Outline of trigonometry
| Trigonometry |
|---|
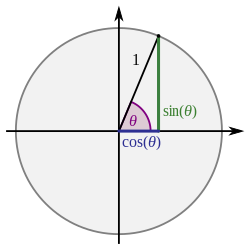 |
| Reference |
| Laws and theorems |
| Calculus |
| Mathematicians |
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to trigonometry:
Trigonometry – branch of mathematics that studies the relationships between the sides and the angles in triangles. Trigonometry defines the trigonometric functions, which describe those relationships and have applicability to cyclical phenomena, such as waves.
Basics[edit]

- Geometry – mathematics concerned with questions of shape, size, the relative position of figures, and the properties of space. Geometry is used extensively in trigonometry.
- Angle – the angle is the figure formed by two rays, called the sides of the angle, sharing a common endpoint, called the vertex of the angle. Angles formed by two rays lie in a plane, but this plane does not have to be a Euclidean plane.
- Ratio – a ratio indicates how many times one number contains another
Content of trigonometry[edit]
Scholars[edit]
- Archimedes
- Aristarchus
- Aryabhata
- Bhaskara I
- Claudius Ptolemy
- Euclid
- Hipparchus
- Madhava of Sangamagrama
- Ptolemy
- Pythagoras
- Regiomontanus
History[edit]
- Aristarchus's inequality
- Bhaskara I's sine approximation formula
- Greek astronomy
- Indian astronomy
- Jyā, koti-jyā and utkrama-jyā
- Madhava's sine table
- Ptolemy's table of chords
- Rule of marteloio
- Āryabhaṭa's sine table
Fields[edit]
- Acoustics
- Architecture
- Astronomy
- Biology
- Cartography
- Chemistry
- Civil engineering
- Computer graphics
- Cryptography
- Crystallography
- Economics
- Electrical engineering
- Electronics
- Game development
- Geodesy
- Mechanical engineering
- Medical imaging
- Meteorology
- Music theory
- Number theory
- Oceanography
- Optics
- Pharmacy
- Phonetics
- Physical science
- Probability theory
- Seismology
- Statistics
- Surveying
Physics[edit]
Astronomy[edit]
Chemistry[edit]
Geography, geodesy, and land surveying[edit]
- Hansen's problem
- Snellius–Pothenot problem
- Great-circle distance – how to find that distance if one knows the latitude and longitude.
- Resection (orientation)
- Vincenty's formulae
- Geographic distance
- Triangulation in three dimensions
[edit]
Engineering[edit]
Analog devices[edit]
Calculus[edit]
- Inverse trigonometric functions
- List of integrals of trigonometric functions
- List of integrals of inverse trigonometric functions
- Regiomontanus' angle maximization problem
- Tangent half-angle substitution
- Trigonometric integral
- Trigonometric substitution
- Applications
Other areas of mathematics[edit]
- For examples of trigonometric functions as generating functions in combinatorics, see Alternating permutation.
- Dirichlet kernel
- Euler's formula
- Exact trigonometric values
- Exponential sum
- Trigonometric integral
- Trigonometric polynomial
- Trigonometric series
Geometric foundations[edit]
- Altern base
- Angle
- Angle excess
- Angular distance
- Angular unit
- Degree (angle)
- Gon (angle) (aka Grad, Gradian)
- Radian
- Turn (angle)
- Brocard points
- Chord (geometry)
- Circle (also see List of circle topics)
- Hypotenuse
- Opposites post
- π (pi)
- Ptolemy's theorem
- Pythagorean theorem
- Regiomontanus' angle maximization problem
- Thales' theorem
- Trigonometric function
- Trigonometry of a tetrahedron
- Triangle (also see List of triangle topics)
Trigonometric functions[edit]
- Sine, Cosine, Tangent (trigonometric function), Cotangent, Secant (trigonometric function), Cosecant – see Trigonometric function
- atan2
- cis—see Euler's formula
- Cofunction
- Exsecant
- Gudermannian function
- Inverse trigonometric functions
- Jyā, koti-jyā and utkrama-jyā
- Versine
Trigonometric identities[edit]
- De Moivre's formula
- Euler's formula
- Hermite's cotangent identity
- Lagrange's trigonometric identities
- Morrie's law
- Proofs of trigonometric identities
- Pythagorean trigonometric identity
- Tangent half-angle formula
Solution of triangles[edit]
More advanced trigonometric concepts and methods[edit]
- Chebyshev polynomials
- Conway triangle notation
- Exact trigonometric constants
- Generalized trigonometry
- Gudermannian function
- Lissajous curve
- Polar sine
- Rational trigonometry
- Spread polynomials
Numerical mathematics[edit]
- Abbe error
- Hypot
- Prosthaphaeresis
- Trigonometric interpolation
- Kunstweg, an algorithm for computing sines, introduced in the late 1500s
Trigonometric tables[edit]
- Generating trigonometric tables
- Āryabhaṭa's sine table
- Bhaskara I's sine approximation formula
- Madhava's sine table
- Ptolemy's table of chords, written in the second century A.D.
- Rule of marteloio
- Canon Sinuum, listing sines at increments of two arcseconds, published in the late 1500s
Spherical trigonometry[edit]
Mnemonics[edit]
Lists[edit]
- List of integrals of trigonometric functions
- List of integrals of inverse trigonometric functions
- List of trigonometric identities
- Table of mathematical symbols
See also[edit]
- Algebra
- Hyperbolic function
- List of exponential topics
- Outline of geometry
- Precalculus
- Spherical geometry
- Table of mathematical symbols
External links[edit]
Wikibooks has a book on the topic of: Trigonometry
- An introduction to trigonometry
- Benjamin Banneker's Trigonometry Puzzle at Convergence
- Dave's short trig course
- Trigonometric Delights, by Eli Maor, Princeton University Press, 1998. Ebook version, in PDF format, full text presented.
- Trigonometry by Alfred Monroe Kenyon and Louis Ingold, The Macmillan Company, 1914. In images, full text presented.
- Trigonometry FAQ
- Trigonometry on Mathwords.com index of trigonometry entries on Mathwords.com
- Trigonometry on PlainMath.net Trigonometry Articles from PlainMath.Net
