Gadoleic acid
Appearance
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
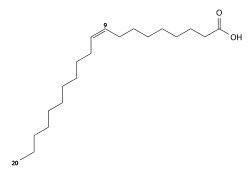
| Preferred IUPAC name
(9Z)-Icos-9-enoic acid | |
| Other names
cis-9-Eicosenoic acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.291.826 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H38O2 | |
| Molar mass | 310.522 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 23 to 24 °C (73 to 75 °F; 296 to 297 K)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Gadoleic acid (20:1 n−11) is an unsaturated fatty acid. It is a prominent component of some fish oils including cod liver oil.[2] It is one of a number of eicosenoic acids. Its name is derived from a combination of the genus for cod (Gadus) and the Latin word oleum (oil), which itself is derived from the Ancient Greek ἔλαιον (elaion) meaning olive oil.
References
[edit]- ^ Vesely, V. (1930). "Sur les acides gadoléique et sélacholéique synthétiques". Collection of Czechoslovak Chemical Communications. 2: 95–107. doi:10.1135/cccc19300095.
- ^ "Cod-liver oil". Encyclopædia Britannica.
