Sultanate of Banjar
This article needs additional citations for verification. (April 2022) |
Sultanate of Banjar كسلطانن بنجر Kesultanan Banjar | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1526–1860 (restored in 2010–Now without a political power)[1][2] | |||||||||
|
Flag | |||||||||
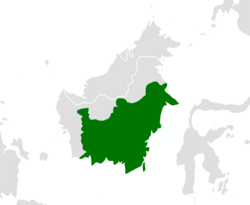 Banjar Sultanate under the reign of Sulaiman of Banjar, c. 1809. | |||||||||
| Status | Sultanate | ||||||||
| Capital | Banjarmasin, Karang Intan, Martapura, Kayu Tangi | ||||||||
| Common languages | Banjar[3] | ||||||||
| Religion | Sunni Islam | ||||||||
| Sultan | |||||||||
• 1526–1550 | Sultan Suriansyah | ||||||||
• 1862–1905 | Sultan Muhammad Seman | ||||||||
• 24 June 2010–Now | Khairul Saleh[1][2] | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
• Established | 1526 | ||||||||
• Disestablished | 1860 (restored in 2010–Now without a political power)[1][2] | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Today part of | Indonesia | ||||||||
| History of Indonesia |
|---|
 |
| Timeline |
|
|
Sultanate of Banjar (Banjar: كسلطانن بنجر, Kasultanan Banjar) was a sultanate located in what is today the South Kalimantan province of Indonesia. For most of its history, its capital was at Banjarmasin.
History
[edit]This section needs additional citations for verification. (April 2022) |
The second king of Negara Daha, Maharaja Sukarama, had four commoner wives, and four sons and one daughter. As Maharaja Sukarama followed the traditional belief of Negara Dipa requiring the king to be of royal blood, he arranged the marriage of his sole daughter, Putri Galuh Baranakan, and the son of his brother, Raden Bagawan, with the name Raden Mantri. The goal of this union (of Mantri and Galuh) was to produce the ideal heir to rule Daha as they would have patrilineal and matrilineal royal blood. The union resulted in Raden Samudra, who was prepared by Sukarama to rule.[4]
However, after Sukarama's death, this succession was challenged by his sons, Pangeran Mangkubumi and Pangeran Tumanggung, who usurped the throne. Raden Samudra escaped from the Kingdom of Daha to the Barito River area, because his safety was in danger, and established a new kingdom at Banjarmasin.[4] With help from Mangkubumi Aria Taranggana, Raden Samudra converted to Islam on 24 September 1526, changing his name to Sultan Suriansyah. Banjar at first paid tribute to the Sultanate of Demak. That state met its demise in the mid-16th century, however, and Banjar was not required to send tribute to the new power in Java, the Sultanate of Pajang.[citation needed]
Banjar rose in the first decades of the 17th century as a producer and trader of pepper. Soon, virtually all of the southwest, southeast, and eastern areas of Kalimantan island were paying tribute to the sultanate. Sultan Agung of Mataram (1613–1646), who ruled north Java coastal ports such as Jepara, Gresik, Tuban, Madura and Surabaya, planned to colonise the Banjar-dominated areas of Kalimantan in 1622, but the plan was cancelled because of inadequate resources.[citation needed]
In the 18th century, Prince Tamjidullah I successfully transferred power to his dynasty and set Prince Nata Dilaga as its first sultan with Panembahan Kaharudin Khalilullah. Nata Dilaga became the first king of the dynasty as Tamjidullah I in 1772, on the day of his accession calling himself Susuhunan Nata Alam.[citation needed]
The son of Sultan Muhammad Aliuddin Aminullah named Prince Amir, a grandson of Sultan Hamidullah, fled to the Pasir, and requested the help of his uncle Arung Tarawe (and Ratu Dewi). Amir then returned and attacked the Sultanate of Banjar with a large force of Bugis people in 1757, and tried to retake the throne of Susuhunan Nata Alam. Fearing the loss of his throne and the fall of the kingdom to the Bugis, Susuhunan Nata Alam requested the assistance of the Dutch East India Company (VOC), who dispatched a force under Captain Hoffman. The combined force defeated the Bugis, sending Amir to flee back to Pasir. After a long time, he tried to meet with Barito Banjar nobles, who disliked the VOC. Following this, Amir was arrested and exiled to Sri Lanka in 1787, and Banjar became a Dutch protectorate.[citation needed]

The Dutch increased their presence in the 19th century, taking territory from the sultanate and interfering in the appointment of its rulers. Resistance led to the Banjarmasin War (1859–1863) and the abolition of the sultanate in 1860. Afterwards, the area was governed by regents in Martapura (Pangeran Jaya Pemenang) and in Amuntai (Raden Adipati Danu Raja). The regency was finally abolished in 1884. The last claimant to the throne died in 1905.[citation needed]
List of sultans of Banjar
[edit]Revival
[edit]As of 2010, the sultanate was revived for cultural purposes in Martapura by Ir. Haji Gusti Khairul Saleh, an Indonesian politician and regent of Banjar Regency who claimed to be a descendant of the royal family.[5] He also planned to rebuild the Banjar royal palace using his own private fund.[6][7][8][9]
Family tree
[edit]| Family Tree of Banjar Monarchs | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b "Salinan arsip". Archived from the original on 27 December 2013. Retrieved 27 December 2013.
- ^ a b "Salinan arsip". Archived from the original on 6 September 2014. Retrieved 27 May 2015.
- ^ Sosial Budaya Provinsi Kalimantan Selatan – indonesia.go.id
- ^ a b Pikriadi, Nor (10 October 2014). "Perjalanan Kesultanan Banjar dari Legitimasi Politik hingga Indentitas Kultural". Naditira Widya. 8 (2). Archived from the original on 29 April 2019. Retrieved 28 October 2022.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ Media, Kompas Cyber (7 December 2011). "Kesultanan Banjar Kembali Dibangkitkan". KOMPAS.com (in Indonesian). Retrieved 10 August 2020.
- ^ "Sultan Banjar Minta Dibangun Prototipe Kerajaan dan Keraton Sultan Suriansyah". kumparan (in Indonesian). Retrieved 10 August 2020.
- ^ "Sultan Khairul Saleh Punya Obsesi, Munculkan Kembali Bangunan Kerajaan Banjar di Kuin". Banjarmasin Post (in Indonesian). Retrieved 10 August 2020.
- ^ Agency, ANTARA News. "Banjarmasin Siap Bangun Keraton Banjar". ANTARA News Kalimantan Selatan. Retrieved 10 August 2020.
- ^ "Sultan Khairul Saleh Siapkan Kompleks Pemakaman Keluarga Kesultanan Banjar, Disini Lokasinya". Banjarmasin Post (in Indonesian). Retrieved 10 August 2020.





