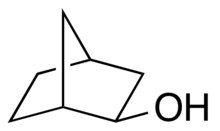
exo-Norborneol
Appearance
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
rel-(1R,2R,4S)-Bicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-2-ol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.133 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H12O | |
| Molar mass | 112.172 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 124 to 126 °C (255 to 259 °F; 397 to 399 K) |
| Boiling point | 176 to 177 °C (349 to 351 °F; 449 to 450 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | Fisher MSDS |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
exo-Norborneol is an alcohol containing the norbornane skeleton. Commercially available, this colorless compound may be prepared by the reaction of norbornene with formic acid, followed by hydrolysis of the resultant exo-norbornyl formate.[1]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Kleinfelter, Donald C.; von R. Schleyer, Paul (1962). "2-Norbananone". Organic Syntheses. 42: 79. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.042.0079.
Further reading
[edit]- Reaction of organic compounds under high temperature – dilute acid (HTDA) conditions. III. The perdeuteration of bicyclo[2.2.1]heptanes PDF
- Stille, J. K.; Sonnenberg, Fred M. (1966). "The Reaction of endo- and exo-2-Norborneol with Thionyl Chloride". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 88 (21): 4915. doi:10.1021/ja00973a027.
