Mainspring (firearms)

In firearms, the mainspring is a spring in the firing mechanism which stores the energy required to ignite the primer of the cartridge.[1] The mainspring may be called a striker spring[2] on striker-fired firearms, or hammer spring[3] on hammer-fired firearms. After the trigger mechanism has been released, the tensioned mainspring will drive the firing pin or hit the firing pin so that it is driven.
Mainsprings can come in many shapes, such as a cylindrical spring (Mosin-Nagant, TT-33, Colt M1911), plate spring (Nagant revolver model 1895, Makarov pistol) or spiral spring (Kalashnikov). On a number of automatic firearms, the recoil spring may also function as a mainspring (FN Browning M1900, Degtyaryov machine gun, and some submachine guns).
Mainsprings should not be confused with the type of firing pin spring which is utilised in some designs instead of free-floating firing pins to prevent slamfire.
-
Parts sketch of the firing mechanism on Russian infantry rifle model 1845. Number 8 shows the main spring.
-
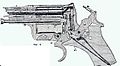
Nagant revolver with tensioned trigger. The mainspring (bottom right) consists of two leaf arms, and also acts as a trigger spring.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ "Mainspring". www.hallowellco.com. Retrieved 2022-07-18.
- ^ Association, National Rifle. "An Official Journal Of The NRA | Striker-Spring Fatigue: Is It a Problem?". An Official Journal Of The NRA. Retrieved 2022-07-18.
- ^ US 8132350, Alves, Joseph E., "Hammer spring assembly for a firearm", published 2012-03-13
- Andrzej Ciepliński, Ryszard Woźniak: Encyklopedia współczesnej broni palnej (od połowy XIX wieku). Warszawa: Wydawnictwo WiS, 1994, s. 212. ISBN 83-86028-01-7.
- Боевая пружина// Военная энциклопедия: (в 18 т.) / под ред. В. Ф. Новицкого (и др.). – СПб.; (М.): Тип. т-ва И. В. Сытина, 1911 – 1915.
- Жук А. Б. Энциклопедия стрелкового оружия. – М.: Воениздат, 1998.
- Материальная часть стрелкового оружия / Под ред. А. А. Благонравова. — М.: Оборонгиз НКАП, 1945.