Template:POTD/2015-02-26
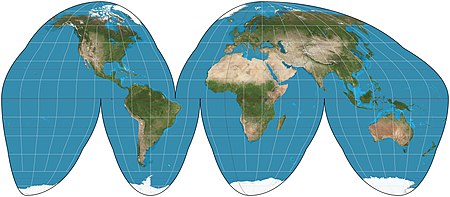
The Goode homolosine projection is a map projection invented by John Paul Goode in 1923 as an alternative to the Mercator projection. This pseudocylindrical, equal-area projection is generally presented with multiple interruptions. The most common form, seen here, interrupts the South Pacific, the North and South Atlantic (separately), the Indian Ocean, and the entire 180th meridian. A composite projection, Goode's homolosine uses the Mollweide projection for higher latitudes and the sinusoidal projection for lower latitudes.Map: Strebe, using Geocart