Radial head fracture
| Radial head fracture | |
|---|---|
 | |
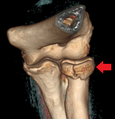
| Radial head fracture (red arrow) with posterior and anterior sail sign (blue arrows) | |
| Specialty | Orthopedic |
| Symptoms | Pain or tenderness over the radial head; bruising; swelling; limited range of motion. |
| Causes | Fall on an outstretched arm |
| Diagnostic method | Based on of clinical symptoms and medical imaging |
| Treatment | Varies according to severity of injury but may include: immobilization followed by range of motion exercises; joint aspiration with mobilization; surgical correction |
Radial head fractures are a common type of elbow fracture that typically occurs after a fall on an outstretched arm.[1] They account for approximately one third of all elbow fractures and are frequently associated with other injuries of the elbow.[2][3] Radial head fractures are diagnosed by a clinical assessment and medical imaging.[2][4] A radial head fracture is treated according to the severity of the injury and its Mason-Johnston classification. Treatment may be surgical or nonsurgical. Stable isolated fractures typically have excellent outcomes.[5] Unstable fractures with other associated injuries have varying outcomes. Common adverse outcomes include stiffness, pain, poor bone healing, and hardware complications.[6]
Diagnosis and classification[edit]
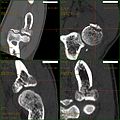
Radial head fractures are diagnosed from a clinical assessment and diagnostic imaging. Clinical assessment may include pain or tenderness at the radial head, bruising, swelling, and a limited range of motion of the injured elbow.[2] Diagnostic imaging may include ultrasound, plain radiography (x-ray imaging), Computed tomography scan (CT), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).[2][4] A fat pad sign may be present on diagnostic imaging and may indicate a radial head fracture.[5]
A diagnosed radial head fracture can be classified according to the Mason-Johnston system.[3]
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Non-displaced fracture |
| 2 | Minimal displacement with angulation or impression (>2mm) |
| 3 | Comminuted fracture with dislocation |
| 4 | Radial head fracture with dislocation of the elbow |
-
CT scan showing a radial head fracture
-
Radial head fracture seen on 3D CT reconstruction
Treatment[edit]
Radial head fracture treatment is informed by the Mason-Johnston classification, patient symptoms, and fracture stability. An unstable fracture will involve fracture displacement, fractures to adjacent structures and injury to other associated soft tissues. A stable type 1 radial head fracture is typically managed with conservative measures including joint aspiration, immobilization in a sling for a few days and followed by early range of motion exercises.[2][6] If range of motion is still limited after joint aspiration it may indicate a mechanical block which is treated surgically.[5] Stable type 2 radial head fractures may be treated as a type 1 if the displacement is minimal. Unstable type 2 - 4 fractures generally warrant surgery. Surgical correction can include fracture fragment excision, radial head reconstruction, open reduction and internal fixation, and radial head excision with artificial replacement.[6] Associated structures that were damaged during the injury may also need to be repaired.
Rehabilitation exercises are recommended and tailored to fracture and treatment type. It is recommended to wait 6 weeks before resuming load bearing with a stable type 1 fracture and 10-12 weeks following surgery for unstable type 2-4 fractures.[7]
Prognosis and Complications[edit]
Stable type 1 and 2 radial head fractures often have good outcomes with most cases regaining complete range of motion and having minimal residual stiffness or pain.[5] Outcomes for unstable type 2-4 radial head fractures vary greatly depending on the severity of the injury and the surgical intervention.[5][6] Some of the more common complications of unstable radial head fractures includes stiffness, poor bone healing, nerve damage, and pain/prominent hardware.[6]
References[edit]
- ^ Daniel K Nishijima. "Elbow Fracture". Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ^ a b c d e Bennett, James B. (September 1993). "Radial head fractures: Diagnosis and management". Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery. 2 (5): 264–273. doi:10.1016/S1058-2746(09)80088-8. PMID 22959508.
- ^ a b Kaas, Laurens; van Riet, Roger P.; Vroemen, Jos P.A.M.; Eygendaal, Denise (June 2010). "The epidemiology of radial head fractures". Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery. 19 (4): 520–523. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2009.10.015. PMID 20149972.
- ^ a b Pavić, Roman; Margetić, Petra; Hnatešen, Dijana (November 2015). "Diagnosis of occult radial head and neck fracture in adults". Injury. 46: S119–S124. doi:10.1016/j.injury.2015.10.050. PMID 26584731.
- ^ a b c d e Duckworth, A. D.; McQueen, M. M.; Ring, D. (February 2013). "Fractures of the radial head". The Bone & Joint Journal. 95-B (2): 151–159. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.95B2.29877. ISSN 2049-4394. PMID 23365021.
- ^ a b c d e Rosenblatt, Yishai; Athwal, George S.; Faber, Kenneth J. (April 2008). "Current Recommendations for the Treatment of Radial Head Fractures". Orthopedic Clinics of North America. 39 (2): 173–185. doi:10.1016/j.ocl.2007.12.008. PMID 18374808.
- ^ Hackl, Michael; Leschinger, Tim; Uschok, Stephan; Müller, Lars Peter; Wegmann, Kilian (December 2017). "Rehabilitation of elbow fractures and dislocations". Obere Extremität. 12 (4): 201–207. doi:10.1007/s11678-017-0425-1. ISSN 1862-6599. S2CID 79629978.