Portal:Energy
| Main page | New articles & Tasks |
 The Energy Portal Welcome to Wikipedia's Energy portal, your gateway to energy. This portal is aimed at giving you access to all energy related topics in all of its forms.
|
Page contents: Selected article • Selected image • Selected biography • Did you know? • General images • Quotations • Related portals • Wikiprojects • Major topics • Categories • Help • Associated Wikimedia |
Introduction
Energy (from Ancient Greek ἐνέργεια (enérgeia) 'activity') is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat and light. Energy is a conserved quantity—the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed; matter and energy may also be converted to one another. The unit of measurement for energy in the International System of Units (SI) is the joule (J).
Common forms of energy include the kinetic energy of a moving object, the potential energy stored by an object (for instance due to its position in a field), the elastic energy stored in a solid object, chemical energy associated with chemical reactions, the radiant energy carried by electromagnetic radiation, and the internal energy contained within a thermodynamic system. All living organisms constantly take in and release energy.
Due to mass–energy equivalence, any object that has mass when stationary (called rest mass) also has an equivalent amount of energy whose form is called rest energy, and any additional energy (of any form) acquired by the object above that rest energy will increase the object's total mass just as it increases its total energy.
Human civilization requires energy to function, which it gets from energy resources such as fossil fuels, nuclear fuel, or renewable energy. The Earth's climate and ecosystems processes are driven by the energy the planet receives from the Sun (although a small amount is also contributed by geothermal energy). (Full article...)
Selected article
To avoid dangerous climate change, the energy policy of the European Union has set a 2°C [3.6°F] limit to the temperature rise, compared to pre-industrial levels. Of this, 0.8°C has already taken place and another 0.5°C is already committed. The 2°C rise is associated with a carbon dioxide concentration of 400–500 ppm by volume; as of January 2007 it was 383 ppm by volume, and rising at 2 ppm annually. Unless significant action is taken soon the 2°C limit is likely to be exceeded.
Strategies for moving to a low-carbon economy include development of new technologies, particularly renewable energy; electric and hybrid vehicles; fuel cells; public transportion; zero-energy buildings; Zero-Net-Energy USA Federal Buildings; energy conservation; carbon taxes; enhancing natural carbon dioxide sinks; population control; and carbon capture and storage. Environmental groups also encourage individual-lifestyle and political action, as well as action by business.
The Kyoto Protocol, covering more than 160 countries and over 55% of global emissions provides an international mitigation framework. The United States, the world's largest greenhouse gas emitter; and Kazakhstan have refused to ratify the treaty. China and India, two other large emitters, have ratified the treaty but are exempt from cutting emissions. International talks on a successor to the treaty, which ends in 2012, have begun.
Selected image

Photo credit: Postdlf
Lightning is a highly visible form of energy transfer.
Did you know?

- Buildings constructed to the German Passivhaus standard use 75% to 95% less energy for space heating and cooling than current new buildings in the United States?
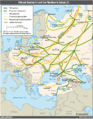
- Crossing 4,000 km (2,500 miles), the Druzhba pipeline is the world's longest oil pipeline?
- Coal is ground to a powder before being burnt in fossil fuel power plants?
- Compact fluorescent lamps (pictured) use about 1/4 of the energy of normal incandescent light bulbs, and pay for themselves after about 500 hours of use?
- Nuclear power in France produces 78% of all the country's electricity - more than in any other nation?
- Positive lightning bolts are typically six to ten times more powerful than normal lightning — and aircraft are not designed to withstand them?
- Dark energy is a hypothetical form of energy which permeates all of space?
Selected biography
Edison invented the first commercially practical electric light bulb which, by 1879 would burn for hundreds of hours. He was able to sell the concept to homes and businesses by mass-producing them and creating a complete system for the generation and distribution of electricity.
Edison patented an electric distribution system in 1880, and in January 1882 he switched on the first steam generating power station at Holborn Viaduct in London, UK. The direct current (DC) supply system provided electricity supplies to street lamps and a number of private dwellings within a short distance of the station. The first investor-owned electric utility, Pearl Street Station, New York City, started generating on September 4, 1882, providing 110 volts direct current to 59 customers in lower Manhattan.
Life magazine (USA), in a special double issue, placed Edison first in the list of the "100 Most Important People in the Last 1000 Years," noting that the light bulb he promoted "lit up the world." He was ranked thirty-fifth on Michael H. Hart's list of the most influential figures in history.
In the news
- 10 July 2024 – Russian invasion of Ukraine
- Two Ukrainians are killed by Russian drone and missile attacks on a port in southern Odesa Oblast, Ukraine, which damaged port infrastructure, an energy facility, and a civilian ship. (Reuters)
General images
Quotations
- "If we already have the Kyoto protocol, why invent another proposal and not just implement one that already exists? If a country is incapable of implementing the result of an international treaty that has established rules and regulations, it won't end up implementing those rules voluntarily."" – Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva, 2007
- "Climate change is a challenge China must cope with to realize sustainable development... Implementing a climate change containment policy may cost a fortune, but the cost will be even higher if we delay. Early action is imperative." – Ma Kai, 2007
- "The consequences of restricting the development of developing nations will be much more serious than the consequences of global warming." – Ma Kai, 2007
Related portals
WikiProjects
WikiProjects connected with energy:
Other WikiProjects that may be of interest:
Major topics
Major categories
National energy supply, use & conservation
National electricity sector
Politics, economics, environment
- Climate change
- Energy conservation
- Energy economics
- Energy crises
- Energy development
- Energy policy
- Peak oil
Energy sources
- Fuels
- Biofuels
- Fossil fuels
- Fusion power
- Nuclear technology
- Renewable energy
- Energy conversion
- Electric power
- Energy storage
Energy-related design
Scientific usage
Help

Puzzled by energy?
Can't answer your question?
Don't understand the answer?
- Ask at the reference desk
- Read the Wikipedia help pages
For further ideas, to leave a comment, or to learn how you can help improve and update this portal, see the talk page.
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus