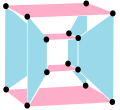
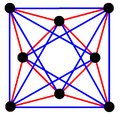
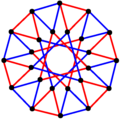
Regular and uniform complex polytopes
Complex Polygons (C2)[edit]
The complex reflection group is p[q]r, order  [1] has, configuration matrix:[2]
[1] has, configuration matrix:[2]


 =
= 

 (Order 2p2 and p2) - Related to p-p duoprisms
(Order 2p2 and p2) - Related to p-p duoprisms
Regular
| G(p,1,2) |
|
k-face |
fk |
f0 |
f1 |
k-fig
|
Notes
|
| A1 |
   |
( )
|
f0
|
p2 |
2 |
{ } |
G(p,1,2)/A1 = 2p2/2 = p2
|
| p[ ] |
   |
p{ }
|
f1
|
p |
2p |
( ) |
G(p,1,2)/p[ ] = 2p2/p = 2p
|
|
Quasiregular
| p[]p[] |
|
k-face |
fk |
f0 |
f1 |
k-fig
|
Notes
|
|
   |
( )
|
f0
|
p2 |
1 |
1 |
{ } |
p[]p[] = p2
|
| p[] |
   |
p{ }
|
f1
|
p |
p |
* |
( ) |
p[]p[]/p[] = p
|
| p[] |
   |
p{ }
|
p |
* |
p |
p[]p[]/p[] = p
|
|

 (order pq) - related to p-q duoprism
(order pq) - related to p-q duoprism
Quasiregular
| p[]q[] |
|
k-face |
fk |
f0 |
f1 |
k-fig
|
Notes
|
|
   |
( )
|
f0
|
pq |
1 |
1 |
{ } |
p[]q[] = pq
|
| p[] |
   |
p{ }
|
f1
|
p |
q |
* |
( ) |
p[]q[]/p[] = q
|
| q[] |
   |
q{ }
|
q |
* |
p |
p[]q[]/q[] = p
|


 =
= 

 (order 18 and 9) - related to 3-3 duoprism
(order 18 and 9) - related to 3-3 duoprism
Regular
| M2 |
  
|
k-face |
fk |
f0 |
f1 |
k-fig
|
Notes
|
| A1 |
   |
( )
|
f0
|
9 |
2 |
{ } |
M2/A1 = 18/2 = 9
|
| L1 |
   |
3{ }
|
f1
|
3 |
6 |
( ) |
M2/L1 = 18/3 = 6
|
|
Quasiregular
L2
1 |
  
|
k-face |
fk |
f0 |
f1 |
k-fig
|
Notes
|
|
   |
( )
|
f0
|
9 |
1 |
1 |
{ } |
L2
1 = 9
|
| L1 |
   |
3{ }
|
f1
|
3 |
3 |
* |
( ) |
L2
1/L1 = 9/3 = 3
|
  
|
3 |
* |
3
|
|


 (order 6) - related to triangular prism
(order 6) - related to triangular prism
Quasiregular
| L1A1 |
  
|
k-face |
fk |
f0 |
f1 |
k-fig
|
Notes
|
|
   |
( )
|
f0
|
6 |
1 |
1 |
{ } |
L1A1 = 6
|
| L1 |
   |
3{ }
|
f1
|
3 |
2 |
* |
( ) |
L1A1/L1 = 6/3 = 2
|
| A1 |
   |
{ }
|
2 |
* |
3 |
L1A1/A1 = 6/2 = 3
|


 (Order 18) - related 3-3 duopyramid
(Order 18) - related 3-3 duopyramid
Regular
| M2 |
  
|
k-face |
fk |
f0 |
f1 |
k-fig
|
Notes
|
| L1 |
   |
( )
|
f0
|
6 |
3 |
3{ } |
M2/L1 = 18/3 = 6
|
| A1 |
   |
{ }
|
f1
|
2 |
9 |
( ) |
M2/A1 = 18/2 = 9
|


 (Order 18)
(Order 18)
Quasiregular
| M2 |
  
|
k-face |
fk |
f0 |
f1 |
k-fig
|
Notes
|
|
   |
( )
|
f0
|
18 |
1 |
1 |
{ } |
M2 = 18
|
| A1 |
   |
{ }
|
f1
|
2 |
9 |
* |
( ) |
M2/A1 = 18/2 = 9
|
| L1 |
   |
3{ }
|
3 |
* |
6 |
M2/L1 = 18/3 = 6
|
Möbius–Kantor polygon 

 =
= 

 , (order 24)
, (order 24)
Regular
| L2 |
  
|
k-face |
fk |
f0 |
f1 |
k-fig
|
Notes
|
| L1 |
   |
( )
|
f0
|
8 |
3 |
3{ } |
L2/L1 = 4!/3 = 8
|
   |
3{ }
|
f1
|
3 |
8 |
( )
|


 =
= 

 (order 48 and 24)
(order 48 and 24)
Regular
| G6 |
  
|
k-face |
fk |
f0 |
f1 |
k-fig
|
Notes
|
| A1 |
   |
( )
|
f0
|
24 |
2 |
{ } |
G6/A1 = 48/2 = 24
|
| L1 |
   |
3{ }
|
f1
|
3 |
16 |
( ) |
G6/L1 = 48/3 = 16
|
|
Quasiregular
| L2 |
  
|
k-face |
fk |
f0 |
f1 |
k-fig
|
Notes
|
|
   |
( )
|
f0
|
24 |
1 |
1 |
{ } |
L2 = 24
|
| L1 |
   |
3{ }
|
f1
|
3 |
8 |
* |
( ) |
L2/L1 = 24/3 = 8
|
  
|
3 |
* |
8
|
|
Complex polyhedra (C3)[edit]
There are 9 unique regular and uniform complex polyhedra from 14 Wythoff constructions (ringed patterns) in the L3 and M3 Shephard groups. These polyhedra can be seen a complex analogues of tetrahedral symmetry and octahedral symmetry of the regular tetrahedron, cube, and octahedron.
| Type |
L3 =      , order 648 , order 648 |
M3 =      , order 1296 , order 1296
|
| Regular |
     = =      |
(27,72,27) |
     |
(54,216,72) |
     = =      |
(72,216,54)
|
| Truncation |
     = =      |
(27,72+216,27+27) |
     |
(648,216+432,72+72) |
     = =      |
(648,216+432,72+72)
|
| Quasiregular |
     = =      |
(27,216,54+54) |
     = =      |
(216,432,54+72)
|
| Cantellation |
     = =      |
(216,216+216,27+27+72) |
     |
(216,216+432,54+72)
|
| Cantitruncation |
     = =      |
(648,216+216+216,27+27+72) |
     |
(1296,432+432+648,54+54+216)
|




 =
= 



 - analogous to real tetrahedron
- analogous to real tetrahedron
Regular
| L3 |
    
|
k-face |
fk |
f0 |
f1 |
f2 |
k-fig
|
Notes
|
| L2 |
     |
( )
|
f0
|
27 |
8 |
8 |
3{3}3 |
L3/L2 = 27*4!/4! = 27
|
| L1L1 |
     |
3{ }
|
f1
|
3 |
72 |
3 |
3{ } |
L3/L1L1 = 27*4!/9 = 72
|
| L2 |
     |
3{3}3
|
f2
|
8 |
8 |
27 |
( ) |
L3/L2 = 27*4!/4! = 27
|
Rectified Hessian polyhedron[edit]




 =
= 



 - analogous to real octahedron
- analogous to real octahedron
Regular
| M3 |
    
|
k-face |
fk |
f0 |
f1 |
f2 |
k-fig
|
Notes
|
| M2 |
     |
( )
|
f0
|
72 |
9 |
6 |
3{4}2 |
M3/M2 = 1296/18 = 72
|
| L1A1 |
     |
3{ }
|
f1
|
3 |
216 |
2 |
{ } |
M3/L1A1 = 1296/3/2 = 216
|
| L2 |
     |
3{3}3
|
f2
|
8 |
8 |
54 |
( ) |
M3/L2 = 1296/24 = 54
|
|
Quasiregular
| L3 |
    
|
k-face |
fk |
f0 |
f1 |
f2 |
k-fig
|
Notes
|
| L1L1 |
     |
( )
|
f0
|
72 |
9 |
3 |
3 |
3{ }×3{ } |
L3/L1L1 = 648/9 = 72
|
| L1 |
     |
3{ }
|
f1
|
3 |
216 |
1 |
1 |
{ } |
L3/L1 = 648/3 = 216
|
| L2 |
     |
3{3}3
|
f2
|
8 |
8 |
27 |
* |
( ) |
L3/L2 = 648/24 = 27
|
    
|
8 |
8 |
* |
27
|
|
Truncated Hessian polyhedron[edit]




 =
= 



 - analogous to real truncated tetrahedron
- analogous to real truncated tetrahedron
Truncated
| L3 |
    
|
k-face |
fk |
f0 |
f1 |
f2 |
k-fig
|
Notes
|
| L1 |
     |
( )
|
f0
|
27 |
1 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
|
L3/L1 = 648/24 = 27
|
| L1L1 |
     |
3{ }
|
f1
|
3 |
72 |
* |
3 |
0 |
|
L3/L1L1 = 648/3/3 = 72
|
| L1 |
    
|
3 |
* |
216 |
1 |
2 |
|
L3/L1 = 648/3 = 216
|
| L2 |
     |
t(3{3}3)
|
f2
|
24 |
8 |
8 |
27 |
* |
( ) |
L3/L2 = 648/24 = 27
|
     |
3{3}3
|
8 |
0 |
8 |
* |
27
|
Cantellated Hessian polyhedron[edit]




 =
= 



 - analogous to real cuboctahedron
- analogous to real cuboctahedron
Cantellated
| L3 |
    
|
k-face |
fk |
f0 |
f1 |
f2 |
k-fig
|
Notes
|
| L1 |
     |
( )
|
f0
|
216 |
1 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
0 |
3{ }×{ } |
L3/L1 = 648/3 = 216
|
     |
3{ }
|
f1
|
3 |
216 |
* |
2 |
0 |
0 |
{ }
|
    
|
3 |
* |
216 |
1 |
1 |
0
|
| L2 |
     |
3{3}3
|
f2
|
8 |
8 |
0 |
27 |
* |
* |
( ) |
L3/L2 = 648/24 = 27
|
| L1L1 |
     |
3{ }×3{ }
|
9 |
3 |
3 |
* |
72 |
* |
L3/L1L1 = 648/9 = 72
|
| L2 |
     |
3{3}3
|
8 |
0 |
8 |
* |
* |
27 |
L3/L2 = 648/24 = 27
|
|
Rectified
| M3 |
    
|
k-face |
fk |
f0 |
f1 |
f2 |
k-fig
|
Notes
|
| L1A1 |
     |
( )
|
f0
|
216 |
6 |
3 |
2 |
3{ }×{ } |
M3/L1A1 = 1296/6 = 216
|
| L1 |
     |
3{ }
|
f1
|
3 |
432 |
1 |
1 |
{ } |
M3/L1 = 1296/3 = 432
|
| L2 |
     |
3{3}3
|
f2
|
8 |
8 |
54 |
* |
( ) |
M3/L2 = 1296/24 = 54
|
| M2 |
     |
3{4}2
|
9 |
6 |
* |
72 |
M3/M2 = 1296/18 = 72
|
|
Cantitruncated Hessian polyhedron[edit]




 =
= 



 - analogous to real truncated octahedron
- analogous to real truncated octahedron
Truncated
| M3 |
    
|
k-face |
fk |
f0 |
f1 |
f2 |
k-fig
|
Notes
|
| A1 |
     |
( )
|
f0
|
648 |
? |
? |
? |
? |
|
M3/L1 = 1296/2 = 648
|
| L1A1 |
     |
3{ }
|
f1
|
3 |
216 |
* |
? |
? |
|
M3/L1A1 = 1296/3/2 = 216
|
| L1 |
    
|
3 |
* |
432 |
? |
? |
|
M3/L1 = 1296/3 = 432
|
| L2 |
     |
t(3{3}3)
|
f2
|
24 |
8 |
8 |
54 |
* |
( ) |
M3/L2 = 1296/24 = 54
|
| M2 |
     |
3{4}2
|
9 |
0 |
6 |
* |
72 |
M3/M2 = 1296/48 = 27
|
|
Cantitruncated
| L3 |
    
|
k-face |
fk |
f0 |
f1 |
f2 |
k-fig
|
Notes
|
|
     |
( )
|
f0
|
648 |
? |
? |
? |
? |
? |
? |
|
L3 = 648
|
| L1 |
     |
3{ }
|
f1
|
3 |
216 |
* |
* |
? |
? |
? |
|
L3/L1 = 648/3 = 216
|
    
|
3 |
* |
216 |
* |
? |
? |
?
|
    
|
3 |
* |
* |
216 |
? |
? |
?
|
| L2 |
     |
3{3}3
|
f2
|
24 |
8 |
8 |
0 |
27 |
* |
* |
( ) |
L3/L2 = 648/24 = 27
|
| L1L1 |
     |
3{ }×3{ } |
9 |
3 |
0 |
3 |
* |
72 |
* |
L3/L1/L1 = 648/3/3 = 72
|
| L2 |
     |
3{3}3 |
24 |
0 |
8 |
8 |
* |
* |
27 |
L3/L2 = 648/24 = 27
|
|
Double Hessian polyhedron[edit]
Double Hessian polyhedron 



 - analogous to real cube
- analogous to real cube
Regular
| M3 |
    
|
k-face |
fk |
f0 |
f1 |
f2 |
k-fig
|
Notes
|
| L2 |
     |
( )
|
f0
|
54 |
8 |
8 |
3{3}3 |
M3/L2 = 1296/24 = 54
|
| L1A1 |
     |
{ }
|
f1
|
2 |
216 |
3 |
3{ } |
M3/L1A1 = 1296/3/2 = 216
|
| M2 |
     |
2{4}3
|
f2
|
6 |
9 |
72 |
( ) |
M3/M2 = 1296/18 = 72
|
Truncated double Hessian polyhedron[edit]




 - analogous to real truncated cube
- analogous to real truncated cube
Truncated
| M3 |
    
|
k-face |
fk |
f0 |
f1 |
f2 |
k-fig
|
Notes
|
| L1 |
     |
( )
|
f0
|
648 |
? |
? |
? |
? |
|
M3/L1 = 1296/3 = 432
|
| L1A1 |
     |
{ }
|
f1
|
2 |
216 |
* |
? |
? |
|
M3/L1A1 = 1296/6 = 216
|
| L1 |
     |
3{ }
|
3 |
* |
432 |
? |
? |
|
M3/L1 = 1296/3 = 432
|
| M2 |
     |
t(3{4}2)
|
f2
|
24 |
8 |
8 |
72 |
* |
( ) |
M3/M2 = 1296/18 = 72
|
| L2 |
     |
3{3}3
|
8 |
0 |
8 |
* |
72 |
M3/L2 = 1296/24 = 54
|
Cantellated double Hessian polyhedron[edit]




 - analogous to real rhombicuboctahedron
- analogous to real rhombicuboctahedron
Cantellated
| M3 |
    
|
k-face |
fk |
f0 |
f1 |
f2 |
k-fig
|
Notes
|
| L1 |
     |
( )
|
f0
|
216 |
1 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
0 |
|
M3/L1 = 1296/3 = 216
|
| A1 |
     |
{ }
|
f1
|
3 |
648 |
* |
2 |
0 |
0 |
{ } |
M3/A1 = 1296/2 = 648
|
| L1 |
     |
3{ }
|
3 |
* |
216 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
M3/L1 = 1296/3 = 216
|
| M2 |
     |
3{4}2
|
f2
|
9 |
6 |
0 |
72 |
* |
* |
( ) |
M3/M2 =1296/18 = 72
|
| L1A1 |
     |
3{ }×{ }
|
6 |
3 |
2 |
* |
216 |
* |
M3/L1A1 = 1296/6 = 216
|
| L2 |
     |
3{3}3
|
8 |
0 |
8 |
* |
* |
54 |
M3/L2 = 1296/24 = 54
|
Cantitruncated double Hessian polyhedron[edit]




 - analogous to real truncated cuboctahedron
- analogous to real truncated cuboctahedron
Cantitruncated
| M3 |
    
|
k-face |
fk |
f0 |
f1 |
f2 |
k-fig
|
Notes
|
|
     |
( )
|
f0
|
1296 |
? |
? |
? |
? |
? |
? |
|
M3 = 1296
|
| L1 |
     |
3{ }
|
f1
|
3 |
432 |
* |
* |
? |
? |
? |
|
M3/L1 = 1296/3 = 432
|
    
|
3 |
* |
432 |
* |
? |
? |
?
|
| A1 |
     |
{ }
|
3 |
* |
* |
648 |
? |
? |
? |
M3/A1 = 1296/2 = 648
|
| L2 |
     |
t(3{3}3)
|
f2
|
24 |
8 |
8 |
0 |
54 |
* |
* |
( ) |
M3/L2 = 1296/24 = 54
|
| L1A1 |
     |
3{ }×{ } |
6 |
3 |
0 |
2 |
* |
216 |
* |
M3/L1/A1 = 1296/6 = 216
|
| M2 |
     |
t(3{4}2) |
18 |
0 |
9 |
6 |
* |
* |
27 |
M3/M2 = 1296/48 = 27
|
Witting polytope (C4)[edit]
Witting polytope - 





 - Real representation 421 polytope
- Real representation 421 polytope
| L4 |
      
|
k-face |
fk |
f0 |
f1 |
f2 |
f3 |
k-fig
|
Notes
|
| L3 |
       |
( )
|
f0
|
240 |
27 |
72 |
27 |
3{3}3{3}3 |
L4/L3 = 216*6!/27/4! = 240
|
| L3L1 |
       |
3{ }
|
f1
|
3 |
2160 |
8 |
8 |
3{3}3 |
L4/L3L1 = 216*6!/4!/3 = 2160
|
       |
3{3}3
|
f2
|
8 |
8 |
2160 |
3 |
3{ }
|
| L3 |
       |
3{3}3{3}3
|
f3
|
27 |
72 |
27 |
240 |
( ) |
L4/L3 = 216*6!/27/4! = 240
|








 - Honeycomb of Witting polytope: L5 is order 155520N - Real representation 521 honeycomb
- Honeycomb of Witting polytope: L5 is order 155520N - Real representation 521 honeycomb
| L5 |
        
|
k-face |
fk |
f0 |
f1 |
f2 |
f3 |
f4 |
k-figure
|
Notes
|
| L4 |
         |
( )
|
f0
|
N |
240 |
2160 |
2160 |
240 |
3{3}3{3}3{3}3 |
L5/L4 = N
|
| L3L1 |
         |
3{ }
|
f1
|
3 |
80N |
27 |
72 |
27 |
3{3}3{3}3 |
L5/L3L1 = NL4/L3L1 = 80N
|
| L2L2 |
         |
3{3}3
|
f2
|
8 |
8 |
270N |
8 |
8 |
3{3}3 |
L5/L2L2 = NL4/L2L2 = 270N
|
| L3L1 |
         |
3{3}3{3}3
|
f3
|
27 |
72 |
27 |
80N |
3 |
3{ } |
L5/L3L1 = NL4/L3L1 = 80N
|
| L4 |
         |
3{3}3{3}3{3}3
|
f4
|
240 |
2160 |
2160 |
240 |
N |
( ) |
L5/L4 = NL4/L4 = N
|
- ^ Lehrer & Taylor 2009, p.87
- ^ Complex Regular Polytopes, p. 117





![]()
![]()
![]() =
= ![]()
![]()
![]() (Order 2p2 and p2) - Related to p-p duoprisms
(Order 2p2 and p2) - Related to p-p duoprisms
![]()
![]()
![]() (order pq) - related to p-q duoprism
(order pq) - related to p-q duoprism
![]()
![]()
![]() =
= ![]()
![]()
![]() (order 18 and 9) - related to 3-3 duoprism
(order 18 and 9) - related to 3-3 duoprism
![]()
![]()
![]() (order 6) - related to triangular prism
(order 6) - related to triangular prism
![]()
![]()
![]() (Order 18) - related 3-3 duopyramid
(Order 18) - related 3-3 duopyramid
![]()
![]()
![]() (Order 18)
(Order 18)
![]()
![]()
![]() =
= ![]()
![]()
![]() , (order 24)
, (order 24)
![]()
![]()
![]() =
= ![]()
![]()
![]() (order 48 and 24)
(order 48 and 24)
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() =
= ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() - analogous to real tetrahedron
- analogous to real tetrahedron
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() =
= ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() - analogous to real octahedron
- analogous to real octahedron
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() =
= ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() - analogous to real truncated tetrahedron
- analogous to real truncated tetrahedron
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() =
= ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() - analogous to real cuboctahedron
- analogous to real cuboctahedron
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() =
= ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() - analogous to real truncated octahedron
- analogous to real truncated octahedron
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() - analogous to real cube
- analogous to real cube
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() - analogous to real truncated cube
- analogous to real truncated cube
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() - analogous to real rhombicuboctahedron
- analogous to real rhombicuboctahedron
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() - analogous to real truncated cuboctahedron
- analogous to real truncated cuboctahedron
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() - Real representation 421 polytope
- Real representation 421 polytope
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() - Honeycomb of Witting polytope: L5 is order 155520N - Real representation 521 honeycomb
- Honeycomb of Witting polytope: L5 is order 155520N - Real representation 521 honeycomb


