Portal:North America
The North America Portal
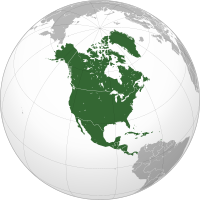
North America is a continent in the Northern and Western Hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Caribbean Sea, and to the west and south by the Pacific Ocean. The region includes the Bahamas, Bermuda, Canada, the Caribbean, Central America, Clipperton Island, Greenland, Mexico, Saint Pierre and Miquelon, Turks and Caicos Islands, and the United States.
North America covers an area of about 24,709,000 square kilometers (9,540,000 square miles), representing approximately 16.5% of the Earth's land area and 4.8% of its total surface area. It is the third-largest continent by size after Asia and Africa, and the fourth-largest continent by population after Asia, Africa, and Europe. As of 2021[update], North America's population was estimated as over 592 million people in 23 independent states, or about 7.5% of the world's population. In human geography, the terms "North America" and "North American" can refer to Canada, the United States, Mexico, and Greenland or, alternatively, Canada, Greenland and the US (Mexico being classified as part of Latin America) or simply Canada and the US (Greenland being classified as either Arctic or European (due to its political status as a part of Denmark) and Mexico classified as Latin American).
It is unknown with certainty how and when first human populations first reached North America. People were known to live in the Americas at least 20,000 years ago, but various evidence points to possibly earlier dates. The Paleo-Indian period in North America followed the Last Glacial Period, and lasted until about 10,000 years ago when the Archaic period began. The classic stage followed the Archaic period, and lasted from approximately the 6th to 13th centuries. Beginning in 1000 AD, the Norse were the first Europeans to begin exploring and ultimately colonizing areas of North America.
In 1492, the exploratory voyages of Christopher Columbus led to a transatlantic exchange, including migrations of European settlers during the Age of Discovery and the early modern period. Present-day cultural and ethnic patterns reflect interactions between European colonists, indigenous peoples, enslaved Africans, immigrants from Europe, Asia, and descendants of these respective groups. (Full article...)
The Texas Revolution (October 2, 1835 – April 21, 1836) was a rebellion of colonists from the United States and Tejanos (Hispanic Texans) against the centralist government of Mexico in the Mexican state of Coahuila y Tejas. Although the uprising was part of a larger one, the Mexican Federalist War, that included other provinces opposed to the regime of President Antonio López de Santa Anna, the Mexican government believed the United States had instigated the Texas insurrection with the goal of annexation. The Mexican Congress passed the Tornel Decree, declaring that any foreigners fighting against Mexican troops "will be deemed pirates and dealt with as such, being citizens of no nation presently at war with the Republic and fighting under no recognized flag". Only the province of Texas succeeded in breaking with Mexico, establishing the Republic of Texas. It was eventually annexed by the United States.
The revolution began in October 1835, after a decade of political and cultural clashes between the Mexican government and the increasingly large population of Anglo-American settlers in Texas. The Mexican government had become increasingly centralized and the rights of its citizens had become increasingly curtailed, particularly regarding immigration from the United States. Mexico had officially abolished slavery in Texas in 1829, and the desire of Anglo Texans to maintain the institution of chattel slavery in Texas was also a major cause of secession. Colonists and Tejanos disagreed on whether the ultimate goal was independence or a return to the Mexican Constitution of 1824. While delegates at the Consultation (provisional government) debated the war's motives, Texians and a flood of volunteers from the United States defeated the small garrisons of Mexican soldiers by mid-December 1835. The Consultation declined to declare independence and installed an interim government, whose infighting led to political paralysis and a dearth of effective governance in Texas. An ill-conceived proposal to invade Matamoros siphoned much-needed volunteers and provisions from the fledgling Texian Army. In March 1836, a second political convention declared independence and appointed leadership for the new Republic of Texas. (Full article...)
Angus Lewis Macdonald PC QC (August 10, 1890 – April 13, 1954), popularly known as 'Angus L.', was a Canadian lawyer, law professor and politician from Nova Scotia. He served as the Liberal premier of Nova Scotia from 1933 to 1940, when he became the federal minister of defence for naval services. He oversaw the creation of an effective Canadian navy and Allied convoy service during World War II. After the war, he returned to Nova Scotia to become premier again. In the election of 1945, his Liberals returned to power while their main rivals, the Conservatives, failed to win a single seat. The Liberal rallying cry, "All's Well With Angus L.," was so effective that the Conservatives despaired of ever beating Macdonald. He died in office in 1954.
Macdonald's more than 15 years as premier brought fundamental changes. Under his leadership, the Nova Scotia government spent more than $100 million paving roads, building bridges, extending electrical transmission lines and improving public education. Macdonald dealt with the mass unemployment of the Great Depression by putting the jobless to work on highway projects. He felt direct government relief payments would weaken moral character, undermine self-respect and discourage personal initiative. However, he also faced the reality that the financially strapped Nova Scotia government could not afford to participate fully in federal relief programs that required matching contributions from the provinces. (Full article...)
The Spanish conquest of Honduras was a 16th-century conflict during the Spanish colonization of the Americas in which the territory that now comprises the Republic of Honduras, one of the seven states of Central America, was incorporated into the Spanish Empire. In 1502, the territory was claimed for the king of Spain by Christopher Columbus on his fourth and final trip to the New World. The territory that now comprises Honduras was inhabited by a mix of indigenous peoples straddling a transitional cultural zone between Mesoamerica to the northwest, and the Intermediate Area to the southeast. Indigenous groups included Maya, Lenca, Pech, Miskitu, Mayangna (Sumu), Jicaque, Pipil and Chorotega. Two indigenous leaders are particularly notable for their resistance against the Spanish; the Maya leader Sicumba, and the Lenca ruler referred to as Lempira (a title meaning "Lord of the Mountain").
In March 1524, Gil González Dávila became the first Spaniard to arrive in what is now Honduras with the intention of conquest. He founded the first Spanish port upon the Caribbean coast, Puerto de Caballos, which became an important staging post for later expeditions. The early decades of the Spanish conquest of Honduras were beset by jurisdictional disputes between different Spanish colonies attempting to invade the territory, which resulted in conflict between rival expeditions launched from Mexico, Hispaniola, and Panama. The Spanish territory was reorganised as Higueras in the west, and Honduras in the east. As the Spanish became established throughout Central America, the colony of Honduras-Higueras became involved in territorial disputes with neighbouring colonies in Nicaragua, Guatemala and El Salvador. (Full article...)Did you know...
- ... that the Ulster cherry is named after Ulster County, New York, a region where sweet cherries are produced commercially?
- ... that Vermont coppers (pictured) were the currency used in Vermont before it became a U.S. state in 1791?
- ...that the Soufrière Hills volcano is an active complex stratovolcano with many lava domes forming its summit on the Caribbean island of Montserrat?
- ... that Raul Macias, a Cuban-Mexican boxer parlayed his popularity into a successful career in telenovelas?
- ...that Lucy Hobbs Taylor was the first female dentist in the United States?
Selected panorama

Topics
Categories
List articles
Related portals
Northern America
Central America
Caribbean
WikiProjects
 North America
North America-
 Canada
Canada -
 Greenland
Greenland -
 Mexico
Mexico -
 Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Pierre and Miquelon -
 United States
United States  Central America
Central America-
 Belize
Belize -
 Costa Rica
Costa Rica -
 El Salvador
El Salvador -
 Guatemala
Guatemala -
 Honduras
Honduras -
 Nicaragua
Nicaragua -
 Panama
Panama  Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica Caribbean
Caribbean-
 Antigua and Barbuda
Antigua and Barbuda -
 Bahamas
Bahamas -
 Barbados
Barbados -
 Bermuda
Bermuda -
 Cuba
Cuba -
 Dominica
Dominica -
 Dominican Republic
Dominican Republic -
 Grenada
Grenada -
 Haiti
Haiti -
 Jamaica
Jamaica -
 Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico -
 Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Kitts and Nevis -
 Saint Lucia
Saint Lucia -
 Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines -
 Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus



























