Shaigiya tribe
| Shaigiya الشايقية | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Ethnicity | Sudanese Arabs |
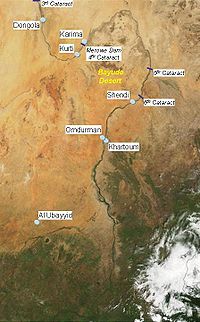
| Location |
|
| Population | 845,000[1] |
| Demonym(s) | Shaiqi or Shaigi |
| Language | Sudanese Arabic |
| Religion | Sunni Islam |
The Shaigiya, Shaiqiya, Shawayga or Shaykia (Arabic: الشايقيّة) are an Arabized Nubian[2][3][4][5][6] tribe. They are part of the Sudanese Arabs and are also one of the three prominent Sudanese Arabs tribes in North Sudan, along with the Ja'alin and Danagla. The tribe inhabits the region of Dar al-Shayqiya, which stretches along the banks of the Nile River from Korti to the end of 4th Nile cataract and includes their tribal capital of Merowe Sheriq and parts of the Bayuda desert.
Although speaking Sudanese Arabic today it was reported by various 19th-century sources that the Shaiqiya were bilingual in Arabic and Dongolawi, a Nubian language.[7] Some modern authors proposed that the Shaiqiya spoke Nobiin rather than Dongolawi.[8][9][10]
In the 20th century, Shaiqi tribe are among those along the Nile, who have been affected by the Merowe Dam.[11]
Origin and lineage
[edit]Despite claims to Abbasid descent, the Shaigiya have been classified as Arabised Nubians.[12] They claim descent from a Hejazi Arab named Shaig, a descendant of Abbas (an uncle of the Islamic prophet Muhammad) who came from the Arabian Peninsula in the 7th century following the Arab conquest of Egypt.[13] Allegedly, he and his family settled in Sudan and intermixed with the local Nubians, creating this tribe. However, historically it seems the tribe has originated in 15th century as a hybrid of various tribes settled in the area.[14] According to Nicholls, at the start of the 20th century, the tribe nobles denied to have Arab origins and said that they were indigenous to Sudan and that they have always inhabited the same territory as today.[15]
Although speaking Sudanese Arabic today, the Shaigiya have formerly spoken a Nubian language as late as the 19th century.[16] Several travellers noted that they were bilingual in Arabic and Dongolawi, the language of the Danagla further downstream. Some modern authors believe that the Shaiqiya spoke Nobiin rather than Dongolawi.[7] The historian Jay Spaulding analyzed several Arabic Shaiqi documents from the mid-19th century and found a widespread use of objective suffix particles which, he believes, had their root in Nobiin. He concludes that the pre-Arabic language of the Shaiqiya, which he calls Old Shaiqi, was closely related to Nobiin if not identical.[17] The archaeologist Ali Osman, too, claimed that the Nubian words that survive in the Shaiqi dialect are of Nobiin origin.[18] Arabization was rapidly advancing in 19th-century Sudan due to the perceived superiority of Arabic to Nubian and other African languages.[19] Among the Shaiqiya, Nubian reportedly survived until the turn of the 20th century.[20] As late as 1918 it was reported that Nubian (Dongolawi) was still spoken as far upstream as Karima near Jebel Barkal.[21]
History
[edit]
During the medieval period Dar Shaiqiya was part of the heartland of the Christian Nubian kingdom of Makuria.[22] The Shaigiya are first mentioned in 1529,[23] when an Italian visitor to Upper Egypt remarked that pyramids could be found in the country of the "Xiogeia".[24] They were subjects of the Funj Sultanate,[23] which extended as far north as Dongola.[24] From the sixteenth century until colonization, the Shaigiya had many prominent Islamic schools which attracted students from all over Sudan.[25] Around 1690 the tribe broke loose from the Kingdom of Funj, defeating the Abdelab governor, and were the only independent tribe in the region. The first account of the Shaigiya tribesmen was given by the Scottish traveller James Bruce in his book Travels to Discover the Source of the Nile (1790) who noticed the tribe migrated from more southern regions to its present homeland around 1772.

Still the best early description came from an adventurer and historian John Lewis Burckhardt, who, mesmerized by the Shaigiya, spent some time with the tribe. His accounts of the events were published at 1819 in the "Travels in Nubia". The predatory character of the tribe speaks of change from Bruce's time, "My guide, in constant dread of the Shaiqiya would not allow me to light a fire although the nights were getting very cold".[26] Evidently, the tribe was ruled by two Macs (the title given by the kings of Funj to tribal chiefs), Mac Jaweesh and Mac Zubeir. Military training of the Shaiqiya youth was brutal, and at very early age they were capable of launching spears from a horseback by astonishing precision. Their unexplainable intolerance of other tribes led to raids against their neighbours and beyond. They attacked villages and caravans as far as Wadi Halfa in the north, and Shendi in the south forcing some families of the neighbouring tribes to emigrate westwards (Danagla). Constantly attacking the town of Shendi and killing some of local Mac Nimr's uncles forced the Ja'Alin to seek help from the king of Funj, who at his political decline was too weakened and unable to help. Burckhardt who spent time in Merowe around 1807 gives us more description of the tribe
"Shaiqiya are continually at war. They all fight on horseback, in coats of mail. Fire-arms are not common amongst them, their only weapons being lance, target and sabre. They are all mounted on Dongola Stallions and are famous for their horsemanship. Their youth conduct raids sometimes as far as Darfur. The Shaiqiya are perfectly independent people, and possess great wealth in corn and cattle. They are renowned for their hospitality; and the person of their guest, or companion is sacred. If the traveller possesses a friend among them and has been plundered on the road, his property will be recovered, even if it has been taken by the King. Many of them can write and read. Their learned men are held in great respect by them; they have schools, wherein all the sciences are taught, which form the course of the Mohammedan study, Mathematics and Astronomy excepted. Such of the Shaiqiya as are soldiers, indulge in frequent use of wine and spirits made of dates."
— W.Burckhardt, Travels in Nubia (published in 1819)
They were challenged around 1811 at Dongola by the Mamelukes, but continued to dominate a considerable part of Nubia.[27] Roused by Mihera Bint Abboud, they resisted the Turkish/Egyptian invasion in 1820, at the battle of Korti after refusing to submit and were defeated due to the use of fire-arms and cannons and retreated southwards. Mac Jaweesh along the majority of his men sought asylum in Shendi in hope to persuade the Ja'Ali chief Mac Nimr to join forces against the much stronger enemy. Mac Nimr declined the offer and the Shaiqiya were handed over to the Turks, who promised to pardon the Shaiqiya warriors and return their land if they accepted the service in Turkish ranks. After the deal was struck Shaiqiya were used during the suppression of the Ja'Alin revolt (1822) and demonstrated astonishing brutality. For their services they obtained lands of the Ja'Alin between Shendi and Khartoum (15°37′59″N 32°31′59″E / 15.633°N 32.533°E).[27]

In the Mahdist War of 1884/85, General Gordon's first fight was to rescue a few Shaiqiya, still serving with the invader and besieged in a fort at Al Halfaya,[27] just north of Khartoum. The fortress at Al-Ubayyid in 1883, was held by Major Ahmed Hussein Pasha (Suarab Section) and despite Hicks Pasha's attempt to relieve him, the fortress fell to the Mahdi. (Major Hussein escaped to Egypt in 1891 and came back during the reconquest in 1898. His family still resides in Omdurman, Khartoum North and Hajar al Asal.) His grandchildren went as far as Germany and America, where they go by the name of Hussein.
In April 1884, Saleh Bey (Saleh Wad el Mek), head of the tribe, and 1,400 men surrendered to the Mahdi's forces. Numbers of Shaigiya continued in the service of General Gordon, and this led to the proscription of the tribe by the Mahdi. When Khartoum fell, Saleh's sons were sought out and executed by the Dervishes.[27]
On the reconquest of the Sudan by the Anglo-Egyptian army (1896/98), it was found that the Shaigiya were reduced to a few hundred families.[27] After this, the tribe thrived. They figured prominently in the Egyptian Army and later the Sudan Defence Force. General Ibrahim Abboud, decorated with the MBE for his valour at Keren in 1941, was a Shaiqi from the Onia section and later President of the Sudan in 1964.
Culture
[edit]
They are known for their bravery, generosity, and enlightenment. "They are the one to hunt the Lion."[citation needed] Freedom-loving and hospitable, they had schools in which all Muslim science was taught, and were rich in corn and cattle. Their fighting men, mounted on horses of the famous Dongola breed, were feared throughout the eastern Sudan. Their chiefs wore coats of mail and carried shields of hippopotamus or crocodile skin. Their arms were lance, sword or javelin.[27] The Shaigiya are divided into twelve sections or sub tribes, each descended from one of the twelve sons of the founder, Shaig. Many jokes involve a Shaigi quarrelling with a Ja'li. Many times the Shaigi is the sharp, and Ja'li is the stubborn.
They have adopted the tribal marking custom of cutting three horizontal lines on the cheeks of their children. This was done with a heated knife, but is now a dying custom.
Communication
[edit]Members of the Shaigiya tribe speak and write in Arabic. Some sections living towards the Red Sea area have a language that is akin to what the Hadendoa speak. They are reported to have a pronunciation which deletes the last letter of some words. A common name for a male is Al-Sir, which is from the Turkish language and means leader. A common name for a female that hardly anyone uses outside of the tribe is "Had-Alraid", which means the most love you can give to someone or something.[citation needed]
Art forms
[edit]
There is a special instrument that can be heard in Shaigi tribal music: the tambour, or tanbūra, a kind of lyre. The Shaigiya used to make their homes from bricks made of mud and cow dung, as other North African and Arab ethnic groups had done. The roofs were made of straw to keep the houses cool. The most common form for men to put art on their bodies is the wearing of henna on their hands for a wedding. Women put henna on for their own marriage only.
Institutions
[edit]Family
[edit]In the rural areas of the various sub-tribes (or Dars), extended family life features strongly. It is quite common that multiple generations will stay in one house (mother, father, grandfather, grandmother, children, aunts, uncles, cousins). Most households in the Shaigiya tribe consist of extended families. Some men have more than one wife. The head of the house is the father. If the father is not in the home then the mother is the head. If the mother is incapable, then the uncle takes over. The uncle is usually the father’s brother and must act as the father. If the uncle cannot fulfil the role, then the grandfather will take over.
Religion
[edit]The main religion of the Shaigiya tribe is Sunni Islam.
Schooling
[edit]Most children attend government school. Women are usually the teachers, while the men are farming and planting. All lessons are important, but most emphasized are religion, languages, and mathematics. Religion is considered important, and for this, many children attend traditional religious schools, called khalwa in Sudan. This is a place, where kids go to before they enter a public school to learn classical Arabic and memorize the Quran.
Social behavior
[edit]Children in the Shaigiya tribe like to play a kind of game called Seega, which is similar to tic-tac-toe. First they draw a big square with 9 small squares inside on the sand, two children play, each has five stones, each stone of a different color. Each tries to align their own stones in a line of 3, while the other blocks and tries to prevent his/her adversary from making a straight line.
The Shaygiya greeting is similar to most other tribal Sudanese greetings or Muslim greetings. When the Shaigiya people meet someone who is older, they say, “As-salamu alaykum ya haj” or “Marhaban ya haj”, pat their hands on the left shoulder and then shake hands. If they meet their friend, they would say “Marhaban" or “Ezayakum”. Ladies hug each other and shake hands.
When there is a wedding, the groom applies henna, a kind of black decoration that people usually put on their hands and feet. Henna is applied as a paste made of dried and powdered Lawsonia leaves, with added oil and water. Brides use it in a decorative manner, usually with floral decorations. If applied once, it takes on a reddish hue, twice will turn it black.
Eating habits are typical almost throughout Sudan: breakfast is around 10am, lunch is at 3pm and dinner at 7pm. The main course will always be a kind of bread called gurrasa, which is made of flour. It is usually dipped into meat curries. They have black tea with sugar after every meal.
When someone dies, funeral rites for the dead are carried out immediately. The families of the dead wear black or white, and the men take the corpse, wash it and cover it with large white sheet and bury it. Widows usually mourn for a stipulated four-month and ten day period.
When a baby is born, the baby’s mother and the town's women ululate (zaghareed) to announce the baby's arrival, and after 7 days, the family hosts a party to give the newborn baby a name.
Social structure
[edit]Most mornings, men work in the fields tending their crops. Hunting is also popular. Wives take care of children and give food to their husbands when they are working in the field. Boys in the Shaigiya tribe help in the field after school. Girls stay at home to help their mothers and make themselves more beautiful (decorate themselves with fancy clothes and other decorations). They are not allowed to go out very much until they are 15 years old. The leader of a family always is the father, but when troubles come to the leader, the mother or the uncle of this family will lead instead.
Notes
[edit]- ^ "Sudan". Retrieved September 18, 2024.
- ^ O'Fahey 1996, p. 406: "Despite claims to Abbasid descent, the Shaykiyya are undoubtedly Arabised and Islamised Nubians".
- ^ Thelwall 1982, p. 50.
- ^ Kramer, Lobban & Fluehr-Lobban 2013, p. 382.
- ^ Adams 1977, pp. 557–558, 562.
- ^ Werner 2013, p. 29.
- ^ a b Gerhards 2023, pp. 139–140.
- ^ Spaulding 1990, p. 288.
- ^ Bechhaus-Gerst 1996, pp. 25–26.
- ^ Gerhards 2023, p. 140.
- ^ "Tide of censure for African dams". Retrieved May 14, 2021.
- ^ O'Fahey, R. S. (2012-04-24), "S̲h̲āyḳiyya", Encyclopaedia of Islam, Second Edition, Brill, retrieved 2023-07-12
- ^ Nicholls, W. (May 14, 1913). The Shaikiya. An account of the Shaikiya tribes and of the history of Dongola Province from the XIVth to the XIXth century. Dublin : Hodges. Retrieved May 14, 2021 – via Internet Archive.
- ^ MacMichael, H. A. (March 17, 2011). A History of the Arabs in the Sudan: And Some Account of the People who Preceded them and of the Tribes Inhabiting Dárfūr (Reissue ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge Library Collection - African Studies. ISBN 978-1108010252.
- ^ Nicholls, W. (2 July 2012). The Shaikiya: An Account of the Shaikiya Tribes and of the History of Dongola Province from the Xivth to the Xixth Century (Classic Reprint ed.). Forgotten Books. ISBN 978-0267726547. Retrieved 21 January 2023.
- ^ O'Fahey & Spaulding 1974, pp. 28–29.
- ^ Spaulding 1990, pp. 287–288.
- ^ Shinnie 1984, p. 176.
- ^ Gerhards 2023, pp. 144–145.
- ^ Gerhards 2023, p. 139.
- ^ West 1918, p. 28.
- ^ Gerhards 2023, p. 147.
- ^ a b O'Fahey 1996, p. 406.
- ^ a b O'Fahey & Spaulding 1974, p. 28.
- ^ Karrar 1992, pp. 16–19.
- ^ W. Burckhardt, Travels in Nubia, 1819
- ^ a b c d e f One or more of the preceding sentences incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Shagīa". Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 24 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 769.
References
[edit]- The discovery of the source of Nile, J. Bruce 1790
- Travels in Nubia, 1819 W. Burckhardt
- Adams, William Y. (1977). Nubia. Corridor to Africa. Princeton University. ISBN 0691093709.
- Bechhaus-Gerst, Marianne (1996). Sprachwandel durch Sprachkontakt am Beispiel des Nubischen im Niltal (in German). Köppe. ISBN 3-927620-26-2.
- Gerhards, Gabriel (2023). "Präarabische Sprachen der Ja'aliyin und Ababde in der europäischen Literatur des 19. Jahrhunderts". Der Antike Sudan (in German). 34. Sudanarchäologische Gesellschaft zu Berlin e.V: 135–152.
- Karrar, Ali Sahih (1992). The Sufi Brotherhoods in the Sudan. C. Hurst & Company. ISBN 1-85065-111-6.
- Kramer, Robert S.; Lobban, Richard A. Jr.; Fluehr-Lobban, Carolyn (2013). Historical Dictionary of the Sudan. The Scarecrow. ISBN 978-0810861800.
- O'Fahey, R.S.; Spaulding, Jay L. (1974). Kingdoms of the Sudan. Methuen Young Books. ISBN 0416774504.
- O'Fahey, R.S. (1996). "Shaykiyya". The Encyclopedia of Islam. Vol. IX. Brill. p. 406. ISBN 978-90-04-10422-8.
- Shinnie, P.L. (1984). "Life and Language in Mahas today". Rivista degli studi orientali. 58, 1/4: 173–178.
- Spaulding, Jay (1990). "The Old Shaiqi Language in Historical Perspective". History in Africa. 17. Cambridge University: 283–292. doi:10.2307/3171817. JSTOR 3171817. S2CID 153767706.
- Thelwall, Robin (1982). "Linguistic Aspects of Greater Nubian History". In Christopher Ehret; Merrick Posnansky (eds.). The Archaeological and Linguistic Reconstruction of African History. University of California. pp. 39–52. ISBN 0520045939.
- Werner, Roland (2013). Das Christentum in Nubien. Geschichte und Gestalt einer afrikanischen Kirche (in German). Lit.
- West, Louis C. (1918). "Dongola Province of the Anglo-Egyptian Sudan". Sudan Notes and Records. 5, 1: 22–37.
Further reading
[edit]- Ibrahim, Hayder (1979). The Shaiqiya: The cultural and social change of a Northern Sudanese riverain people. Steiner. ISBN 3515029079.
- The Shaikiya. An account of the Shaikiya tribes and of the history of Dongola Province from the XIVth to the XIXth century (1913)
- The Making of the Modern Sudan, KDD Henderson 1953, Faber and Faber
- History of Sudan, P.M. Holt and M.W. Daly 1981
- Anglo-Egyptian Sudan, edited by Count Gleichen (London, 1905)
- Ethnology of the Egyptian Sudan, A. H. Keane, (London, 1884)
- The Shaikiya of the Northern Sudan, Nicholls, 1903, Dublin
