Portal:Devonian
The Devonian Portal
The Devonian (/dəˈvoʊni.ən, dɛ-/ də-VOH-nee-ən, deh-) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era during the Phanerozoic eon, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the preceding Silurian period at 419.2 million years ago (Ma), to the beginning of the succeeding Carboniferous period at 358.9 Ma. It is named after Devon, South West England, where rocks from this period were first studied.
The first significant evolutionary radiation of life on land occurred during the Devonian, as free-sporing land plants (pteridophytes) began to spread across dry land, forming extensive coal forests which covered the continents. By the middle of the Devonian, several groups of vascular plants had evolved leaves and true roots, and by the end of the period the first seed-bearing plants (pteridospermatophytes) appeared. This rapid evolution and colonization process, which had begun during the Silurian, is known as the Silurian-Devonian Terrestrial Revolution. The earliest land animals, predominantly arthropods such as myriapods, arachnids and hexapods, also became well-established early in this period, after beginning their colonization of land at least from the Ordovician period.
Fishes, especially jawed fish, reached substantial diversity during this time, leading the Devonian to often be dubbed the Age of Fishes. The armored placoderms began dominating almost every known aquatic environment. In the oceans, cartilaginous fishes such as primitive sharks became more numerous than in the Silurian and Late Ordovician. Tetrapodomorphs, which include the ancestors of all four-limbed vertebrates (i.e. tetrapods), began diverging from freshwater lobe-finned fish as their more robust and muscled pectoral and pelvic fins gradually evolved into forelimbs and hindlimbs, though they were not fully established for life on land until the Late Carboniferous. (Full article...)
Selected Devonian Article
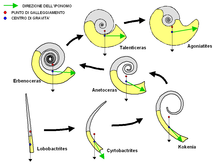
The Bactritida are a small order of more or less straight-shelled (orthoconic) cephalopods that first appeared during the Emsian stage of the Devonian period (407 million years ago) with questionable origins in the Pragian stage before 409 million years ago, and persisted until the Carnian pluvial event in the upper middle Carnian stage of the Triassic period (231 million years ago). They are considered ancestors of the ammonoids, as well as of the coleoids (octopus, squid, cuttlefish, and the extinct belemnites).
Bactritids are distinguished from the more primitive nautiloids by the small size and globular shape of the protoconch, the so-called embryonic shell. Nautiloids have relatively large embryonic shells, and living species lay a few large eggs. In contrast, bactritids and ammonoids produced large numbers of small eggs, each housing a small embryonic shell. (Full article...)List of selected Devonian articles
|
|---|
Selected Devonian land plant article
List of selected Devonian articles
|
|---|
Selected Devonian formation
List of selected Devonian formation articles
|
|---|
Selected Devonian fish article
Selected Devonian invertebrate
Ammonoids are extinct spiral shelled cephalopods comprising the subclass Ammonoidea. They are more closely related to living coleoids (i.e., octopuses, squid and cuttlefish) than they are to shelled nautiloids (such as the living Nautilus). The earliest ammonoids appeared during the Devonian, with the last species vanishing during or soon after the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. They are often called ammonites, which is most frequently used for members of the order Ammonitida, the only living group of ammonoids from the Jurassic up until their extinction.
Ammonites are excellent index fossils, and linking the rock layer in which a particular species or genus is found to specific geologic time periods is often possible. Their fossil shells usually take the form of planispirals, although some helically spiraled and nonspiraled forms (known as heteromorphs) have been found.
The name "ammonite", from which the scientific term is derived, was inspired by the spiral shape of their fossilized shells, which somewhat resemble tightly coiled rams' horns. Pliny the Elder (d. 79 AD near Pompeii) called fossils of these animals ammonis cornua ("horns of Ammon") because the Egyptian god Ammon (Amun) was typically depicted wearing rams' horns. Often, the name of an ammonite genus ends in -ceras, which is from κέρας (kéras) meaning "horn". (Full article...)List of selected Devonian invertebrates articles
|
|---|
Need help?
Do you have a question about Devonian that you can't find the answer to?
Consider asking it at the Wikipedia reference desk.
Subcategories
Related portals
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus