Draft:Maemo Leste
 | Draft article not currently submitted for review.
This is a draft Articles for creation (AfC) submission. It is not currently pending review. While there are no deadlines, abandoned drafts may be deleted after six months. To edit the draft click on the "Edit" tab at the top of the window. To be accepted, a draft should:
It is strongly discouraged to write about yourself, your business or employer. If you do so, you must declare it. Where to get help
How to improve a draft
You can also browse Wikipedia:Featured articles and Wikipedia:Good articles to find examples of Wikipedia's best writing on topics similar to your proposed article. Improving your odds of a speedy review To improve your odds of a faster review, tag your draft with relevant WikiProject tags using the button below. This will let reviewers know a new draft has been submitted in their area of interest. For instance, if you wrote about a female astronomer, you would want to add the Biography, Astronomy, and Women scientists tags. Editor resources
Last edited by Citation bot (talk | contribs) 34 days ago. (Update) |
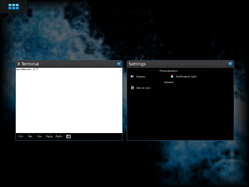 | |
| Developer | Maemo Leste open-source community |
|---|---|
| OS family | Unix-like |
| Working state | Active |
| Source model | Open source |
| Marketing target | Operating system for smartphones |
| Update method | ROM flashing or dpkg (package manager) |
| Package manager | dpkg |
| Platforms | ARM, ARM64, x86-64 |
| Kernel type | Monolithic (Linux) |
| Default user interface | Hildon |
| Official website | maemo-leste |
Maemo Leste is a free and open-source mobile operating system,[1] a mainline Linux distribution for smartphones, tablets and electronic devices.[2] It is based on Devuan[3] ("Debian minus systemd"[4]), plus Maemo components.[5] It is totally independent of Android.
History
[edit]Maemo was a Debian-based distribution developed by Nokia in the early 2000s. It was used on the 700 and 800-series Nokia phones, and finally on the N900, N9, N950 and similar phones.[3] After Nokia was taken over by Microsoft and switched to Microsoft Lumia OS, the open-source community continued to provide software support and make new software work on the old phones, which remain in use 15 years after they came out, as of 2024[update]. Maemo Leste is an updated version of the Maemo OS.[4][6]
Initiated in 2018 by Ivan Jelincic and Merlijn Wajer,[7] the project aims to reuse the Maemo components in a fully FOSS environment.[8] Its target users are menbers of OSS communities.
Maemo Leste is based on Devuan, with mainline kernel; it is used with the Hildon GUI. It ports much of Maemo 5 "Fremantle", but eliminates the closed-source components that made Fremantle hard to maintain, while maintaining the Fremantle API.[8][3]
Funding
[edit]Maemo Leste is partly financed by the EU grants: NGI[9] and NLNet.[10]
Compatible devices
[edit]Various devices can operate Maemo Leste:[3]
See also List of open-source mobile phones; a mobile which can run mainline Linux can run Maemo Leste, though not all functionality may work.
References
[edit]- ^ "Maemo Leste Wiki". leste.maemo.org. Retrieved 2024-07-30.
- ^ "Maemo Leste". archive.fosdem.org. Retrieved 2024-07-30.
- ^ a b c d Merlijn Wajer (May 11, 2023). "Maemo Leste: A Debian/Devuan based mobile hacker OS" (PDF).Wajer, Merlijn B. W. (2019). "Maemo Leste: Mobile Hacker OS". doi:10.5446/44392.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ a b T., Raffaele (3 April 2020). "Large Maemo Leste update brings camera and TV output to 11-year old Nokia N900, PowerVR GPU support for Motorola Droid 4". TuxPhones - Linux phones, tablets and portable devices. Retrieved 4 October 2024.
- ^ "Maemo Leste". archive.fosdem.org. Retrieved 2024-07-30.
- ^ "Ten years of Nokia N900". postmarketOS. Retrieved 4 October 2024.
- ^ "Maemo Leste". DAPSI - Data Portability & Services Incubator. Retrieved 2024-07-30.
- ^ a b "Regaining control of your smartphone with postmarketOS and Maemo Leste". archive.fosdem.org. Retrieved 2024-07-30.
- ^ "Maemo Leste Telepathy". Next Generation Internet. 2024-01-08. Retrieved 2024-07-30.
- ^ "NLnet; Maemo Leste". nlnet.nl. Retrieved 2024-07-30.
