry". Phosphorus, Sulfur, and Silicon and the Related Elements. 43 (1–2): 1–24. doi:10.1080/10426508908040276.
- ^ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "sulfines". doi:10.1351/goldbook.S06108
- ^ Block E., Gillies J.Z., Gillies C.W., Bazzi A.A., Putman D., Revelle L.K., Wang D., Zhang X. (1996). "Allium Chemistry: Microwave Spectroscopic Identification, Mechanism of Formation, Synthesis, and Reactions of (E,Z)-Propanethial S-Oxide, the Lachrymatory Factor of the Onion (Allium cepa)". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 118 (32): 7492–7501. doi:10.1021/ja960722j.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ G. Rindorf; L. Carlsen (1979). "The crystal and molecular structures of the thiobenzophenone S-oxide and thiobenzophenone". Acta Crystallogr. B35 (5): 1179–1182. Bibcode:1979AcCrB..35.1179R. doi:10.1107/S0567740879005835.
