User:Maskewmo/sandbox
Chemical safety is the practice of minimizing risk of exposure to chemicals to persons handling the chemicals, and to the surrounding environment, as well as the communities and ecosystems of animals within that environment.
Common Safety Practices
[edit]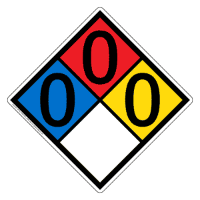
The most basic and common chemical safety practices include minor things such as wearing safety standard gloves, or proper headwear like goggles or other equipment. Wearing closed toed shoes, long pants/socks, and shirts/lab coats to protect the stomach, back and forearm.[1] Always know what chemicals you are working with.
Familiarizing the four chemical hazards: flammability, corrosivity, toxicity, and reactivity is important when handling chemicals. Always read labels before starting a chemical experiment.[2] Before working with chemicals look up its NFPA diamond to have a visual representation on if specific chemical is hazardous or not. The diamond is scaled from 0 meaning the chemicals is not hazardous to 4 meaning that the chemical is extremely dangerous . [3]
Red represents it fire hazard: 0- it will not burn, 1-hazard above 200oF, 2- above 100oF, 3- below 100oF, and 4- below 73oF
Blue represents health hazard: 0- Normal Material, 1- slightly hazardous, 2- hazardous, 3- extreme danger, 4- deadly
Yellow represent reactivity: 0- stable, 1- unstable if heated, 2- violent chemical change, 3- explosive, 4- very explosive
White represent special hazards: ACID- acid, ALK- alkali, COR- corrosive, ☢- Radioactive, W- Do Not Use H2O
Tips:
[edit]- Watch safety training video's before handling chemicals
- Keeping workspace clean
- Label all test tubs, flask, beakers, and/or other containers
- Review and practice experimental methods
- Read Safety data sheets to recognize its hazardous properties
- Have a partner. Its safer to work with someone than alone.
- Absolutely no horseplay, eating smoking or drinking when handling chemicals.
- Never use broken glassware
- Always dilute acids/bases by adding water, slowly!
Lab Techniques & Safety Video
Accidents
[edit]Accidents occur due to failures in proper conduct of chemical safety, whether it be something minor such as forgetting to apply gloves or proper clothing when handling harmful chemicals, to major incidents such as forgetting to check the temperatures of nuclear rods in a nuclear reactor. Preparing for accidents is key to chemical safety. It's important always know where fire extinguishers, fist aid kits, chemical spill kits, eye wash stations and disposal waste containers are in case of emergencies. before disposing acids or bases use sodium carbonate or bicarbonate to neutralize acids and citric acid or ascorbic acid when neutralizing a base. [4]
If chemicals are exposed to:
- Face/eyes- remember that you know where the eye wash station is, flush your face with goggles on and then off for 15 minutes. Call for help!
- Body: clean the affect after with cool water for 15 minutes. Call for help if any burns or rashes occur.
- Inhalation: Immediately get fresh air.
 This is a user sandbox of Maskewmo. You can use it for testing or practicing edits.
This is a user sandbox of Maskewmo. You can use it for testing or practicing edits.
This is not the sandbox where you should draft your assigned article for a dashboard.wikiedu.org course.
To find the right sandbox for your assignment, visit your Dashboard course page and follow the Sandbox Draft link for your assigned article in the My Articles section.
- ^ "Appropriate Lab Attire | Environmental Health & Safety". ehs.gatech.edu. Retrieved 2021-02-16.
- ^ "Chemistry Safety". Science Buddies. Retrieved 2021-02-16.
- ^ "National Fire Protection Association Hazard Identification System". American Chemical Society. Retrieved 2021-02-27.
- ^ "Safety Basics & RAMP". American Chemical Society. Retrieved 2021-02-27.

