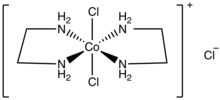
trans-Dichlorobis(ethylenediamine)cobalt(III) chloride
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(OC-6-12′)-Dichloridobis(ethane-1,2-diamine-κ2N,N′)cobalt(1+) chloride(1−)
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H16Cl3CoN4 | |
| Molar mass | 285.48 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | green solid |
| Melting point | decomposes |
| good | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P305+P351+P338 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
trans-Dichlorobis(ethylenediamine)cobalt(III) chloride is a salt with the formula [CoCl2(en)2]Cl (en = ethylenediamine). It is a green diamagnetic solid that is soluble in water. It is the monochloride salt of the cationic coordination complex [CoCl2(en)2]+. One chloride ion in this salt readily undergoes ion exchange but the two other chlorides are less reactive, being bound to the metal center. The more stable cis-dichlorobis(ethylenediamine)cobalt(III) chloride is also known.
Synthesis
[edit]The compound is synthesized by the reaction of cobalt(II) chloride and ethylenediamine in hydrochloric acid in the presence of oxygen:
- 4 CoCl2 + 8 en + 4 HCl + O2 → 4 trans-[CoCl2(en)2]Cl + 2 H2O
The initial product contains HCl, which is removed by heating. Alternatively, (carbonato)bis(ethylenediamine)cobalt(III) chloride reacts with hydrochloric acid at 10 °C to give the same species.[1]
- [Co(CO3)(en)2]Cl + 2 HCl → trans-[CoCl2(en)2]Cl + CO2 + H2O
Related complexes
[edit]This salt is more soluble than cis-dichlorobis(ethylenediamine)cobalt(III) chloride. This pair of isomers were significant in the development of the area of coordination chemistry.[2] The chiral cis isomer is obtained by heating the trans isomer. Both isomers of dichlorobis(ethylenediamine)cobalt(III) have often been used in stereochemical studies. The trans isomer cation has idealized D2h point group symmetry, whereas the cis isomer cation has C2 symmetry.
Tris(ethylenediamine)cobalt(III) chloride in contrast to the bis(ethylenediamine) complexes does not undergo substitution.
References
[edit]- ^ Springbørg, J.; Schaffer, C. E. (1973). "Dianionobis(Ethylenediamine)Cobalt(III) Complexes". Inorganic Syntheses. Vol. 14. pp. 63–77. doi:10.1002/9780470132456.ch14. ISBN 978-0-470-13245-6.
- ^ Jörgensen, S.M. "Ueber Metalldiaminverbindungen" J. prakt. Chem. (in German), 1889, volume 39, page 8. doi:10.1002/prac.18890390101
