User:Mr. Ibrahem/Rifamycin
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Aemcolo |
| Other names | Rifamycin sodium |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a619010 |
| License data | |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | Rifamycins[1] |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Chemical and physical data | |
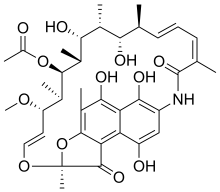
| Formula | C37H47NO12 |
| Molar mass | 697.778 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Rifamycin, sold under the brand name Aemcolo, is an antibiotics used to treat travelers' diarrhea.[1] It is not recommended if a fever or bloody stool is present.[1] It is taken by mouth.[1]
Common side effects include headache and constipation.[1] Other side effects may include Clostridium difficile associated diarrhea.[2] Safety in pregnancy and breastfeeding is unclear.[3] It is in the rifamycins class of medications.[1]
Rifamycin was approved for medical use in the United States for treatment is 2018.[1] In the United States a course of treatment costs about 190 USD as of 2021.[4]
References[edit]
- ^ a b c d e f g h i "Rifamycin Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 25 January 2021. Retrieved 17 October 2021.
- ^ "DailyMed - AEMCOLO- rifamycin tablet, delayed release". dailymed.nlm.nih.gov. Archived from the original on 17 October 2021. Retrieved 17 October 2021.
- ^ "Rifamycin (Aemcolo) Use During Pregnancy". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 17 April 2021. Retrieved 17 October 2021.
- ^ "Aemcolo Prices and Aemcolo Coupons - GoodRx". GoodRx. Retrieved 17 October 2021.
