Transliteration of Ancient Egyptian
As used for Egyptology, transliteration of Ancient Egyptian is the process of converting (or mapping) texts written as Egyptian language symbols to alphabetic symbols representing uniliteral hieroglyphs or their hieratic and demotic counterparts. This process facilitates the publication of texts where the inclusion of photographs or drawings of an actual Egyptian document is impractical.
Transliteration is not the same as transcription. Transliteration is the representation of written symbols in a consistent way in a different writing system, while transcription indicates the pronunciation of a text. For the case of Ancient Egyptian, precise details of the phonology are not known completely. Transcription systems for Ancient Egyptian do exist, but they rely on linguistic reconstruction (depending on evidence from the Coptic language and other details) and are thus theoretical in nature. Egyptologists rely on transliteration in scientific publications.
Standards
[edit]Important as transliteration is for Egyptology, there is no one standard scheme in use for hieroglyphic and hieratic texts. However, there are a few closely related systems that can be regarded as conventional. Many non-German-speaking Egyptologists use the system described in Gardiner 1954, whereas many German-speaking scholars opt for that used in the Wörterbuch der ägyptischen Sprache (Erman and Grapow 1926–1953), the standard dictionary of the ancient Egyptian language. However, there is a growing trend, even among English-speaking scholars, to adopt a modified version of the method used in the Wörterbuch (e.g., Allen 2000).
Although these conventional methods of transliteration have been used since the second half of the nineteenth century to the present time, there have been some attempts to adopt a modified system that seeks to use the International Phonetic Alphabet to a certain extent. The most successful of these is that developed by Wolfgang Schenkel (1990), and it is being used fairly widely in Germany and other German-speaking countries. More recent is a proposal by Thomas Schneider (2003) that is even closer to the IPA, but its usage is not presently common. The major criticism of both of these systems is that they give an impression of being scientifically accurate with regard to the pronunciation of Egyptian, though the actual accuracy is debatable. Moreover, the systems represent only the theoretical pronunciation of Middle Egyptian and not the older and later phases of the language, which are themselves to be transliterated with the same system.
Table of transliteration schemes
[edit]Although the system of Egyptian hieroglyphs is very complicated, there are only 24 consonantal phonemes distinguished, according to Edel (1955)[1] transliterated and ordered alphabetically in the sequence:
- ꜣ j ꜥ w b p f m n r h ḥ ḫ ẖ z s š q k g t ṯ d ḏ
A number of variant conventions are used interchangeably depending on the author.
The following table shows several transliteration schemes. The first column shows the uniliteral hieroglyph (see #Uniliteral signs below) corresponding to the sound.
| Glyph | Brugsch | Erman | Budge | Erman & Grapow |
Gardiner | Edel | Manuel de Codage |
Hodge | Schenkel | Hannig; Allen |
Hoch | Schneider | Leiden Unified | Conventional Egyptological pronunciation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1889 | 1894 | 1910 | 1926–1953 | 1957 | 1955[1] | 1988 | 1990 | 1991 | 1995; 2000 |
1997 | 2003 | 2023 | ||
| 𓄿 | ꜣ | ꜣ | a | ꜣ | ꜣ | ꜣ | A | ꜣ | ꜣ | ꜣ | ꜣ | ɹ | ꜣ | /ɑ, ɑː/ |
| 𓇋 | ʾ | ı͗ | ȧ | ı͗, j | ı͗ | j | i | ʔ | ı͗ | j | ı͗ | ı͗ | ı͗ | /i, iː, j/ |
| 𓏭 | " | ï | i | j | y | (n.a.)[2] | y | y | ı͗ | j | y | ı͗ | ï | /iː/ |
| 𓇌 | ʾʾ | y | i | j | y | j | i*i | y | y | y | y | y | y | /iː/ |
| 𓂝 | ꜥ | ꜥ | ā | ꜥ | ꜥ | ꜥ | a | ꜥ | ꜥ | ꜥ | ꜥ | ɗ | ꜥ | /ɑː/ |
| 𓅱 | w | w | u | w | w | w | w | w | w | w | w | w | w | /w, uː/ |
| 𓃀 | b | b | b | b | b | b | b | b | b | b | b | b | b | /b/ |
| 𓊪 | p | p | p | p | p | p | p | p | p | p | p | p | p | /p/ |
| 𓆑 | f | f | f | f | f | f | f | f | f | f | f | f | f | /f/ |
| 𓅓 | m | m | m | m | m | m | m | m | m | m | m | m | m | /m/ |
| 𓈖 | n | n | n | n | n | n | n | n | n | n | n | n | n | /n/ |
| 𓂋 | r, l | r | r, l | r | r | r | r | r | r | r | r | l | r | /ɾ/ |
| 𓉔 | h | h | h | h | h | h | h | h | h | h | h | h | h | /h/ |
| 𓎛 | ḥ | ḥ | ḥ | ḥ | ḥ | ḥ | H | ḥ | ḥ | ḥ | ḥ | ḥ | ḥ | /ħ, h/ |
| 𓐍 | ḫ | ḫ | χ, kh | ḫ | ḫ | ḫ | x | x | ḫ | ḫ | ḫ | ḫ | ḫ | /x/ |
| 𓄡 | ḫ | ḫ | χ, kh | ẖ | ẖ | ẖ | X | x̯ | ẖ | ẖ | ẖ | ẖ | ẖ | /ç/ |
| 𓊃 | s | s | s | s | s (z) | z | z | z | s | z | s | s | z | /z, s/ |
| 𓋴 | s | s | s | ś | s (ś) | s | s | s | ś | s | s | ś | s | /s/ |
| 𓈙 | š | š | ś, sh | š | š | š | S | š | š | š | š | š | š | /ʃ/ |
| 𓈎 | ḳ | ḳ | q | ḳ | ḳ | q | q | q | ḳ | q | q | ḳ | q | /k, q/ |
| 𓎡 | k | k | k | k | k | k | k | k | k | k | k | k | k | /k/ |
| 𓎼 | g | g | ḳ | g | g | g | g | g | g | g | g | g | g | /ɡ/ |
| 𓏏 | t | t | t | t | t | t | t | t | t | t | t | t | t | /t/ |
| 𓍿 | ṯ | ṯ | θ, th | ṯ | ṯ | ṯ | T | č | č | ṯ | ṯ | c | ṯ | /tʃ/ |
| 𓂧 | d | d | ṭ | d | d | d | d | d | ṭ | d | d | ḍ | d | /d/ |
| 𓆓 | ḏ | ḏ | t', tch | ḏ | ḏ | ḏ | D | ǧ | č̣ | ḏ | ḏ | c̣ | ḏ | /dʒ/ |
The vowel /ɛ/ is conventionally inserted between consonants to make Egyptian words pronounceable in English.
Examples
[edit]The following text is transliterated below in some of the more common schemes. Note that most of the hieroglyphs in this text are not uniliteral signs, but can be found in the List of Egyptian hieroglyphs.
| |
Unicode: 𓇓𓏏𓊵𓏙𓊩𓁹𓏃𓋀𓅂𓊹𓉻𓎟𓍋𓈋𓃀𓊖𓏤𓄋𓈐𓏦𓎟𓇾𓈅𓏤𓂦𓈉
(This text is conventionally translated into English as "an offering that the king gives; and Osiris, Foremost of Westerners [i.e., the Dead], the Great God, Lord of Abydos; and Wepwawet, Lord of the Sacred Land [i.e., the Necropolis]." It can also be translated "a royal offering of Osiris, Foremost of the Westerners, the Great God, Lord of Abydos; and of Wepwawet, Lord of the Sacred Land" [Allen 2000:§24.10].)
Erman and Grapow 1926–1953
- ḥtp-dỉ-nśwt wśỉr ḫntj ỉmntjw nṯr ꜥꜣ nb ꜣbḏw wp-wꜣwt nb tꜣ ḏśr
Gardiner 1953
- ḥtp-dỉ-nswt wsỉr ḫnty ỉmntỉw nṯr ꜥꜣ nb ꜣbḏw wp-wꜣwt nb tꜣ ḏsr
Buurman, Grimal, et al. 1988
- Htp-di-nswt wsir xnty imntiw nTr aA nb AbDw wp-wAwt nb tA Dsr
- A fully encoded, machine-readable version of the same text is:
- M23-X1:R4-X8-Q2:D4-W17-R14-G4-R8-O29:V30-U23-N26-D58-O49:Z1-F13:N31-Z2-V30:N16:N21*Z1-D45:N25
Schenkel 1991
- ḥtp-dỉ-nswt wsỉr ḫnty ỉmntjw nčr ꜥꜣ nb ꜣbč̣w wp-wꜣwt nb tꜣ č̣sr
Allen 2000
- ḥtp-dj-nswt wsjr ḫntj jmntjw nṯr ꜥꜣ nb ꜣbḏw wp-wꜣwt nb tꜣ ḏsr
Schneider 2003
- ḥtp-ḍỉ-nśwt wśỉr ḫnty ỉmntjw ncr ɗɹ nb ɹbc̣w wp-wɹwt nb tɹ c̣śr
Demotic
[edit]As the latest stage of pre-Coptic Egyptian, demotic texts have long been transliterated using the same system(s) used for hieroglyphic and hieratic texts. However, in 1980, Demotists adopted a single, uniform, international standard based on the traditional system used for hieroglyphic, but with the addition of some extra symbols for vowels and other letters that were written in the demotic script. The Demotic Dictionary of the Oriental Institute of the University of Chicago (or CDD) utilises this method. As this system is likely only of interest to specialists[according to whom?], for details see the references below.
- Cenival, Françoise de (1980). "Unification des méthodes de translittération". Enchoria. 10: 2–4.
- Johnson, Janet H (1980). "CDDP Transliteration System". Enchoria. 10: 5–6.
- Johnson, Janet (2000). Thus wrote 'Onchsheshonqy: an introductory grammar of Demotic, Third Edition. Oriental Institute of the University of Chicago. ISBN 978-0-918986-49-8. Retrieved 28 August 2018.
- Tait, William John (1982). "The Transliteration of Demotic". Enchoria. 11: 67–76.
- Thissen, Heinz-Josef (1980). "Zur Transkription demotischer Texte". Enchoria. 10: 7–9.
Encoding
[edit]In 1984 a standard, ASCII-based transliteration system was proposed by an international group of Egyptologists at the first Table ronde informatique et égyptologie and published in 1988 (see Buurman, Grimal, et al., 1988). This has come to be known as the Manuel de Codage (or MdC) system, based on the title of the publication, Inventaire des signes hiéroglyphiques en vue de leur saisie informatique: Manuel de codage des textes hiéroglyphiques en vue de leur saisie sur ordinateur. It is widely used in e-mail discussion lists and internet forums catering to professional Egyptologists and the interested public.
Although the Manuel de codage system allows for simple "alphabetic" transliterations, it also specifies a complex method for electronically encoding complete ancient Egyptian texts, indicating features such as the placement, orientation, and even size of individual hieroglyphs. This system is used (though frequently with modifications) by various computer programs developed for typesetting hieroglyphic texts (such as SignWriter, WinGlyph, MacScribe, InScribe, Glyphotext, WikiHiero, and others).
Unicode
[edit]With the introduction of the Latin Extended Additional block to Unicode version 1.1 (1992), the addition of Egyptological alef and ayin to Unicode version 5.1 (2008) and the addition of Glottal I alias Egyptological yod to Unicode version 12.0 (2019), it is now possible to fully transliterate Egyptian texts using a Unicode typeface. The following table lists only the special characters used for various transliteration schemes (see above).
Egyptological alef, ayin, and yod
[edit]Three characters that are specific to the discipline are required for transliterating Egyptian:
- Alef (
 , two Semitistic alephs, one set over the other (Lepsius); approximated by the digit ⟨3⟩ in ASCII);[3]
, two Semitistic alephs, one set over the other (Lepsius); approximated by the digit ⟨3⟩ in ASCII);[3] - Ayin (
 , a Semitistic ayin);
, a Semitistic ayin); - Yod (
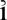 , i with a Semitistic aleph instead of the dot, both yod and alef being considered possible sound values in the 19th century).[4]
, i with a Semitistic aleph instead of the dot, both yod and alef being considered possible sound values in the 19th century).[4]
Although three Egyptological and Ugariticist letters were proposed in August 2000,[5] it was not until 2008 (Unicode 5.1) two of the three letters were encoded: aleph and ayin (minor and capital). Another two proposals were made regarding the Egyptological yod,[6][7] the eventual result of which was to accept the use of the Cyrillic psili pneumata (U+0486 ◌҆ COMBINING CYRILLIC PSILI PNEUMATA) as one of several possible diacritics for this purpose. The other options use the superscript comma (U+0313) and the right half ring above (U+0357). A new attempt for a sign called LETTER I WITH SPIRITUS LENIS was made in 2017.[8] Within the Egyptological community objections were made concerning this name.[9] The proposed name was changed to EGYPTOLOGICAL YOD[10] before finally becoming GLOTTAL I.[11] The sign was added in March 2019 with the release of Unicode 12.0. One of the first fonts that implemented the full set of signs is New Athena Unicode.[12]
| Designation | Lowercase | Capital |
|---|---|---|
| Egyptological alef | ꜣ U+A723 |
Ꜣ U+A722 |
| Egyptological ayin | ꜥ U+A725 |
Ꜥ U+A724 |
| Egyptological yod | U+A7BD |
Ꞽ U+A7BC |
Before the usage of the above-mentioned Unicode signs, various workarounds were in practice, e.g.
| Designation | Lowercase | Capital |
|---|---|---|
| Middle English yogh[13] | ȝ U+021D |
|
| Reverse sicilicus[13] | ʿ U+02BF |
|
| Right half ring above [14] | i͗ U+0069 U+0357 |
I͗ U+0049 U+0357 |
| ı͗ U+0131 U+0357 [15] | ||
| I with hook above [13] | ỉ U+1EC9 |
Ỉ U+1EC8 |
| Cyrillic psili pneumata | i҆ U+0069 U+0486 |
I҆ U+0049 U+0486 |
| Superscript comma | i̓ U+0069 U+0313 |
I̓ U+0049 U+0313 |
Uniliteral signs
[edit]Middle Egyptian is reconstructed as having had 24 consonantal phonemes. There is at least one hieroglyph with a phonetic value corresponding to each of these phonemes.
The table below gives a list of such "uniliteral signs" along with their conventional transcription and their conventional "Egyptological pronunciation" and probable phonetic value.
Many hieroglyphs are coloured, though the paint has worn off most stone inscriptions. Colors vary, but many glyphs are predominantly one colour or another, or a particular combination (such as red on the top and blue on the bottom). In some cases, two graphically similar glyphs may be distinguished solely by colour, though in other cases it's not known if the choice of colour had any meaning.
| Sign | Egyptological transliteration and pronunciation | Phonetic values (IPA)[16][17][18][19] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hieroglyph | Sign Colour | Depiction | Transliteration | Say (modern)[20] | Notes | Old Egyptian | Middle Egyptian |
| 𓄿 | Polychrome | Egyptian vulture | ꜣ | ah | Called alef/aleph or hamza, a glottal stop |
some form of liquid; proposed values include /ʀ/, /r/, /l/, /ɫ/ |
variously /ʀ/, /ʔ/, and /j/ |
| 𓇋 | Green | Flowering reed | ꞽ or j | ee | Called yod | /j/ or /ʔ/ (?) | |
| 𓇌 | Green | Pair of reeds | y or j | y or ee | Called yod or y | not used | /j/ |
| 𓏭 | Blue | Pair of strokes | y or j or ï | not used | /j/ or /i/ (?) | ||
| 𓂝 | Red | Forearm | ꜥ | ah | Called ayin | /ʕ/, or debatably /d/[21] | /ʕ/; /d/ perhaps retained in some words and dialects |
| 𓅱 𓏲 | Yellow | Quail chick or its hieratic abbreviation |
w | w or oo | Called wau/waw |
/w/ | |
| 𓃀 | Red | Lower leg | b | b | /b/ | ||
| 𓊪 | Green | Reed mat or stool | p | p | /p/ | ||
| 𓆑 | Yellow | Horned viper | f | f | /f/ | ||
| 𓅓 | Yellow | Owl | m | m | /m/ | ||
| 𓈖 | Black | Ripple of water | n | n | /n/ | ||
| 𓂋 | Red | Human mouth | r | r | /ɾ/, sometimes /l/ (dialectally always /l/) |
variously /ɾ/, /l/, /j/, ∅ (dialectally /l/, /j/, ∅) | |
| 𓉔 | Blue | Reed shelter | h | h | /h/ | ||
| 𓎛 | Green | Twisted wick | ḥ | h | An emphatic h, a voiceless pharyngeal fricative, called second H, dotted H |
/ħ/ | |
| 𓐍 | Green | Sieve or placenta | ḫ | kh | Voiceless velar fricative, called third H | /χ/ ~ /x/, or speculatively /ɣ/(?) | |
| 𓄡 | Attested in multiple colors | Animal belly and tail | ẖ | kh; hy as in human | A softer sound, a voiceless palatal fricative, called fourth H |
/ç/, or speculatively /x/(?) | |
| 𓊃 | Red | Door bolt | z or s | z/s | very unclear; proposed values include /z/, /t͡s/, /sʼ/, /θ/ |
/s/ | |
| 𓋴 | Red | Folded cloth | s or ś | s | /s/ | ||
| 𓈙 𓈚 𓈛 𓈜 | Blue | Garden pool | š | sh | Called shin | /ʃ/ | |
| 𓈎 | Blue | Hill slope | ḳ or q | q | An emphatic k, a voiceless uvular plosive, called Q or dotted k |
/kʼ/ or /qʼ/(?) (exact phonetic distinction from ⟨g⟩ unclear) | |
| 𓎡 𓎢 | Green | Basket with handle | k | k | /k/ | ||
| 𓎽 𓎼 | Red | Jar stand | g | g | /kʼ/ or /g/(?) (exact phonetic distinction from ⟨q⟩ unclear) | ||
| 𓏏 | Blue | Bread loaf | t | t | /t/ | /t/ ~ ∅ | |
| 𓍿 | Green | Tethering rope or hobble | ṯ or č | ch | Called second T | /c/ | /c/ ~ /t/ ~ ∅ |
| 𓂧 | Red | Hand | d or ṭ | d | /tʼ/ | ||
| 𓆓 | Yellow | Cobra | ḏ or č̣ | j | Called second D | /cʼ/ | /cʼ/ ~ /tʼ/ |
See also
[edit]- List of Egyptian hieroglyphs
- Egyptian biliteral signs
- Egyptian triliteral signs
- Egyptian transliteration schemes
References
[edit]Citations
[edit]- ^ a b E. Edel, Altägyptische Grammatik, Analecta Orientalia 34, 39, Rome (1955, 1964).
- ^ In Old Egyptian, 𓏭 is used as dual classifier only (cf. E. Edel: Altägyptische Grammatik).
- ^ Carsten Peust, Egyptian Phonology: Introduction to the Phonology of a Dead Language (Göttingen, 1999), 127.
- ^ Peust, Egyptian Phonology, p. 50, 99ff.
- ^ Everson, Michael. Proposal to add 6 Egyptological characters to the UCS, 2000-08-27
- ^ Everson, Michael and Bob Richmond, EGYPTOLOGICAL YOD and Cyrillic breathing, 2008-04-08
- ^ Everson, Michael, Proposal to encode Egyptological Yod and similar characters in the UCS, 2008-08-04
- ^ Michel Suignard, Proposal to encode Egyptological Yod and similar characters in the UCS, 2017-05-09 (cf. the later 2008 proposal).
- ^ "The Egyptian June 2017 Archive by thread". evertype.com. Retrieved Dec 29, 2022.
- ^ Moore, Lisa (2018-02-02). "L2/17-362: UTC #153 Minutes".
- ^ Moore, Lisa (2018-11-20). "L2/18-183: UTC #156 Minutes".
- ^ "New Athena Unicode Font Download". apagreekkeys.org. Retrieved Dec 29, 2022.
- ^ a b c See IFAO - Polices de caractères
- ^ "New Athena Unicode Font Download". ucbclassics.dreamhosters.com. Retrieved Dec 29, 2022.
- ^ "Unicode - Glossing Ancient Languages". wikis.hu-berlin.de. Retrieved Dec 29, 2022.
- ^ Loprieno, Antonio (2001) "From Ancient Egyptian to Coptic" in Haspelmath, Martin et al. (eds.), Language Typology and Language Universals
- ^ Peust, Carsten (1999) Egyptian Phonology: An Introduction to the Phonology of a Dead Language, Göttingen: Peust und Gutschmidt Verlag GbR
- ^ Allen, James P. (2013) The Ancient Egyptian Language: An Historical Study, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
- ^ Kammerzell, Frank (2005). Old Egyptian and Pre-Old Egyptian : Tracing Linguistic Diversity in Archaic Egypt and the Creation of the Egyptian Language. Achet. ISBN 9783933684202. Retrieved Dec 29, 2022 – via edoc.bbaw.de.
- ^ Allen, James Paul. 2000. Middle Egyptian: An Introduction to the Language and Culture of Hieroglyphs. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, chapter 2.6.
- ^ Gensler, Orin D. (2014) "A typological look at Egyptian *d > ʕ" in Grossman, Eitan; Haspelmath, Martin; and Richter, Tonio Sebastian (eds.), Egyptian-Coptic Linguistics in Typological Perspective
Bibliography
[edit]- Allen, James Paul (2000). Middle Egyptian: An Introduction to the Language and Culture of Hieroglyphs. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Buurman, Jan; Grimal, Nicolas-Christophe; Hainsworth, Michael; Hallof, Jochen; van der Plas, Dirk (1988). Inventaire des signes hiéroglyphiques en vue de leur saisie informatique: Manuel de codage des textes hiéroglyphiques en vue de leur saisie sur ordinateur. Mémoires de l'Académie des Inscriptions et Belle-Lettres (Nouvelle Série). Vol. 8 (3rd ed.). Paris: Institut de France.
- Erman, Adolf; Grapow, Hermann, eds. (1971) [published 1926–1953, J. C. Hinrichs'schen Buchhandlungen, Liepzig]. Wörterbuch der aegyptischen Sprache im Auftrage der deutschen Akademien. Vol. 1–6. Berlin: Akademie-Verlag.
- Gardiner, Alan Henderson (1957). Egyptian Grammar; Being an Introduction to the Study of Hieroglyphs (3rd ed.). Oxford: Griffith Institute.
- Hannig, Rainer (1995). Großes Handwörterbuch Ägyptisch–Deutsch: die Sprache der Pharaonen (2800–950 v. Chr.). Kulturgeschichte der antiken Welt. Vol. 64. Mainz am Rhein: Verlag Philipp von Zabern. ISBN 9783805317719.
- Kammerzell, Frank (2005). "Old Egyptian and Pre-Old Egyptian: Tracing linguistic diversity in Archaic Egypt and the creation of the Egyptian language". In Seidlmayer, Stephan Johannes (ed.). Texte und Denkmäler des ägyptischen Alten Reiches. Thesaurus Linguae Aegyptiae. Vol. 3. Berlin: Brandenburgische Akademie der Wissenschaften. pp. 165–247. ISBN 3-933684-20-X.
- Schenkel, Wolfgang (1990). Einführung in die altägyptische Sprachwissenschaft. Orientalistische Einführungen. Darmstadt: Wissenschaftliche Buchgesellschaft. doi:10.11588/diglit.47786. ISBN 3-534-03506-2.
- Schenkel, Wolfgang (1991). Tübinger Einführung in die klassisch-ägyptische Sprache und Schrift. Tübingen: W. Schenkel. doi:10.11588/diglit.13942.
- Schneider, Thomas (2003). "Etymologische Methode, die Historizität der Phoneme und das ägyptologische Transkriptionsalphabet". Lingua Aegyptia: Journal of Egyptian Language Studies (in German). 11: 187–199.
- International Congress of Egyptologists (2023). "The Leiden Unified Transliteration". Archived from the original on 2023-08-13.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link)
External links
[edit]- Manuel de Codage: technical details of electronic transliteration of Egyptian texts
- Unicode-based transliteration system adopted by the Institut Français d'Archéologie Orientale. Description and downloadable keyboard layouts.
- Online encoding converter for converting ASCII-based transliterations into Unicode.

