Air-to-air combat losses between the Soviet Union and the United States

After World War II, there were many instances of air-to-air combat between the Soviet Union and the United States.
Korean War[edit]
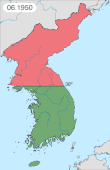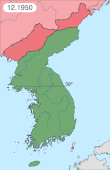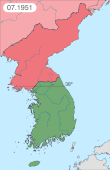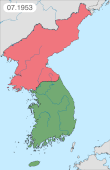
During the Korean War formally the air forces did not meet, as the Soviet Union was not a combatant in the conflict. In August 1945 the USSR declared war on Japan and commenced their offensive campaigns against the Japanese Army. Moving into Japanese occupied Korea, the Soviets gained a foothold in that region, ultimately making it North Korea, and an ally to the Soviet Union. Nearly 72,000 Soviet personnel served in North Korea and their presence was concealed by both the Soviet and American governments.[1] Following the outbreak of the Korean War, air dogfights between USSR and US pilots were numerous. The Soviets flew planes with Chinese or North Korean markings, and were initially forbidden from speaking Russian over the airwaves.[1] The ban was soon lifted due to obvious problems with using Korean to communicate in critical battle situations.[2]
During the conflict the American F-86 Sabre pilots claimed to have destroyed 792 MiG-15s in air-to-air combat for a loss of 78 Sabres – a phenomenal 10 to 1 kills-to-losses ratio.[3] The Soviets claimed to have downed over 600 Sabres.[4][5] More recent research by Lake Dorr and Warren Thompson has claimed the actual ratio was closer to 2 : 1.[6] A 2009 RAND review concluded that the actual kill : loss ratio was 1.8 : 1 overall, and likely closer to 1.3 : 1 against MiGs flown by Soviet pilots.[7][8]
Vietnam War[edit]
Unlike North Korea, Nationalist China invaded French Indochina (Vietnam) in 1945 to regain the region from the occupying Japanese military at the end of World War II,[9][relevant?] but were unable to gain a foothold in North Vietnam. Student North Vietnamese MiG pilots were sent to China and the Soviet Union for up to three years for training. Also student North Vietnamese SAM operators were sent to the USSR for about six to nine months of training.[10][11] Soviet and Chinese Communist pilots were restricted to test flying MiGs which had been exported to North Vietnam from their countries.[12][13] Due to the urgency brought on by Operation Rolling Thunder, and until North Vietnamese missilemen could be trained, Soviet PVO SAM Anti-Aircraft Missile operator/instructors were quickly deployed to North Vietnam in 1965, and through 1966 were reportedly responsible for downing approximately 48 US aircraft during the war.[14][15] There is one reported ace pilot from the USSR, Col. Vadim Shcherbakov who is credited with 6 air-to-air kills.[16]
Cold War[edit]
During the Cold War many nations including the Soviet Union and the United States were fiercely protective of their airspaces. Aircraft which entered an opposing nation's airspace were often shot down in air-to-air combat. The incidents produced a heightened sense of paranoia on both sides that resulted in the downing of civilian craft. Many of the aircraft listed at that link were not shot down as a result of Cold War paranoia by US or USSR aircrews, but rather direct action by active combatants (for example, the two Air Rhodesia flights).
The table lists air combat losses outside of the war zones, such as Korean War or Vietnam War. It does not include losses to ground-based defenses, and it does not include civilian aircraft.
See also[edit]
- Post–World War II air-to-air combat losses
- 1958 C-130 shootdown incident
- 1960 RB-47 shootdown incident
- 1964 T-39 shootdown incident
References[edit]
Footnotes[edit]
- ^ a b Brune 1996, p. 215
- ^ Yevgeny Pepelyayev – top ace of the Korean War by Diego Zampini
- ^ War Monthly (1976). MIG V Sabre, by Rodney Steel (p. 48).
- ^ Sewell, Stephen L. "Russian Claims from the Korean War 1950–53." Archived 1 November 2006 at the Wayback Machine korean-war.com. Retrieved: 19 July 2011.
- ^ Zhang, Xiaoming. Red Wings over the Yalu: China, the Soviet Union, and the Air War in Korea. College Station, Texas: Texas A&M University Press, 2002. ISBN 1-58544-201-1.
- ^ Dorr, Robert F., Jon Lake and Warren E. Thompson. Korean War Aces. London: Osprey Publishing, 2005. ISBN 1-85532-501-2.
- ^ Stillion, John and Scott Perdue. "Air Combat Past, Present and Future." Archived 6 October 2012 at the Wayback Machine Project Air Force, Rand, August 2008. Retrieved 11 March 2009.
- ^ Igor Seidov and Stuart Britton. Red Devils over the Yalu: A Chronicle of Soviet Aerial Operations in the Korean War 1950–53 (Helion Studies in Military History). Helion and Company 2014. ISBN 978-1909384415. Page: 554.
- ^ Toperczer, Istvan. MiG-17 and MiG-19 Units, p. 7
- ^ Toperczer, MiG-17 and MiG-19 Units, pp. 10–15
- ^ Davies p.53
- ^ Toperczer, MiG-21 Units, p. 77
- ^ Michel, p. 297
- ^ Davies, pp. 8, 40
- ^ Zampini, Diego (2010). "Robin Olds: Mastermind of Operation Bolo". acepilots.com. Retrieved April 12, 2010.
- ^ "Task Force Russia – Report 17 March–16 April 1993 18th Report". Library of Congress. Archived from the original on 24 March 2019. Retrieved 2018-06-19.
- ^ a b Samuel 2001, p. 150
- ^ Baer, Dennis (2010). "The Consolidated PB4Y-2 Privateer". aviation-history.com. Archived from the original on October 19, 2010. Retrieved April 4, 2010.
- ^ Zhang 2004, p. 241
- ^ "VP-6 P2V Shootdown of a Soviet MIG off Vladivostok 1950 – Patron Sic Blue Sharks Association". www.vp-6.org. Retrieved 2018-12-20.
- ^ Goebel, Greg (2010). "The Lockheed P2V Neptune & Martin Mercator". Retrieved April 4, 2010.
- ^ a b c d e f g Polmar 2001, p. 20
- ^ Grossnick and Armstrong 1997
- ^ a b c Goldrich, Robert L. (2010). "Published Cold War Shoot Down Incidents". aiipowmia.com. Archived from the original on June 11, 2009. Retrieved April 4, 2010.
- ^ Globalsecurity.org (2010). "RB-66 Destroyer". Globalsecurity.org. Retrieved April 4, 2010.
- ^ Samuel 2001, p. 151
Bibliography[edit]
- Brune, Lester H. (1996). The Korean War: Handbook of the literature and research (1996 ed.). Greenwood Publishing Group. ISBN 0-313-28969-7.
- Davies, Peter. F-105 Wild Weasel vs SA-2 "Guideline" SAM, Vietnam 1965–73. Osprey 2011. ISBN 978-1-84908-471-0.
- Michel III, Marshal L. Clashes, Air Combat Over North Vietnam 1965–1972. Naval Institute Press, 1997. ISBN 978-1-59114-519-6.
- Toperczer, Istvan. MiG-17 and MiG-19 Units of the Vietnam War. Osprey Combat Aircraft #25. ISBN 978-1-84176-162-6.
- Toperczer, Istvan. MiG-21 Units of the Vietnam War. Osprey Combat Aircraft #29. ISBN 978-1-84176-263-0.
- Polmar, Norman (2001). Spyplane: the U-2 history declassified (2001 ed.). Zenith Imprint. ISBN 0-7603-0957-4.
- Samuel, Wolfgang W. E. (2001). I always wanted to fly: America's Cold War airmen=. University Press of Mississippi. ISBN 1-57806-399-X.
- Zhang, Xiaoming (2004). Red Wings Over the Yalu: China, the Soviet Union, and the Air War in Korea. Texas A&M University Press. ISBN 1-58544-340-9.