John Ralston (artist)
John Ralston (1789–1833) was a Scottish artist who spent most of his life and career in Manchester, England. He was primarily a marine and landscape painter, but his best-known works depict the city's medieval and early modern architecture before its demolition and replacement during the Industrial Revolution.
Though his talents were acclaimed by his contemporaries, and he was seen as an important early figure in the emergence of Manchester as a centre of the arts, it never translated into popular or financial success and he died in relative poverty and obscurity.
Early life
[edit]Ralston was 44 at the time of his death in November 1833, implying that his birth year was either 1788 or 1789; sources published after his death, including those written by people who knew him, consistently prefer 1789.[1][2][3][4] He was born in Scotland, though the exact date and location are unknown. The Ralston name is traditionally associated with the historical counties of Renfrewshire and Ayrshire, and he may be the "John Ralston" born in Eastwood on 6 December 1788; the other John Ralstons that appear in parish birth records for 1789 were all born in Argyll and Bute.[5][6]
Artistic career
[edit]Education
[edit]Manchester had been a large market town (and the centre of Lancashire's textiles industry) for several centuries, but as the 19th century dawned the city was experiencing an unprecedented population boom due to the Industrial Revolution. Large cotton mills and other factories were being constructed rapidly, as well as new slums to house the thousands of immigrants from elsewhere in the United Kingdom and overseas who came to work in "Cottonopolis".[7] However, the city was not associated with the arts; even as late as the 1870s, the prominent Victorian art critic John Ruskin believed that Manchester could "produce no good art and no good literature" due to its intense focus on commerce and industry.[8][9]

In this context, it is unsurprising that Ralston came to Manchester because his father—an engraver for calico printing—had moved the family south to Strines in Derbyshire when searching for work when Ralston was a child, rather than the city being chosen specifically as a destination for studying art.[4] At 17 he became a pupil of Joseph Parry, or "Old Parry" as he was known to his contemporaries—a Liverpool-born painter who was given the title of "The Father of Art in Manchester" after relocating to the city in 1790 and earning acclaim for his depictions of everyday urban life.[4][10][11][12] However, with his "predilection being for landscape," he was soon passed on to John Rathbone, an oils and watercolours landscape painter known in his day as "the Manchester Wilson."[13][14][15]
Francis Dukinfield Astley was Ralston's first patron; he "was enabled to trace, in the rude attempts of the unassuming boy, the budding power of Linnaeus which ripened to so great maturity."[16] Astley's father, John Astley, had eked out a living as a professional painter for many years before marrying a wealthy widow and inheriting her fortune, and Francis was himself an amateur painter and patron of many local artists with a substantial collection of Old Masters—he had Ralston produce several copies as part of his training.[4][17][18]
Sources are inconsistent as to whether Astley first spotted Ralston's talent and arranged for his training by Parry and Rathbone, or whether he was connected with Astley by his teachers.[4][16] Some modern sources mistakenly claim that Ralston moved to Manchester specifically to study at the Manchester School of Art, which was not founded until five years after his death.[14][19]
Art
[edit]Ralston lived at 26 Brazennose Street from the time he settled in Manchester until shortly before his death.[20] By the late 1810s he had built a reputation as a skilled artist, and much like his teacher Rathbone he had a bias towards "picturesque" rural scenes, with "mouldering castles, ruined abbeys, and dilapidated cottages" his typical subjects.[21] However, he was most well-regarded as a marine painter, which he was said to have "thoroughly mastered."[16][22][23][4]
He typically drew graphite sketches from nature and then later produced oil paintings back in his studio, "rarely" producing colour sketches or watercolours while outside.[4] In his later years his tastes evolved, and he became increasingly as interested in Manchester's new urban environments as much as traditional agrarian scenes.[11][12][21]
Views of the Ancient Buildings in Manchester
[edit]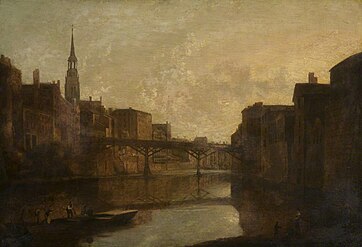
Like many of the UK's rapidly growing cities during the Industrial Revolution, Manchester's existing medieval urban fabric came to be seen as a hindrance by civic leaders—its small, old wooden buildings were unable to host large machinery, and its narrow streets limited the flow of traffic. In 1821 Parliament passed the Manchester Streets Improvement Act, which empowered local commissioners to begin a 12-year project of modernising the city centre by widening several key roads by up to 15 feet either side, as well as lowering them all to a uniform level. The most dramatic impact was on Market Stead Lane (now known as Market Street), the city's main east–west throroughfare, which had to be lowered up to six feet in some stretches, and where some of the city's most well-known buildings were demolished.[24][25]
The early 1820s saw a boom in the publication of topographical engravings across England, out of a widespread concern that views of "traditional" buildings and streets needed to be preserved before they were lost forever.[26] The same year the Act passed, Ralston was commissioned by local publisher D. & P. Jackson to document Market Street before its transformation.[20] The prospectus announcing the series, Views of the Ancient Buildings in Manchester, stated that subscribers could expect 20 lithographs, split across four volumes—although in the end only just over half of the pictures were actually published between 1823 and 1825, which were then gathered and republished as a single volume after Ralston's death.[26][20]
It is unknown why Views was cut short. In 1869, Manchester's deputy mayor Thomas Baker (himself an antiquarian) reported that the series had had 124 subscribers ("a sufficiently large list"), and that the original engraved plates were by that point in the hands of private collectors—with most owned by John Knowles. He listed the titles of the pieces in Views as follows:
- Dedication page (including illustration by Mather Brown of "a female figure holding an escutcheon bearing the bendlet of Manchester")
- Market Place, Manchester
- The late Dr. White's house, King Street
- Market Street (depicting Sharp's ironmongery shop and Hyde's tea warehouse)
- Market Street (view towards the Exchange, including Newall's grocery shop)
- Market Street, Manchester (another view towards the Exchange, including Styan's gun shop)
- Blackfriars Bridge (the old footbridge, dismantled in 1817 and presumably first sketched by Ralston around that time)
- Top of Market Street, Manchester (depicting the Swan coach office opposite the corner of Brown Street)
- Middle Market Street, Manchester (depicting the state lottery office)
- Mr. Hyde's Shop, Market Street (two versions, with a large crowd, including a coach and four horses, in front of the shop)
- Salford Cross (figures in the street are credited to Denis Dighton)
- Salford Cross (an alternative view with slightly different perspective)[20]
At least one further drawing was published in the series, but not included in the collected volume which Baker was describing—Smithy Door looking to Cateaton Street (1825)—though he had seen its plate exhibited in 1857 and noted its similarity to the other pieces in Views.[20] This "missing 13th plate" resurfaced in an auction at Sotheby's in 1975, allowing its inclusion in a reprint of Views published in 1989 by historian Hugh Broadbent which used the original plates for all the pieces.[27][26]
Eight pencil drawings in the style of the Views (all dated 1822) were uncovered by a private collector in 1875 and published in the book Olde Manchester to "complete" the set, but Smithy Door was not among them. Instead, it was included in an appendix of "other plates illustrative of Manchester in bygone days." These nine drawings also have a "rough and unfinished character" compared to the pieces that appeared in the final version of Views—for example, the Olde Manchester version of Smithy Door depicts fewer people in the street, and the view of Manchester Cathedral in the distance is obscured.[17][27] Ralston first sketched the scenes in Views on location in pencil, then returned home to produce more detailed, "final" versions, from which the lithographic plates were copied—the nine sketches included in Olde Manchester were likely Ralston's original first drafts for plates which were never produced. (He also produced oil paintings of some of the scenes in Views several years later; they tend to be traditional landscapes, with less of a focus on architectural detail.)[17]
-
Market Place, Manchester (1823)—reproduction published in 1875; likely derived from an original sketch in 1821.
-
Market Stead Lane, Manchester (c.1825)—a later oil painting of the scene from Market Place, Manchester (1823).
-
First version of Salford Cross (c.1823)—additional figures by Denis Dighton.
-
Second version of Salford Cross (c.1823)
-
Old Smithy Door, Manchester (1822)—graphite sketch, looking toward the Cathedral.
-
Smithy Door looking to Cateaton Street (1825)—final lithograph version; additional figures by Dighton.
Though not considered especially remarkable during Ralston's lifetime, Views is his most enduring body of work as it contains the only known images of several of the buildings and landmarks within (such as the Salford Cross).[28] In comparison to other depictions of Manchester's buildings at the time—and especially H. G. James' Views in Lithography of Old Halls, Etc., in Manchester and the Vicinity (1821-1825), the other substantial print series commissioned in response to the Manchester Streets Improvement Act—Ralston's drawings are considered to be the highest-quality attempt at visually recording pre-modern Manchester's architectural heritage still available.[26][29] The prints are also seen as relatively faithful representations of the city's street life, and have been reproduced in a number of history books, magazines, newspapers, and academic texts.[30][31][24][32][33][34]
Influence and position within Manchester art world
[edit]
The landscape painter George Wilfred Anthony—who also penned art criticism in The Manchester Guardian as "Gabriel Tinto"—studied under Ralston in the 1820s.[35][36]
In 1823, a group of local leaders voted to establish the "Manchester Institution for the Promotion of Literature, Science and the Arts" at a meeting to address the widely held perception of Manchester as a cultural backwater (and especially relative to the city's greatest rival, Liverpool). The Royal Manchester Institution (as it would shortly become known) purchased a plot of land on Mosley Street for the construction of a large headquarters and exhibition space, designed by the architect Charles Barry, in 1825.[37]
However, the building (now Manchester Art Gallery) would not be finished until 1835; in the meantime, the Institution held the very first painting exhibition in Manchester, in 1827, at 83 Market Street.[38] Ralston was one of 18 local artists selected for inclusion.[33] Until 1830—when enough of the Mosley Street building had been completed for a partial opening—the Institution would hold a series of further exhibitions at 83 Market Street, featuring both nationally and internationally renowned works alongside those of artists working locally. In each of these exhibitions there was a core group of Manchester-based artists—Ralston, brothers Charles and Michael Pease Calvert, Henry Liverseege, Arthur Perigal, Thomas Henry Illidge, and James Parry (son of Joseph)—whose works were always included.[39]
However, despite this critical success Ralston consistently struggled to actually sell his works. For example, The Manchester Courier's report on a September 1830 exhibition at the Royal Institution noted that Ralston's Storm is "[a] most splendid and spirited production; the execution is vigorous, and the colouring deep and effective, though tender ... and [we] very much doubt if there be half a dozen men in the kingdom who could surpass it," but then added that it was "(unsold!)"—almost in disbelief.[40]
The historian Janet Wolff has pointed out that Ralston was not unusual at this time, noting that the stereotype of the "starving artist" was very much grounded in fact in 19th century Manchester. Of the first generation of Manchester-based artists who were either involved in the foundation of the Royal Manchester Institution, or exhibited there in its first decade, all of Ralston, Liverseege, William Bradley, brothers David Henry Parry and James Parry (both sons of Old Parry), James Gregory Pollitt, and Henry James Holding died from either poverty or illness; there were also a number of high-profile painters who came to the city to explore its emerging art market—such as Mather Brown—who quickly left after failing to find a foothold.[24]
Reflecting these concerns about their financial security, in 1830 a group of painters, sculptors, and architects formed "the Manchester Artists", a "fraternity society" which was intended to represent their interests within Manchester's nascent cultural establishment. Ralston was one of six men—alongside Perigal, Illidge, Charles Calvert, James Parry, and William Bury—who were elected as the "nucleus" of this new society.[41][42]
Despite the best attempts of the city's elites to encourage a homegrown art scene, the general public was less enthusiastic—in a report on an exhibition at the Royal Institution in 1832, The Manchester Courier bemoaned "a lamentable falling off in the number of productions by our resident artists," with the blame laid squarely at the feet of "our fellow townsmen" for not "encouraging resident talent." The writer notes that Illidge, Perigal, Bradley, and Benjamin Rawlinson Faulkner had all left the city to make more money elsewhere, leaving behind a "general desertion and sterility"; two of Ralston's works, Sea Calm and A View of the Friends' Meeting House, were cited as rare examples among what was left to exhibit "which really deserve the attention of the lover of excellence in art."[43]
Death and legacy
[edit]By the early 1830s Ralston's career and health were both faltering. He died on 1 November 1833, aged 44, after being bedridden for several days, and reportedly while living in a workhouse after having fallen into severe poverty. He was survived by his widow and one son.[44][16][24][22]
Many in Manchester's artistic and cultural community hailed Ralston's "unappreciated" talent upon his death.[23][45][46][4] George Wilfred Anthony, writing in 1857, called Ralston "a man of extremely simple manners; he possessed not the acuteness or business habits of a man of the world, but his honesty of purpose was undeniable," and he "became neglected for newer, certainly not better men."[4] Anthony also partly attributed his commercial failure to a lack of focus, as Ralston was just as passionate about playing the violin as painting: "Often while busily employed on a Picture the remembrance of some strain of melody, haply [sic] snatched from a symphony of Beethoven's rehearsed on the previous evening, would vibrate through his mind, when out came his fiddle, and adieu to all thoughts of his picture."[4] Richard Cudmore—leader of the Manchester Gentleman's Orchestra, of which Ralston was a founding member—is quoted as having told him "if it wasn't for that confounded fiddle you'd be a great man."[4][47]
Ralston's most extensive (and effusive) obituary was published in the March 1834 edition of Arnold's Magazine of the Fine Arts. The author reported that Ralston's cause of death was "ossification of the heart," which they believed to be a literalised manifestation of his heartbreak at never achieving popular recognition:
...[H]e drew and painted from nature with unabated enthusiasm until within a few days of his decease; indeed, when entirely confined to his bed, "the ruling passion, strong even in death," still swayed him, and it gave him pleasure to converse on subjects of Art with those of his professional brethren who hastened to cheer in his sickness one whom they admired for his genius, and loved for the plain, manly, simplicity of his character. A more grateful man perhaps never existed; he never forgot a favor; and often have we heard him, with his peculiar strength and feeling, express his sense of obligation for those little kindnesses and attentions which are usually suffered to pass without observation, as the every day offices of "gentle humanity." ...
The merely pretty and ornamental he despised, he looked for mind, and grappled with a giant's strength with the real difficulties of Art―he dived deep, and not merely skimmed the surface; hence, to superficial observers, his works seemed rude and tasteless. Those, however, who really understood and valued excellence in Art, at once acknowledged the hand of a master, and the powerful impress of truth. Perhaps the strongest proof of this may be found in the high estimation always evinced by his brother artists, those best calculated by previous study to appreciate his abilities and the extent of his acquirements. ...
If it be asked, why Mr. Ralston with all his talent and industry failed to become popular? Our answer is (in conjunction with the causes before glanced at) that he was a shy, sensitive, retiring man; he obtruded not his claims on public attention, he suffered in quiet, and at last sunk under the benumbing influence of continued neglect—he is, however, gone to his rest, and it would be useless to enlarge on the causes which embittered his declining days. Truth and justice, however, demand it should be told, that his end was accelerated by public neglect.
The author ends by suggesting that the tomb of this "gifted and honorable man ... might with propriety be inscribed" with a quote from Plautus: "UT SÆPE SUMMA INGENIA IN OCCULTO LATENT." ("How often the greatest talents are shrouded in obscurity.")[16] The Manchester Times published a similarly sympathetic obituary:
[A]n artist whose excellence in his peculiar walk of art (marine painting) failed to meet with that due appreciation it so eminently deserved—added to which, the cold neglect endured from, the warmth of whose patronising influence ought to have shone on the summer of his life, conjointly produced that "sickness of the soul" (the immediate cause of his dissolution) so keenly felt in the sensitive minds of most professors of art, and from which he only found alleviation in the fondness for his profession and the affectionate endearments of his family, who, let us hope, may now derive that support from his works they so richly deserve, as they gain an additional worth from the knowledge that he who stamped the canvas with its value no longer feels—
The whips and spurs of time,
The proud man's contumely,—
Which patient merit of th' unworthy takes.[22]
Manchester publisher Charles Tavaré, father of artist Frederick Tavaré and uncle of poet Charles Swain, dedicated a poem to his memory:
Artist rever’d, who skilled in Nature's love,
By her was’t blest with genius’ richest store,
Yet who pursued by Fortune’s sullen glooims,
Neglected, sank into an early tomb:
Ah! tho’ a higher meed now crowns thy head,
Pardon these anguish’d tears that on thy dust are shed.[48]
Frederick Tavaré's son, F. L. Tavaré, also became an artist and cited Ralston as a key influence on his own paintings of Manchester landmarks.[48]
In 1834, a mezzotint portrait of Ralston was published by Agnew & Zanetti; the composite image was formed of a portrait by American painter George Freeman (misspelled as "Frieman"/"Frierman" in some advertisements) of Ralston sitting in a chair under a tree, with a copy of one of Ralston's own pastoral landscapes as the background.[49][50][51] It was included in the collected volume of Views of the Ancient Buildings in Manchester which was published after his death.[20] A copy is held by the National Portrait Gallery.[52]

While he never achieved widespread popularity, Ralston's reputation within the Manchester art world persisted for some time. In 1857, a new wing was opened at the Salford Free Museum & Library (now the Salford Museum & Art Gallery) in Peel Park, and an exhibition featuring more than 650 works produced by local artists was planned to mark the occasion.[53] The Peel Park Local Art Exhibition opened on 22 April 1857, only weeks before the opening of the Art Treasures of Great Britain Exhibition less than a mile away—the largest art exhibition ever held in the UK, with more than 16,000 works by internationally renowned masters, both old and new.[54][55] However, James Astbury Hammersley, head of the Manchester School of Art and one of the organisers, insisted in his speech to mark the opening that he welcomed visitors making comparisons between the works in both exhibitions, confident that the city's artists could hold their own against the world's best.[56] Several of Ralston's paintings and drawings were selected, including several original plates from Views of the Ancient Buildings in Manchester, and the exhibition's catalogue highlighted that "the archaeologist is indebted to him for many valuable records of defunct localities of Manchester."[20][57] The success of the exhibition inspired a group of local artists, led by Robert Crozier, to found the Manchester Academy of Fine Arts in 1859.[58][59][26]
His watercolour painting of Mab's Cross was donated to Wigan Central Library in 1905, and was on display there for many years.[60] However, while several museums still hold works by Ralston in their collections—including Manchester Art Gallery, the Salford Museum & Art Gallery, The Whitworth, and Tate Britain—few are now on permanent display.[61][62]
Ralston was buried on 5 November 1833 at St. Stephen's Church in Salford.[63] The exact location of his grave was lost when St. Stephen's was demolished in 1956; the burial ground is now a public park.[64]
References
[edit]- ^ Tate. "John Ralston 1789–1833". Tate. Retrieved 2023-10-10.
- ^ "John Ralston – National Portrait Gallery". www.npg.org.uk. Retrieved 2023-10-10.
- ^ "Discover painter John Ralston". rkd.nl. Retrieved 2023-10-16.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Anthony, G. W. (1857). Catalogue of the first Exhibition of the works of Local Artists.
- ^ Burke, John; Burke, Bernard (1850). A Genealogical and Heraldic Dictionary of the Landed Gentry of Great Britain & Ireland. H. Colburn.
- ^ "Search results | ScotlandsPeople". www.scotlandspeople.gov.uk. Retrieved 2023-10-10.
- ^ "Cottonopolis". Oxford English Dictionary (Online ed.). Oxford University Press. (Subscription or participating institution membership required.)
- ^ "History of the gallery". Manchester Art Gallery. Retrieved 2023-10-10.
- ^ "Thomas Coglan Horsfall and Manchester Art Museum and University Settlement – infed.org". 2019-07-08. Retrieved 2023-10-10.
- ^ "PARRY, JOSEPH (1744–1826), painter and engraver | Dictionary of Welsh Biography". biography.wales. Retrieved 2023-10-10.
- ^ a b "Joseph Parry – Biography". www.artnet.com. Retrieved 10 Oct 2023.
- ^ a b "Joseph Parry | Science Museum Group Collection". collection.sciencemuseumgroup.org.uk. Retrieved 2023-10-10.
- ^ Nicholson, Albert (1896). . Dictionary of National Biography. Vol. 47. p. 309.
- ^ a b "JOHN RALSTON (1789–1833)". Christie's. Retrieved 10 Oct 2023.
- ^ "John Ralston – Biography". www.askart.com. Retrieved 2023-10-10.
- ^ a b c d e Arnold's Magazine of the Fine Arts, and Journal of Literature and Science. M. Arnold. 1834.
- ^ a b c Old Manchester: A Series of Views of the More Ancient Buildings in Manchester and Its Vicinity as They Appeared Fifty Years Ago. J.E. Cornish. 1875.
- ^ "Salford History". salfordhistory.blogspot.com. Retrieved 2023-10-11.
- ^ "John Ralston". www.antique-prints-maps.com. Retrieved 2023-10-11.
- ^ a b c d e f g The Palatine Note-book: For the Intercommunication of Antiquaries, Bibliophiles and Other Investigators Into the History and Literature of the Counties of Lancaster, Chester, Etc. J.E. Cornish.
- ^ a b "Lot 76: JOHN RALSTON (1789–1833)". invaluable.com. 11 May 2005.
- ^ a b c "Deaths". The Manchester Times. 9 Nov 1833. p. 3. Retrieved 2023-10-10.
- ^ a b Axon, William Edward Armytage (1886). The Annals of Manchester: A Chronological Record from the Earliest Times to the End of 1885. J. Heywood, Deansgate and Ridgefield.
- ^ a b c d Wolff, Janet (1988). The Culture of Capital: Art, Power, and the Nineteenth-century Middle Class. Manchester University Press. ISBN 978-0-7190-2460-3.
- ^ Starmans, Barbara J. (2015-05-07). "Manchester Market Street Improvements 1828". Out of My Tree Genealogy. Retrieved 2023-10-11.
- ^ a b c d e Hugh, Broadbent (1989). Views of the Ancient Buildings in Manchester. Printwise Books. ISBN 0-904848-06-X.
- ^ a b French, Owen (21 Nov 1975). "Mystery of the missing 13th print". Manchester Evening News. p. 16.
- ^ Barlow, Nigel (2020-11-17). "A look back to the Past-Salford Cross". About Manchester. Retrieved 2023-10-12.
- ^ James, Henry Gould (1821), Views in Lithography of Old Halls etc in Manchester and the Vicinity, retrieved 2023-11-15
- ^ Barker, Hannah (2017). Family and Business During the Industrial Revolution. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-878602-3.
- ^ Darbyshire, Alfred (1887). A Booke of Olde Manchester and Salford. J. Heywood.
- ^ Moore, James. "High culture and tall chimneys: Art institutions and urban society in Lancashire, 1780–1914". academic.oup.com. Retrieved 2023-10-11.
- ^ a b Shaw, William Arthur (1894). Manchester—Old and New. London: Cassell and Company Ltd. p. 41.
- ^ https://pure.manchester.ac.uk/ws/portalfiles/portal/54583491/FULL_TEXT.PDF
- ^ The Art Journal. Virtue and Company. 1860.
- ^ Bryan, Michael (1886). Dictionary of Painters and Engravers: Biographical and Critical. G. Bell and sons.
- ^ BBC. "A grand old gallery". www.bbc.co.uk. Retrieved 2023-10-10.
- ^ "Manchester Royal Institution Autumn Exhibition". The Manchester Evening News. 1882-09-08. p. 2.
- ^ Fawcett, Trevor (1974). The Rise of English Provincial Art: Artists, Patrons, and Institutions Outside London, 1800–1830. Clarendon Press. ISBN 978-0-19-817328-1.
- ^ "MANCHESTER ROYAL INSTITUTION". Manchester Courier. 11 Sep 1830. p. 4. Retrieved 11 Oct 2023.
- ^ "ASSOCIATED MANCHESTER ARTISTS". Manchester Courier. 6 Mar 1830. p. 1. Retrieved 11 Oct 2023.
- ^ "Dinner of the Manchester Artists". Manchester Courier. 21 Aug 1830. p. 3. Retrieved 11 Oct 2023.
- ^ "ROYAL MANCHESTER INSTITUTION—EXHIBITION OF PAINTINGS &c". Manchester Courier. 22 Sep 1832. p. 3. Retrieved 11 Oct 2023.
- ^ Club, Manchester Literary (1884). Papers of the Manchester Literary Club. H. Rawson & Company.
- ^ Records of Manchester from the earliest period ... to the present time. F. Wilde. 1868.
- ^ "Mr. John Ralston". Lancaster Gazette. 16 Nov 1833. p. 3. Retrieved 2023-10-10.
- ^ Husk, William Henry (1900). . A Dictionary of Music and Musicians. Vol. 1.14. p. 423.
- ^ a b "Notes & Queries. John Ralston, artist". The Manchester City News. 15 Jan 1910. p. 2. Retrieved 10 Oct 2023.
- ^ "PORTRAIT OF MR. RALSTON". Manchester Courier. 1 Nov 1834. p. 2. Retrieved 11 Oct 2023.
- ^ "The Late Mr. Ralston". Manchester Courier. 1 Nov 1834. p. 2. Retrieved 11 Oct 2023.
- ^ "PORTRAIT OF MR. RALSTON". Manchester Courier. 8 Nov 1834. p. 1. Retrieved 11 Oct 2023.
- ^ "John Ralston – National Portrait Gallery". www.npg.org.uk. Retrieved 2023-10-11.
- ^ "SALFORD LOCAL ART EXHIBITION". Manchester Courier. 31 Jan 1857. p. 10. Retrieved 11 Oct 2023.
- ^ Exhibition, 1857 (Manchester), Art Treasures; exhib, Manchester art treasures (1859). Exhibition of art treasures of the United Kingdom, held at Manchester in 1857. Report of the executive committee. George Simms.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "Inauguration of the new wing of Peel Park Museum, Salford". The Manchester Times. 25 Apr 1857. p. 7. Retrieved 11 Oct 2023.
- ^ "LOCAL ART EXHIBITION". Manchester Courier. 25 Apr 1857. p. 9. Retrieved 11 Oct 2023.
- ^ Heywood, Abel (1857). The Pictorial Guide to Manchester and Companion to the Art Treasures Exhibition. A. Heywood.
- ^ "Robert Crozier 1878–91". Manchester Academy of Fine Arts. Retrieved 2023-10-12.
- ^ "Robert Crozier Collection (The University of Manchester Library)". www.library.manchester.ac.uk. Retrieved 2023-10-12.
- ^ "Lancashire's Enoch Arden". Manchester Evening News. 28 Dec 1905. p. 6. Retrieved 11 Oct 2023.
- ^ "Ralston, John, 1789–1833 | Art UK". artuk.org. Retrieved 2023-10-11.
- ^ Tate. "John Ralston 1789–1833". Tate. Retrieved 2023-10-11.
- ^ "Manchester, England, Church of England Deaths and Burials, 1813–1985". Ancestry.com. Retrieved 2023-10-11.
- ^ "St Stephen's Gardens • Salford City Council". www.salford.gov.uk. Retrieved 2023-10-11.







