User:Atgoodwin1/whitenesstheory
Whiteness Theory is understood as a specific theory in Whiteness Studies, examining how white identity affects a non-exhaustive list of identities in an adult's life.[1] This list includes, but is not limited to: social, political, racial, economic, and cultural identity. Whiteness Theory also looks at how whiteness is centric in culture, creating a blindness to the set of privileges associated with White identity, also known as white privilege.[2]
Whiteness Theory is a subset of whiteness studies, where whiteness is an identity that, as a paradox, results from a lack of identity.[2] Whiteness Theory is not to be confused with white privilege, although the privilege associated with white identity is a topic of Whiteness Theory. Critical Whiteness Theory positions whiteness as the default of American culture, and as a result of this default, white people are blind to the advantages and disadvantages of being white due to a lack of cultural subjectiveness towards whiteness.[1] Stemming from the lack of cultural awareness and empathy with racial disprivileges as a result of being white, Whiteness Theory looks at the social, power, and economic challenges that arise from blind, white privilege.[3]
Pillars of Whiteness Theory[edit]
Whiteness as Default[edit]
Whiteness is a socially constructed concept, identified as the normal and centric racial identity. As whiteness is the standard to which racial minorities are compared, whiteness is understood as the default standard.[4] Whiteness Theory establishes whiteness as default, through which social, political, and economic complications arise from whiteness and its creation of color blindness.[3] The ideologies, social norms, and behaviors associated with white culture are the comparative standard to which all races are objectified to.[5]
The defaulting of whiteness establishes a reality in which white people, as victims of their race as centric, do not experience the adversity of those with minority identification. An otherization of minorities can occur with whiteness as a default, where Whiteness Theory identifies whiteness as invisible to those who possess it, resulting in both intended and untended otherization.[6] Whiteness as default presents socioeconomic privileges and advantages over racial minorities, which also might go unrecognized by white people that are not objectified by some other standard of adversity.[4]
Whiteness as Centric[edit]
As whiteness is considered the default race of America, the existing cultural norms of whiteness are classified as the norms of American culture. Such classifications of white culture include stereotypical expectancies of behavior, in which a binary system is created that classifies a person's culture as either "white" or "other."[7] Majority racial status plays a major role for those of white identity creating cultural "norms," as one's behaviors and expectations of how a culture should live and interact is more easily reinforced by association with the majority.[8] Lack of awareness parallels the centric nature of whiteness as majority through self-imposed color blindness, existing through the reality of white privilege.
Whiteness Theory studies the way that white identity passively creates the otherization of color. Color is a construct that can be objectified, made from the existence of whiteness as majority and centric.[9] Such a perception whiteness as "normal" leads to an underrepresentation and misrepresentation of minority individuals.
White Identity[edit]
The idea of whiteness as "normal" reinforces the idea of racial marginalization, through which an identity of whiteness may be created through the antithesis of subjugated "otherized" cultures.[10] Much of white identity is formulated around the absence of an identity. Because there is no association towards being objectified by social, racial, economic, or judicial systems for the middle-class white identifiers, white identity for an individual may be intentionally crafted to suit the wants and needs of the individual.[11] Such a choice of "coloring in" one's whiteness is a reflection of the privileges of whiteness and a lack of diverse community association.[12]
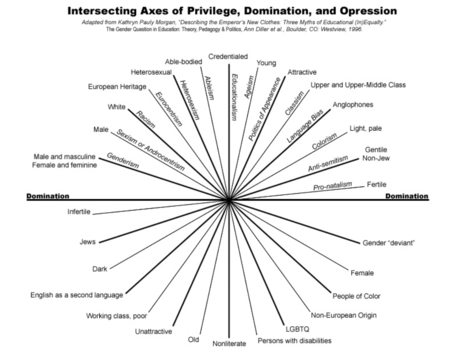
White Privilege[edit]
In the United States, white privilege exists due to the hierarchy of power distribution, where white men were granted institutional power over minorities in the establishment of the country's political, social, and economic systems.[1] White privilege resides in the idea that white people inherit a color blindness due to their majority status, refuting the existence of racism and racial privilege because of a lack of association with those realities.[13] The privileges of being in the majority are unknown by the majority, paradoxically, because they are the majority and are not subjected to the social trials of being a minority.
Lack of discrimination is an underlying principle of white privilege, as the privileges available to the white majority are not as readily enjoyed by those of minority status. Such privileges include, but are not limited to: owning/renting of property, equal racial representation in law and society, unbiased education, assumption of intellectual, social, or financial capability, unbiased credibility.[14] Privilege is multi-faceted in its existence; each of these realities and countless others are the subject of white privilege, as discrimination is faced by minority subjects while trying to enjoy such realities.
White Bias[edit]
White bias is in reference to majority stronghold that white people possess. Those of a particular racial identity (whiteness) have selective preference of granting power and privileges to those of the same ethnicity, referred to as ingroup bias.[15] Such strongholds may be categorically associated to the social, educational, economic, political, racial, and cultural privileges associated by the majority white. Institutionally power is granted hierarchically, and in majority, to those who that associate most with the power holders. Racial bias exists as a barrier to entry for many minority power seekers, where a gatekeeping effect is created by those in the majority who are reluctant to pass power onto the minority, whether through qualification-based or discrimination-based motives.[16]
Socially, institutional slavery, then racism has played a major role in the discrimination of not only African-Americans, but as well other minority affiliations as suboptimal. Economically, access to higher-paying jobs and wage gap discrimination are an ongoing discourse demanding institutional change, both as a result of white bias.[17] Politically, racial bias is seen with the highly sought after Presidential office, where America's first black president Barack Obama was not elected until 2008, being preceded by 43 white presidents by him and being followed by a white president Donald Trump as the 45th.
Whiteness as Unspoken[edit]
Privileges of whiteness are well-known to those of minority status, but not to white people themselves. In efforts of diversity education, white people are often taught to understand the way in which minorities are discriminated against, but not how those of white identity experience a lack of discrimination – this creates an unspoken element of white identity, where white people are often fixated on the objectification of other people, but not as much on the lack of objectification of themselves.[18]
Through the objectification of minorities, race is concerted as the root motivation of such objectification. White identity goes unspoken due to its default and centric nature in culture. Whiteness is only objectified in a situation where whiteness is not normalized or considered the majority. For example, if a person of white identity is immersed in a context where people of minority are situationally the majority by quantity, then the white person (who is usually the situational majority based on quantity) is caught in an uncommon reality where their association with the majority is the subject of otherization.
Critiquing Whiteness[edit]
Communication research revolving around critical race theory seeks to understand the privileges and associations of whiteness. The critical aspect of research involves the realization of white enrichment, where white people have profited from the injustices done unto minorities (see slavery) both knowingly and unknowingly. Systems in the United States more often than not create privileged realities where white people may succeed more than those of minority identity, also allowing those of white identity to more easily change and manipulate the system to their favor.[19]
A component of critical whiteness theory seeks to understand how white people acknowledge their privileges, as well as the corresponding positive or negative behaviors through their acknowledgements. Unique qualitative research is derived from how normative whiteness is in our culture, associated with how color blindness and privilege blindness affect interracial contexts of communication, as well as the white perception of injustices done unto minorities in America.[20]
Whiteness Theory in Communication Studies[edit]
The tenants of white privilege are incorporated into whiteness theory to understand the respective communicative possibilities of each tenant. Studying how white privilege is perceived by white people, how well white people perceive white privilege, how white people think their white privilege affects their identity, how white identity is derived from and conflicts with other racial identities, and how white privilege is perceived by minorities are all a limited set of possibilities created by whiteness theory.[21] These theoretical studies can be manipulated by the following variables of whiteness theory:
- Centric whiteness
- Whiteness as the default
- Whiteness as normative
- Whiteness and rhetoric
- White identity
- White racial culture
- White bias
- White interaction with minorities
- Whiteness and inequality
- White cultural cannibalism
- Whiteness and education
- Whiteness and politics
- Whiteness and popular culture
- Whiteness and gender
References[edit]
- ^ a b c Hartmann, D., Gerteis, J., & Croll, P. R. (2009). An empirical assessment of whiteness theory: Hidden from how many?. Social Problems, 56(3), 403-424.
- ^ a b Cullen, K. A. (2014). A critical race and critical whiteness theory analysis of preservice teachers' racialized practices in a literacy across the curriculum course (Doctoral dissertation, Syracuse University).
- ^ a b Nichols, D. (2010). Teaching critical Whiteness theory: What college and university teachers need to know. Understanding and Dismantling Privilege, 1(1), 1-12.
- ^ a b Green, M. J., Sonn, C. C., & Matsebula, J. (2007). Reviewing whiteness: Theory, research, and possibilities. South African Journal of Psychology, 37(3), 389-419.
- ^ Rogers, R., & Mosley, M. (2006). Racial literacy in a second‐grade classroom: Critical race theory, whiteness studies, and literacy research. Reading Research Quarterly, 41(4), 462-495.
- ^ Ahmed, S. (2012). On being included: Racism and diversity in institutional life. Duke University Press.
- ^ Berger, M. A. (2005). Sight unseen: Whiteness and American visual culture. Univ of California Press.
- ^ Gillborn*, D. (2005). Education policy as an act of white supremacy: Whiteness, critical race theory and education reform. Journal of Education Policy, 20(4), 485-505.
- ^ Giroux, Alexandra. "Communication Interne".
- ^ Frankenberg, R. (1994). Whiteness and Americanness: Examining constructions of race, culture, and nation in white women’s life narratives. race, 62-77.
- ^ Lyubansky, Mikhail Lyubansky. "Psychology Today".
- ^ Reay, D., Hollingworth, S., Williams, K., Crozier, G., Jamieson, F., James, D., & Beedell, P. (2007). A darker shade of pale?'Whiteness, the middle classes and multi-ethnic inner city schooling. Sociology, 41(6), 1041-1060.
- ^ Morris, A., & Kahlor, L. A. (2014). Whiteness Theory in Advertising: Racial Beliefs and Attitudes Toward Ads. Howard Journal of Communications, (4), 415.
- ^ McIntosh, P. (2007). White privilege and male privilege. Race, Ethnicity and Gender: Selected Readings, 377-385.
- ^ "Project Implicit – Harvard.edu".
- ^ Galvan, A. (2015). Soliciting performance, hiding bias: Whiteness and librarianship. the Library with the Lead Pipe.
- ^ Weis, L. (2006). Masculinity, whiteness, and the new economy: An exploration of privilege and loss. Men and Masculinities, 8(3), 262-272.
- ^ McIntosh, P. (1988). "White privilege: Packing the invisible backpack.
- ^ Blum, L. (2008). "White privilege: A mild critique". In". Theory and Research in Education. 6 (309): 311.
- ^ Tranby, E., & Hartmann, D. (2008). Critical whiteness theories and the evangelical “race problem”: Extending Emerson and Smith's Divided by faith. Journal for the Scientific Study of Religion, 47(3), 341-359.
- ^ Hartmann, D., Gerteis, J., & Croll, P. R. (2009). An empirical assessment of whiteness theory: Hidden from how many?. Social Problems, 56(3), 403-424.
