User:Mr. Ibrahem/Benzonatate
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Tessalon, Zonatuss, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682640 |
| License data |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Elimination half-life | 3-8 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| Chemical and physical data | |
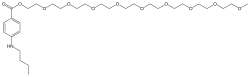
| Formula | C30H53NO11 |
| Molar mass | 603.750 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Benzonatate, sold under the brand name Tessalon among others, is a medication used to try to help with the symptoms of cough and hiccups.[1][2] It is taken by mouth.[1] Use is not recommended in those under the age of ten.[5] Effects generally begin within 20 minutes and last up to eight hours.[1][6]
Side effects include sleepiness, dizziness, headache, upset stomach, skin rash, hallucinations, and allergic reactions.[1] Excessive doses may cause seizures, irregular heartbeat, and death.[5] Chewing or sucking on the capsule can lead to laryngospasm, bronchospasm, and circulatory collapse.[1] It is unclear if use in pregnancy or breastfeeding is safe.[7] It works by numbing stretch receptors in the lungs and suppressing the cough reflex in the brain.[1]
Benzonatate was approved for medical use in the United States in 1958.[1] It is available as a generic medication.[5] In the United States the wholesale cost of is about US$0.12 per 100 mg dose.[8] It is not available in many countries.[9] In 2017, it was the 148th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than four million prescriptions.[10][11]
References[edit]
- ^ a b c d e f g h i "Benzonatate Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 28 December 2021. Retrieved 23 March 2019.
- ^ a b Becker, DE (2010). "Nausea, vomiting, and hiccups: a review of mechanisms and treatment". Anesthesia Progress. 57 (4): 150–6, quiz 157. doi:10.2344/0003-3006-57.4.150. PMC 3006663. PMID 21174569.
- ^ "Benzonatate Use During Pregnancy". Drugs.com. 10 October 2019. Archived from the original on 8 November 2021. Retrieved 20 February 2020.
- ^ "WHOCC - ATC/DDD Index". www.whocc.no. Archived from the original on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 9 September 2020.
- ^ a b c "Drugs for cough". The Medical Letter on Drugs and Therapeutics. 60 (1562): 206–208. 17 December 2018. PMID 30625123.
- ^ "Tessalon - benzonatate capsule". DailyMed. 20 November 2019. Archived from the original on 7 November 2021. Retrieved 21 April 2020.
- ^ "Benzonatate Use During Pregnancy". Drugs.com. 10 October 2019. Archived from the original on 8 November 2021. Retrieved 20 February 2020.
- ^ "NADAC as of 2019-02-27". Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Archived from the original on 6 March 2019. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ^ Walsh, T. Declan; Caraceni, Augusto T.; Fainsinger, Robin; Foley, Kathleen M.; Glare, Paul; Goh, Cynthia; Lloyd-Williams, Mari; Olarte, Juan Nunez; Radbruch, Lukas (2008). Palliative Medicine E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 751. ISBN 9781437721942. Archived from the original on 28 August 2021. Retrieved 9 May 2020.
- ^ "The Top 300 of 2020". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 12 February 2021. Retrieved 11 April 2020.
- ^ "Benzonatate - Drug Usage Statistics". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 8 July 2020. Retrieved 11 April 2020.
