User:Ts2023tv/Lithium peroxide
| This is the sandbox page where you will draft your initial Wikipedia contribution.
If you're starting a new article, you can develop it here until it's ready to go live. If you're working on improvements to an existing article, copy only one section at a time of the article to this sandbox to work on, and be sure to use an edit summary linking to the article you copied from. Do not copy over the entire article. You can find additional instructions here. Remember to save your work regularly using the "Publish page" button. (It just means 'save'; it will still be in the sandbox.) You can add bold formatting to your additions to differentiate them from existing content. |
Lithium Peroxide[edit]
Lithium peroxide is the inorganic compound with the empirical formula Li2O2. It is a nonhygroscopic solid. Because of its high oxygen:mass and oxygen:volume ratios, the solid has been used to remove carbon dioxide and release oxygen from the atmosphere in many space technologies.
Preparation[edit]
It is prepared by the reaction of hydrogen peroxide and lithium hydroxide. This reaction initially produces lithium hydroperoxide:
LiOH + H2O2 → LiOOH + H2O
This lithium hydroperoxide has also been described as lithium peroxide monoperoxohydrate trihydrate (Li2O2·H2O2·3H2O). Dehydration of this material gives the anhydrous peroxide salt:
2 LiOOH → Li2O2 + H2O2
Li2O2 decomposes at about 450 °C to give lithium oxide AND produces high-purity oxygen:
2 Li2O2 → 2 Li2O + O2
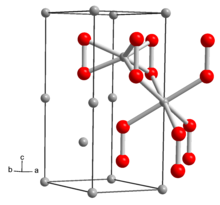
The structure of Li2O2 solid has been determined by X-ray crystallography and density functional theory. The solid features an eclipsed "ethane-like" Li6O2 subunits with an O-O distance of around 1.5 Å.
Uses[edit]
Lithium peroxide is used in air purifiers where weight is important, to absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen in the reaction:
Li2O2 + CO2 → Li2CO3 + 1⁄2 O2
Similar to the reaction of lithium hydroxide with carbon dioxide to release 1 Li2CO3 and 1 H2O, lithium peroxide has high absorption capacity and absorbs more CO2 than does the same weight of lithium hydroxide and offers the bonus of releasing oxygen instead of water. This absorption method, along with the decomposition of Li2O2 to produce high-purity oxygen, is commonly used with applications as a source of oxygen in components of spacecraft or other sealed spaces and apparatuses.
A second use of lithium peroxide, the reversible lithium-oxygen reaction with oxygen from the air is the basis for a prototype lithium–air battery. Rechargeable lithium–oxygen batteries based on the reversible formation and decomposition of Li2O2 has wide applications in vehicle applications, for example. Lithium peroxide has a considerably high theoretical energy density, and using oxygen from the atmosphere allows the battery to eliminate storage of oxygen for its reaction, saving battery weight and size.
Lithium peroxide also acts as a catalyst for polymerization of styrene to polystyrene. The polymerization of styrene to polystyrene typically involves the use of radical initiators via the free radical chain mechanism but lithium peroxide can also initiate radical polymerization reactions under certain conditions, although not as widely used.