Kostanay Region
Kostanay Region
| |
|---|---|
Detail of Naurzum Nature Reserve | |
 Map of Kazakhstan, location of Kostanay Province highlighted | |
| Coordinates: 53°12′N 63°38′E / 53.200°N 63.633°E | |
| Country | |
| Established | 1936 |
| Capital | Kostanay |
| Government | |
| • Akim | Kumar Aksakalov[1] |
| Area | |
• Total | 196,001 km2 (75,676 sq mi) |
| Population (2022-01-01)[2] | |
• Total | 835,686 |
| • Density | 4.3/km2 (11/sq mi) |
| GDP | |
| • Total | KZT 4,182.1 billion US$ 9.058 billion (2022) |
| • Per capita | KZT 5,014,700 US$ 10,861 (2022) |
| Time zone | UTC+5 |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+5 (not observed) |
| Postal codes | 110000 |
| Area codes | +7 (714) |
| ISO 3166 code | KZ-KUS |
| Vehicle registration | 10, P |
| Districts | 16 |
| Cities | 5 |
| Townships | 8 |
| Villages | 255 |
| HDI (2022) | 0.816[4] very high · 3rd |
| Website | www |
Kostanay Region (Kazakh: Қостанай облысы, romanized: Qostanai oblysy; Russian: Костанайская область, romanized: Kostanayskaya oblast) is a region of Kazakhstan. Its administrative center is the city of Kostanay. The population of the region is 835,686. The population living in Kostanay is 207,000 [5] which is equivalent to 23% of the region.
Geography
[edit]Kostanay Region is adjacent to the Russian federal subjects Orenburg Oblast, Chelyabinsk Oblast, Kurgan Oblast, and is near the Ural Mountains. It also touches four other Kazakh regions: Aktobe Region to the southwest, Karaganda Region to the south, Akmola Region to the southeast, and North Kazakhstan Region to the northeast. The Tobol (Tobyl) River, a tributary of the Irtysh River, starts in and flows through the region on its way to Russia. Kostanay Region's area is 197,000 square kilometers, making it the sixth largest of the Kazakh regions.
Flora and fauna
[edit]Resources of an animal and flora of Kostanay Region are suitable for the organization and development of zones and objects of civilized fishery and a hunt, lake-commodity fish culture, hunt facilities development. The fauna of ground animal includes 52 kinds of mammal, 267 is constant or temporarily living birds, 10 kinds of amphibious and kowtowing, in reservoirs 24 kinds of fishes live.
Naurzum reserve (877 km²), 3 natural sanctuaries (1630 km²) and 12 state nature sanctuaries (0.47 km²) with a rich vegetative cover are pride of region.
Natural resources
[edit]The region is characterized of flat relief with inflows of the Ayat, Ubagan, Ui, and Turgay, Saryozen, and Karatorgai rivers. The Northern part occupies the southeast suburb of the West-Siberian lowland, the Turgay Plateau trails in from the south, the Zaural plateu comes from the west, and the Kazakh Uplands comes in from the southwest. River network is sparce.
There are approximately 310 rivers in the region. The largest rivers are Tobol and Torgai. The Tobol river includes the Verhnetobolsk, Karatomar, and Amangeldy water basins. The Kostanay Region has more than 5,000 lakes; the largest ones are located in Torgai dell, Kushmurun, Sarymoin, Aksuat, and Sarykopa. The woodland area is 2,175 km² including 1,512 km² of natural plantings. Due to the Soviet Virgin Lands Campaign, much of the land was ploughed for wheat.
The Kostanay Region is rich in minerals, especially iron ore. Magnetite ores and brown soolits[clarification needed] are deposited from the Sokolovsk, Sarbaiskoe, Kachary, Avatsk, and Lisavosk regions. The total weight of the magnetite and hematite ores from the region combined is 15.7 billion tons, of which 5.7 billion tons are easy to enrich and don't demand a lot of enrichment.[citation needed] The bowels are especially rich in iron ore, brown coal, asbestos, fire-resistant brick clay, flux, cement limestone, glass sand, building stones, among others. There are 19 locations in the region that deposit bauxite, 7 that deposit gold, and one for both silver and nickel.[citation needed]
The Arakaragai and Amankaragai regions are filled with chernozems and pine forests. In the Naurzikmkaragai region, chestnut grounds with pine forests are prominent. The southern part of the region is dominated by grasslands and shrublands.
Water
[edit]The region center, Kostanay, is supplied with water from Amangeldinsky water basins (underground volume 6.7 million cubic meters) and Kostanay deposit of underground waters (operational stocks - 33.5 million cube. m). The city of Lisakovsk gets water from the Verhnetobols water basins (underground volume totals 814 million cubic meters). Regional centers Sarykol, Karasu, and Uzunkol are supplied with water with Ishim water supply line and Sеrgeevsk water basin which is on the territory of the North-Kazakhstan region. 12 big water supply lines on the territory of Kostanay region give water to more than 220 settlements and 5 regional centers. Water delivery of other areas is carried out from local sources (deposits of underground waters). Karatomar water basins (underground volume 516 million cube. m) supply Rudni, Каchar region and Fedorovka.[6]
Archaeology
[edit]According to the Journal of Archaeological Science, in July 2020, scientists from South Ural State University studied two Late Bronze Age horses with the aid of radiocarbon dating from Kurgan 5 of the Novoilinovsky 2 cemetery in the Lisakovsk city. Researcher Igor Chechushkov, indicated that the Andronovites had an ability on horse riding several centuries earlier than many researchers had previously expected. Among the horses investigated, the stallion was nearly 20 years old and the mare was 18 years old. According to scientists, animals were buried with the person they accompanied throughout their lives, and they were used not only for food, but also for harnessing to vehicles and riding.[7]
"It is likely that militarized elite, whose power was based on the physical control of fellow tribesmen and neighbors with the help of riding and fighting skills, was buried in the Novoilinovsky-2 burial ground. The rider has a significant advantage over the infantryman. There may be another explanation: These elite fulfilled the function of mediating conflicts within the collective, and therefore had power and high social status. Metaphorically, this kind of elite can be called Sheriffs of the Bronze Age" said Igor Chechushkov.[8][9]
Climate
[edit]Kostanay Region's climate is continental, with strongly pronounced alternation of four seasons. Average temperatures: January: -18 to -19 °С, July: 19 to 22 °С. In the winter, the temperature can be as cold as -25 to -30 °C. In summer, the temperature can reach 30 °C. Annual amount of precipitation is 300–350 mm in the northern areas and 240 to 280 mm in the south. The growing season is about 150 to 175 days in the north and 180 days in the south.
Demographics
[edit]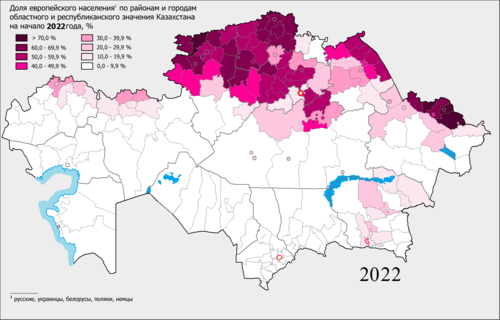
The share of the European population by districts and cities of regional and republican subordination Kazakhstan in 2022 > 70٪ 60.0 – 69.9 % 50.0 - 59.9 % 40.0 - 49.9 % 30.0 - 39.9 % 20.0 - 29.9 % 10.0 - 19.9 % 0.0 - 9.9 % |
As of 2020, the Kostanay Region has a population of 868,549.[10]
Ethnic groups (2020):[11]
Administrative divisions
[edit]The region is administratively divided into sixteen districts and the cities of Kostanay, Arkalyk, Lisakovsk, and Rudny.[12]
- Altynsarin District, with the administrative center in the selo of Obagan;
- Amangeldi District, the selo of Amangeldi;
- Auliekol District, the selo of Auliekol;
- Denisov District, the settlement of Denisovka;
- Fyodorov District, the selo of Fyodorovka;
- Kamysty District, the selo of Kamysty;
- Karabalyk District, the urban-type settlement of Karabalyk;
- Karasu District, the selo of Karasu;
- Kostanay District, the urban-type settlement of Zatobolsk;
- Mendykara District, the selo of Borovskoy;
- Nauyrzym District, the selo of Karamendy;
- Sarykol District, the urban-type settlement of Sarykol;
- Taran District, the selo of Taran;
- Uzunkol District, the selo of Uzunkol;
- Zhangeldi District, the selo of Torgay;
- Zhitikara District, the town of Zhitikara.
- The following five localities in Kostanay Region have town status:[12] Kostanay, Arkalyk, Lisakovsk, Rudny, and Zhetikara.
Public institutions
[edit]Kostanay Region function 8 higher educational institutions: 4 state and 4 not state, and also 6 branches of the Kazakhstan and Russian high schools. One of the basic - Kostanay State University (named after Akhmet Baytursinuli). The total number of students is made by 23,6 thousand person. Also functions 22 colleges in which it is trained over 12,2 thousand pupils.
In 2002-2003 educational year work 723 schools, with a contingent of pupils - 155,5 thousand person.
The state network of culture totals 380 libraries, 201 club establishments, 8 museums, 2 theatres: I. Omarov regional Kazakh drama theatre and regional Russian drama theatre. The regional showroom works.
There are sport objects: two palaces of sports, 26 stadiums, 10 sports complexes and 567 sports halls.
In April 2021, the Shanyrak National Arts Center opened in the town of Tobol in the Kostanay region. The center is home to folk art from regional amateur artists, film, and video. It is the first art center in the region. [13]
Communications
[edit]Kostanay Region has steady automobile outputs in all next regions and the regional centers. The Extent of general-purpose highways makes 9133 km, republican value - 1401 km and local - 7732 km. On territory of area pass from the north on the south and a southeast the main transit roads connecting the regional center with cities of Kazakhstan: Nur-Sultan, Almaty and adjoining areas; Urals: Chelyabinsk, Magnitogorsk, Troitsk, Ekaterinburg; Western Siberia: Kurgan, Tyumen.
Operation length of railways of general purpose, which are taking place on territory of the region, is equal to 1048 km. Function 53 stations conducting cargo and passenger transportations which cover all cities and 11 region.
In Kostanay Region are available three airports with a firm covering of runways: in cities of Kostanay and Arkalyk, settlement Torgai. Runways of the airport of Kostanay can accept types of planes: Tu-134, Tu-154, АН-22, Il-86 and the Boeing. From the international airport of Kostanay regular and charter flights in many cities of Kazakhstan, the CIS, Germany (Frankfurt on Main, Düsseldorf, Hamburg, Stuttgart), to Arab Emirates, Turkey and others are carried out. Here there are points of the boundary and customs control. Mineral oil in Kostanay Region is delivered from the Russian Federation and from oil refineries of Kazakhstan by railway.
The basic monopolist in sphere of telecommunications in Kostanay Region is the branch of "Kazaktelekom". The big development was received with a global network the Internet, cellular communication, an IP-telephony.
Health
[edit]In sanatorium Sosnoviy bor there are hydropathic establishments, which are located on medical sources and have interrepublican value. Treatment is carried out: a gastrointestinal tract, respiratory system, postoperative rehabilitation and a mud baths.
Notable people
[edit]- Kamshat Donenbaeva (1943–2017), 3-term delegate to the Supreme Soviet of the USSR[14]
See also
[edit]External links
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Кумар Аксакалов стал акимом Костанайской области". tengrinews.kz (in Russian). 2022-12-01.
- ^ Agency of statistics of the Republic of Kazakhstan: Численность населения Республики Казахстан по областям с начала 2013 года до 1 февраля 2013 года (russisch; Excel-Datei; 55 kB).
- ^ DOSM. "Department of Statistics Kazakhstan". stat.gov.kz. Archived from the original on 2 January 2024. Retrieved 2023-03-01.
- ^ "Sub-national HDI – Area Database – Global Data Lab". hdi.globaldatalab.org.
- ^ "Official site of Kostanay city". Archived from the original on 2011-07-21. Retrieved 2008-01-15.
- ^ http://www.kostanay.net/modules/about/article.php?storyid=2 Information about Kostanay
- ^ Chechushkov, Igor V.; Usmanova, Emma R.; Kosintsev, Pavel A. (2020-08-01). "Early evidence for horse utilization in the Eurasian steppes and the case of the Novoil'inovskiy 2 Cemetery in Kazakhstan". Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports. 32: 102420. Bibcode:2020JArSR..32j2420C. doi:10.1016/j.jasrep.2020.102420. ISSN 2352-409X. S2CID 225452095.
- ^ "The most ancient evidence of horsemanship in the bronze age". phys.org. Retrieved 2020-07-20.
- ^ "Russian Scientists Have Discovered the Most Ancient Evidence of Horsemanship in the Bronze Age - South Ural State University". www.susu.ru. Retrieved 2020-07-20.
- ^ "Численность населения Республики Казахстан по отдельным этносам на начало 2020 года". Stat.kz. Archived from the original on 2020-05-27. Retrieved 2020-08-03.
- ^ "Численность населения Республики Казахстан по отдельным этносам на начало 2020 года". Stat.kz. Archived from the original on 2020-05-27. Retrieved 2020-08-03.
- ^ a b "Region's districts". Kostanay Region's Akimat. Archived from the original on 2011-10-27. Retrieved 10 June 2012.
- ^ April 2021, Aizada Arystanbek in Culture on 18 (2021-04-18). "National Arts Center Opens in Kostanai Region". The Astana Times. Retrieved 2021-12-14.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "Скончалась Камшат Доненбаева" [Kamshat Donenbayeva dies]. Наша Газета. Kostanay, Kazakhstan. 10 November 2017. Archived from the original on 8 November 2018. Retrieved 8 November 2018.