User:Mr. Ibrahem/Vorinostat
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | Vorinostat /vɒˈrɪnoʊstæt/ vorr-IN-oh-stat Zolinza (/zoʊˈlɪnzə/ zoh-LIN-zə |
| Trade names | Zolinza, Vorinostat MSD, others |
| Other names | Suberanilohydroxamic acid (SAHA) |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a607050 |
| License data |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth (capsules) |
| Drug class | Histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDI)[1] |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 1.8–11%[2] |
| Protein binding | ~71% |
| Metabolism | Liver glucuronidation and β-oxidation CYP system not involved |
| Metabolites | vorinostat O-glucuronide, 4-anilino-4-oxobutanoic acid (both inactive)[3] |
| Elimination half-life | ~2 hours (vorinostat and O-glucuronide), 11 hours (4-anilino-4-oxobutanoic acid) |
| Excretion | Kidney (negligible) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| Chemical and physical data | |
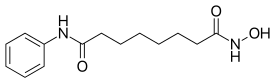
| Formula | C14H20N2O3 |
| Molar mass | 264.325 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Vorinostat, sold under the brand name Zolinza, is a medication used for cutaneous T cell lymphoma (CTCL).[1] Specifically it is used when the disease persists, gets worse, or comes back during or after two other treatments.[1] It is taken by mouth.[1]
Common side effects include diarrhea, tiredness, change in taste, low platelets, hair loss, cough, and fever.[1] Other severe side effects may include blood clots and high blood sugar.[1] Use during pregnancy may harm the baby.[1] It is a histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDI).[1]
Vorinostat was approved for medical use in the United States in 2006.[1] While it was given orphan medication status in Europe in 2004, in 2009 the application for approval was withdrawn.[4] In the United States it costs about 14,600 USD per month as of 2021.[5]
References[edit]
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l "Vorinostat Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 16 September 2021.
- ^ "Withdrawal Assessment Report for Vorinostat MSD 100 mg Hard Capsules (vorinostat)" (PDF). European Medicines Agency. 23 October 2008. p. 9. Archived (PDF) from the original on 15 September 2016. Retrieved 1 September 2016.
- ^ "Zolinza (vorinostat) Capsules. Full Prescribing Information" (PDF). Merck & Co., Inc., Whitehouse Station, NJ 08889, USA. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2 October 2016. Retrieved 1 September 2016.
- ^ "Vorinostat MSD: Withdrawal of the marketing authorisation application". Archived from the original on 22 September 2021. Retrieved 16 September 2021.
- ^ "Zolinza Prices, Coupons & Savings Tips - GoodRx". GoodRx. Archived from the original on 14 June 2016. Retrieved 16 September 2021.
