User:UBeR/GWcleanup
Template:Featured article is only for Wikipedia:Featured articles.


Global warming is the increase in the average temperature of the Earth's near-surface air and oceans in recent decades and its projected continuation.
Global average air temperature near the Earth's surface rose 0.74 ± 0.18 °C (1.3 ± 0.32 °F) during the past century. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) concludes, "most of the observed increase in globally averaged temperatures since the mid-20th century is very likely due to the observed increase in anthropogenic greenhouse gas concentrations,"[1] which leads to warming of the surface and lower atmosphere by increasing the greenhouse effect. Natural phenomena such as solar variation combined with volcanoes have probably had a small warming effect from pre-industrial times to 1950, but a cooling effect since 1950. The basic conclusions have been endorsed by at least 30 scientific societies and academies of science, including all of the national academies of science of the major industrialized countries. The American Association of Petroleum Geologists is the only scientific society that rejects these conclusions,[2][3] and a few individual scientists also disagree with parts of them.[4]
Climate models referenced by the IPCC project that global surface temperatures are likely to increase by 1.1 to 6.4 °C (2.0 to 11.5 °F) between 1990 and 2100.[1] The range of values reflects the use of differing scenarios of future greenhouse gas emissions and results of models with differences in climate sensitivity. Although most studies focus on the period up to 2100, warming and sea level rise are expected to continue for more than a millennium even if greenhouse gas levels are stabilized.[1] This reflects the large heat capacity of the oceans.
An increase in global temperatures can in turn cause other changes, including sea level rise, and changes in the amount and pattern of precipitation. There may also be increases in the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, though it is difficult to connect specific events to global warming. Other effects may include changes in agricultural yields, glacier retreat, reduced summer streamflows, species extinctions and increases in the ranges of disease vectors.
Remaining scientific uncertainties include the exact degree of climate change expected in the future, and how changes will vary from region to region around the globe. There is ongoing political and public debate regarding what, if any, action should be taken to reduce or reverse future warming or to adapt to its expected consequences. Most national governments have signed and ratified the Kyoto Protocol aimed at combating greenhouse gas emissions.
Terminology[edit]
The term "global warming" is a specific example of the broader term climate change, which can also refer to global cooling. In principle, global warming is neutral as to the period or causes, but in both common and scientific usage the term generally refers to recent warming and implies a human influence.[5] The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) uses the term "climate change" for human-caused change, and "climate variability" for other changes.[6] The term "anthropogenic climate change" is sometimes used when focusing on human-induced changes.
Causes[edit]

The climate system varies through natural, internal processes and in response to variations in external forcing factors including solar activity, volcanic emissions, variations in the earth's orbit (orbital forcing) and greenhouse gases. The detailed causes of the recent warming remain an active field of research, but the scientific consensus[7] identifies increased levels of greenhouse gases due to human activity as the main influence. This attribution is clearest for the most recent 50 years, for which the most detailed data are available. Contrasting with the scientific consensus, other hypotheses have been proposed to explain some of the observed increase in global temperatures, including: the warming is within the range of natural variation; the warming is a consequence of coming out of a prior cool period, namely the Little Ice Age; or the warming is primarily a result of variances in solar radiation.[8]
None of the effects of forcing are instantaneous. Due to the thermal inertia of the Earth's oceans and slow responses of other indirect effects, the Earth's current climate is not in equilibrium with the forcing imposed. Climate commitment studies indicate that even if greenhouse gases were stabilized at present day levels, a further warming of about 0.5 °C (0.9 °F) would still occur.[9]
Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere[edit]
The greenhouse effect was discovered by Joseph Fourier in 1824 and was first investigated quantitatively by Svante Arrhenius in 1896. It is the process by which absorption and emission of infrared radiation by atmospheric gases warms a planet's atmosphere and surface.
Greenhouse gases create a natural greenhouse effect, without which, mean temperatures on Earth would be an estimated 30 °C (54 °F) lower, so that Earth would be uninhabitable.[10] Thus scientists do not "believe in" or "oppose" the greenhouse effect as such; rather, the debate concerns the net effect of the addition of greenhouse gases, while allowing for associated positive and negative feedback mechanisms.
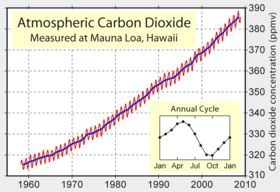
On Earth, the major natural greenhouse gases are water vapor, which causes about 36–70% of the greenhouse effect (not including clouds); carbon dioxide (CO2), which causes 9–26%; methane (CH4), which causes 4–9%; and ozone, which causes 3–7%. The atmospheric concentrations of CO2 and CH4 have increased by 31% and 149% respectively above pre-industrial levels since 1750. These levels are considerably higher than at any time during the last 650,000 years, the period for which reliable data has been extracted from ice cores. From less direct geological evidence it is believed that CO2 values this high were last attained 20 million years ago.[11] "About three-quarters of the anthropogenic [man-made] emissions of CO2 to the atmosphere during the past 20 years are due to fossil fuel burning. The rest of the anthropogenic emissions are predominantly due to land-use change, especially deforestation."[12]
The present atmospheric concentration of CO2 is about 383 parts per million (ppm) by volume.[13] Future CO2 levels are expected to rise due to ongoing burning of fossil fuels and land-use change. The rate of rise will depend on uncertain economic, sociological, technological, natural developments, but may be ultimately limited by the availability of fossil fuels. The IPCC Special Report on Emissions Scenarios gives a wide range of future CO2 scenarios, ranging from 541 to 970 ppm by the year 2100.[14] Fossil fuel reserves are sufficient to reach this level and continue emissions past 2100, if coal, tar sands or methane clathrates are extensively used.[15]
Positive feedback effects such as the expected release of CH4 from the melting of permafrost peat bogs in Siberia (possibly up to 70,000 million tonnes) may lead to significant additional sources of greenhouse gas emissions[16] not included in climate models cited by the IPCC.[1]
Feedbacks[edit]
The effects of forcing agents on the climate are complicated by various feedback processes.
One of the most pronounced feedback effects relates to the evaporation of water. CO2 injected into the atmosphere causes a warming of the atmosphere and the earth's surface. The warming causes more water to be evaporated into the atmosphere. Since water vapor itself acts as a greenhouse gas, this causes still more warming; the warming causes more water vapor to be evaporated, and so forth until a new dynamic equilibrium concentration of water vapor is reached at a slight increase in humidity and with a much larger greenhouse effect than that due to CO2 alone.[17] This feedback effect can only be reversed slowly as CO2 has a long average atmospheric lifetime.
Feedback effects due to clouds are an area of ongoing research and debate. Seen from below, clouds absorb infrared radiation and so exert a warming effect. Seen from above, the same clouds reflect sunlight and so exert a cooling effect. Increased global water vapor concentration may or may not cause an increase in global average cloud cover. The net effect of clouds thus has not been well modeled, however, cloud feedback is second only to water vapor feedback and is positive in all the models that contributed to the IPCC Fourth Assessment Report.[17]
Another important feedback process is ice-albedo feedback.[18] The increased CO2 in the atmosphere warms the Earth's surface and leads to melting of ice near the poles. As the ice melts, land or open water takes its place. Both land and open water are on average less reflective than ice, and thus absorb more solar radiation. This causes more warming, which in turn causes more melting, and this cycle continues.
Positive feedback due to release of CO2 and CH4 from thawing permafrost is an additional mechanism contributing to warming. Possible positive feedback due to CH4 release from melting seabed ices is a further mechanism to be considered.
Solar variation[edit]
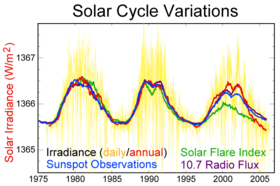
Variations in solar output, possibly amplified by cloud feedbacks, may have contributed to recent warming.[19] A difference between this mechanism and greenhouse warming is that an increase in solar activity should produce a warming of the stratosphere while greenhouse warming should produce a cooling of the stratosphere. Stratospheric warming has not been observed.[20]
Other phenomena such as solar variation combined with volcanoes have probably had a warming effect from pre-industrial times to 1950, but a cooling effect since 1950.[1] However, some research has suggested that the Sun's contribution may have been underestimated. Researchers at Duke University have estimated that the Sun may have minimally contributed about 10–30% of the global surface temperature warming over the period 1980–2002.[21] Similarly, Stott et al. estimate in 2003 that climate models overestimate the relative effect of greenhouse gases compared to solar forcing but also that the cooling effect of volcanic dust and sulfate aerosols has been underestimated.[22] They conclude that even with an enhanced climate sensitivity to solar forcing, most of the warming during the latest decades is attributable to the increases in greenhouse gases.
History[edit]

From the present to the dawn of human settlement[edit]
Global temperatures on both land and sea have increased by 0.75 °C (1.4 °F) relative to the period 1860–1900, according to the instrumental temperature record. This measured temperature increase is not significantly affected by the urban heat island. Since 1979, land temperatures have increased about twice as fast as ocean temperatures (0.25 °C per decade against 0.13 °C per decade).[23] Temperatures in the lower troposphere have increased between 0.12 and 0.22 °C (0.22 and 0.4 °F) per decade since 1979, according to satellite temperature measurements. Temperature is believed to have been relatively stable over the one or two thousand years before 1850, with possibly regional fluctuations such as the Medieval Warm Period or the Little Ice Age.
Based on estimates by NASA's Goddard Institute for Space Studies, 2005 was the warmest year since reliable, widespread instrumental measurements became available in the late 1800s, exceeding the previous record set in 1998 by a few hundredths of a degree.[24] Estimates prepared by the World Meteorological Organization and the Climatic Research Unit concluded that 2005 was the second warmest year, behind 1998.[25][26]
Anthropogenic emissions of other pollutants—notably sulfate aerosols—can exert a cooling effect by increasing the reflection of incoming sunlight. This partially accounts for the cooling seen in the temperature record in the middle of the twentieth century,[27] though the cooling may also be due in part to natural variability.

Paleoclimatologist William Ruddiman has argued that human influence on the global climate began around 8,000 years ago with the start of forest clearing to provide land for agriculture and 5,000 years ago with the start of Asian rice irrigation.[28] Ruddiman's interpretation of the historical record, with respect to the methane data, has been disputed.[29]
Pre-human climate variations[edit]
Earth has experienced warming and cooling many times in the past. The recent Antarctic EPICA ice core spans 800,000 years, including eight glacial cycles timed by orbital variations with interglacial warm periods comparable to present temperatures.[30]
A rapid buildup of greenhouse gases caused warming in the early Jurassic period (about 180 million years ago), with average temperatures rising by 5 °C (9.0 °F). Research by the Open University indicates that the warming caused the rate of rock weathering to increase by 400%. As such weathering locks away carbon in calcite and dolomite, CO2 levels dropped back to normal over roughly the next 150,000 years.[31][32]
Sudden releases of methane from clathrate compounds (the clathrate gun hypothesis) have been hypothesized as a cause for other warming events in the distant past, including the Permian-Triassic extinction event (about 251 million years ago) and the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum (about 55 million years ago).
Climate models[edit]


Scientists have studied global warming with computer models of the climate. These models are based on physical principles of fluid dynamics, radiative transfer, and other processes, with some simplifications being necessary because of limitations in computer power. These models predict that the net effect of adding greenhouse gases is to produce a warmer climate. However, even when the same assumptions of fossil fuel consumption and CO2 emission are used, the amount of projected warming varies between models and there still remains a considerable range of climate sensitivity.
Including uncertainties in the models and in future greenhouse gas concentrations, the IPCC anticipates a warming of 1.1 °C to 6.4 °C (2.0 °F to 11.5 °F) between 1990 and 2100. Models have also been used to help investigate the causes of recent climate change by comparing the observed changes to those that the models project from various natural and human derived causes.
Climate models can produce a good match to observations of global temperature changes over the last century, but "cannot yet simulate all aspects of climate."[33] These models do not unambiguously attribute the warming that occurred from approximately 1910 to 1945 to either natural variation or human effects; however, they suggest that the warming since 1975 is dominated by man-made greenhouse gas emissions.
Most global climate models, when run to project future climate, are forced by imposed greenhouse gas scenarios, generally one from the IPCC Special Report on Emissions Scenarios (SRES). Less commonly, models may be run by adding a simulation of the carbon cycle; this generally shows a positive feedback, though this response is uncertain (under the A2 SRES scenario, responses vary between an extra 20 and 200 ppm of CO2). Some observational studies also show a positive feedback.[34][35][36]
The representation of clouds is one of the main sources of uncertainty in present-generation models, though progress is being made on this problem.[37] There is also an ongoing discussion as to whether climate models are neglecting important indirect and feedback effects of solar variability.
Attributed and expected effects[edit]

Some effects on both the natural environment and human life are, at least in part, already being attributed to global warming. A 2001 report by the IPCC suggests that glacier retreat, ice shelf disruption such as the Larsen Ice Shelf, sea level rise, changes in rainfall patterns, increased intensity and frequency of extreme weather events, are being attributed in part to global warming.[38] While changes are expected for overall patterns, intensity, and frequencies, it is difficult to attribute specific events to global warming. Other expected effects include water scarcity in some regions and increased precipitation in others, changes in mountain snowpack, adverse health effects from warmer temperatures.
Increasing deaths, displacements, and economic losses projected due to extreme weather attributed to global warming may be exacerbated by growing population densities in affected areas.[39] A summary of probable effects and recent understanding can be found in the report made for the IPCC Third Assessment Report by Working Group II;[38] the newer IPCC Fourth Assessment Report summary reports, "There is observational evidence for an increase of intense tropical cyclone activity in the North Atlantic since about 1970, correlated with increases of tropical sea surface temperatures. There are also suggestions of increased intense tropical cyclone activity in some other regions where concerns over data quality are greater. Multi-decadal variability and the quality of the tropical cyclone records prior to routine satellite observations in about 1970 complicate the detection of long-term trends in tropical cyclone activity. There is no clear trend in the annual numbers of tropical cyclones."[1]
Additional anticipated effects include sea level rise of 110 to 770 mm (0.36 to 2.5 feet) between 1990 and 2100,[40] repercussions to agriculture, possible slowing of the thermohaline circulation, reductions in the ozone layer, increased intensity and frequency of hurricanes and extreme weather events, lowering of ocean pH, and the spread of diseases such as malaria[41] and dengue fever.[42] One study predicts 18% to 35% of a sample of 1,103 animal and plant species would be extinct by 2050, based on future climate projections.[43] Mechanistic studies have documented extinctions due to recent climate change: McLaughlin et al. documented two populations of Bay checkerspot butterfly being threatened by precipitation change.[44] Parmesan states, "Few studies have been conducted at a scale that encompasses an entire species"[45] and McLaughlin et al. agreed "few mechanistic studies have linked extinctions to recent climate change."[44]
Economics[edit]
Some economists have tried to estimate the aggregate net economic costs of damages from climate change across the globe. Such estimates have so far failed to reach conclusive findings; in a survey of 100 estimates, the values ran from US$-10 per tonne of carbon (tC) (US$-3 per tonne of carbon dioxide) up to US$350/tC (US$95 per tonne of carbon dioxide), with a mean of US$43 per tonne of carbon (US$12 per tonne of carbon dioxide).[39] One widely publicized report on potential economic impact is the Stern Review; it suggests that extreme weather might reduce global gross domestic product by up to 1%, and that in a worst-case scenario global consumption per head could fall 20%.[46] The reports methodology, advocacy and conclusions has been criticized by many economists, while others have supported the general attempt to quantify economic risk, even if not the specific numbers.
The IPCC's last report says that to stabilize greenhouse-gas concentrations at 550 ppm would require a price of US$20-50 per tonne of carbon by 2020-30. The IPCC's economic models reckon, on average, that if the world adopted such a price the annual global economic growth would be 0.1% a year lower than it otherwise would have been, or put another way, at the end of 2050 the global economy would be 1.3% smaller than had the new pricing not been adopted.[47]
In a summary of economic cost associated with climate change, the United Nations Environment Programme emphasizes the risks to insurers, reinsurers, and banks of increasingly traumatic and costly weather events. Other economic sectors likely to face difficulties related to climate change include agriculture and transport. Developing countries, rather than the developed world, are at greatest economic risk.[48]
Mitigation and adaptation[edit]
The broad agreement among climate scientists that global temperatures will continue to increase has led nations, states, corporations and individuals to implement actions to try to curtail global warming or adjust to it. Many environmental groups encourage action against global warming, often by the consumer, but also by community and regional organizations. There has been business action on climate change, including efforts at increased energy efficiency and (still limited) moves to alternative fuels. One important innovation has been the development of greenhouse gas emissions trading through which companies, in conjunction with government, agree to cap their emissions or to purchase credits from those below their allowances.
The world's primary international agreement on combating global warming is the Kyoto Protocol, an amendment to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), negotiated in 1997. The Protocol now covers more than 160 countries globally and over 55% of global greenhouse gas emissions.[49] The United States, the world's largest greenhouse gas emitter; Australia; and Kazakhstan have refused to ratify the treaty. China and India, two other large emitters, have ratified the treaty but, as developing countries, are exempt from its provisions.
Controversy and politics[edit]
Increased awareness of the scientific findings surrounding global warming has resulted in political and economic debate. Poor regions, particularly Africa, appear at greatest risk from the suggested effects of global warming, while their actual emissions have been negligible compared to the developed world, reports The New York Times.[50] At the same time, developing world exemptions from provisions of the Kyoto treaty have been criticized by the United States and been used as part of its justification for continued non-ratification.[51] In the Western world, the idea of human influence on climate and efforts to combat it has gained wider acceptance in Europe than the United States.[52][53]
Fossil fuel companies such as ExxonMobil have spent large sums of money for public relations to downplay the risks of climate change,[54][55] while environmental groups have launched campaigns emphasizing its impacts.
This issue has sparked debate in the U.S. about the benefits of reducing industrial emissions of greenhouse gases to help the environment, versus any resulting harm due to limitations in economic activity.[56][57] There has also been discussion in several countries about the cost of adopting alternate, cleaner energy sources in order to reduce emissions.[58]
Another point of debate is the degree to which newly developed economies, like India and China, have a right to increase their industrial emissions, especially since China is expected to exceed the United States in total greenhouse gas emissions by 2010,[59] though the U.S. has less than one-fourth of China's population.[60] At an IPCC conference in April 2007, delegates from 120 nations discussed the specific economic and societal costs of mitigating global warming; eventually, delegates approved a report indicating general consensus that the benefits of mitigation are worth any specific costs.[61][62]
Related climatic issues[edit]
A variety of issues are often raised in relation to global warming. One is ocean acidification, the ongoing decrease in the pH of the Earth's oceans. Increased atmospheric CO2 increases the amount of CO2 dissolved in the oceans.[63] CO2 dissolved in the ocean reacts with water to form carbonic acid resulting in acidification. Ocean surface pH is estimated to have decreased from approximately 8.25 to 8.14 since the beginning of the industrial era,[64] and it is estimated that it will drop by a further 0.14 to 0.5 units by 2100 as the ocean absorbs more CO2.Cite error: A <ref> tag is missing the closing </ref> (see the help page).[65] Since organisms and ecosystems are adapted to a narrow range of pH, this raises serious extinction concerns, directly driven by increased atmospheric CO2, that could disrupt food webs and impact human societies that depend on marine ecosystem services.[66]
Another related issue that may have partially mitigated global warming in the late twentieth century is global dimming, the gradual reduction in the amount of global direct irradiance at the Earth's surface. From 1960 to 1990 human-caused aerosols likely precipitated this effect. Scientists have stated with 66–90% confidence that the effects of human-caused aerosols, along with volcanic activity, have offset some of global warming, and that greenhouse gases would have resulted in more warming than observed if not for these dimming agents.[1]
Ozone depletion, the steady decline in the total amount of ozone in Earth's stratosphere, is frequently cited in relation to global warming. Although there are areas of linkage, the relationship between the two is not strong.[67]
References[edit]
- ^ a b c d e f g "Summary for Policymakers" (PDF). Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. 2007-02-05. Retrieved 2007-02-02.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ American Quaternary Association (2006-09-05). "Petroleum Geologists' Award to Novelist Crichton Is Inappropriate" (PDF). Eos. 87 (3): 364.
[AAPG] stands alone among scientific societies in its denial of human-induced effects on global warming.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Climate Change Policy" (cfm). American Association of Petroleum Geologists. Retrieved 2007-03-30.
- ^ American Quaternary Association (2006-09-05). "Petroleum Geologists' Award to Novelist Crichton Is Inappropriate" (PDF). Eos. 87 (3): 364.
Few credible scientists now doubt that humans have influenced the documented rise in global temperatures since the Industrial Revolution.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Climate Change: Basic Information". United States Environmental Protection Agency. 2006-12-14. Retrieved 2007-02-09.
In common usage, 'global warming' often refers to the warming that can occur as a result of increased emissions of greenhouse gases from human activities.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change, Article I". United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change. Retrieved 2007-01-15.
- ^ "Joint science academies' statement: The science of climate change" (ASP). Royal Society. 2001-05-17. Retrieved 2007-04-01.
The work of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) represents the consensus of the international scientific community on climate change science
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Leidig, Michael (2004-07-17). "The truth about global warming - it's the Sun that's to blame". Telegraph.co.uk. Retrieved 2007-04-29.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Meehl, Gerald A.; Washington, Warren M.; Collins, William D.; Arblaster, Julie M.; Hu, Aixue; Buja, Lawrence E.; Strand, Warren G.; Teng, Haiyan (2005-03-18). "How Much More Global Warming and Sea Level Rise". Science. 307 (5716): 1769–1772. doi:10.1126/science.1106663. PMID 15774757. S2CID 12710599. Retrieved 2007-02-11.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Living with Climate Change – An Overview of Potential Climate Change Impacts on Australia. Summary and Outlook" (Document). Australian Greenhouse Office. December 2002.
{{cite document}}: Unknown parameter|accessdate=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|url=ignored (help) - ^ Pearson, Paul N.; Palmer, Martin R. (2000-08-17). "Atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations over the past 60 million years". Nature. 406 (6797): 695–699. doi:10.1038/35021000. PMID 10963587. S2CID 205008176.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Summary for Policymakers". Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. 2001-01-20. Retrieved 2007-01-18.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Tans, Pieter. "Trends in Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide – Mauna Loa". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 2007-04-28.
- ^ Prentice, I. Colin (2001-01-20). "3.7.3.3 SRES scenarios and their implications for future CO2 concentration". Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Retrieved 2007-04-28.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ "4.4.6. Resource Availability". IPCC Special Report on Emissions Scenarios. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Retrieved 2007-04-28.
- ^ Sample, Ian (2005-08-11). "Warming Hits 'Tipping Point'". The Guardian. Retrieved 2007-01-18.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ a b Soden, Brian J. (2005-11-01). "An Assessment of Climate Feedbacks in Coupled Ocean–Atmosphere Models" (PDF). Journal of Climate. 19 (14): 3354-3360. doi:10.1175/JCLI3799.1. S2CID 11576587. Retrieved 2007-04-21.
Interestingly, the true feedback is consistently weaker than the constant relative humidity value, implying a small but robust reduction in relative humidity in all models on average" "clouds appear to provide a positive feedback in all models
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Stocker, Thomas F. (2001-01-20). "7.5.2 Sea Ice". Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Retrieved 2007-02-11.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Marsh, Nigel (November 2000). "Cosmic Rays, Clouds, and Climate" (PDF). Space Science Reviews. 94 (1–2): 215–230. doi:10.1023/A:1026723423896. S2CID 26968619. Retrieved 2007-04-17.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) - ^ Haigh, Joanna D. (2003-01-15). "The effects of solar variability on the Earth's climate". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Physical, Mathematical and Engineering Sciences. 361 (1802): 91–111. doi:10.1098/rsta.2002.1111. S2CID 53007804. Retrieved 2007-03-15.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Scafetta, N.; West, B. J. (2005-09-28). "Estimated solar contribution to the global surface warming using the ACRIM TSI satellite composite" (PDF). Geophysical Research Letters. 32 (18). doi:10.1029/2005GL023849. S2CID 119525360.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Stott, Peter A.; Jones, Gareth S.; Mitchell, John F. B. (2003-12-03). "Do Models Underestimate the Solar Contribution to Recent Climate Change?" (PDF). Journal of Climate. 16 (24): 4079–4093. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(2003)016<4079:DMUTSC>2.0.CO;2. Retrieved 2007-04-16.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Smith, Thomas M. (2005-05-15). "A Global Merged Land–Air–Sea Surface Temperature Reconstruction Based on Historical Observations (1880–1997)" (PDF). Journal of Climate. 18 (12): 2021–2036. doi:10.1175/JCLI3362.1. ISSN 0894-8755. Retrieved 2007-03-14.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Hansen, James E. (2006-01-12). "Goddard Institute for Space Studies, GISS Surface Temperature Analysis". NASA Goddard Institute for Space Studies. Retrieved 2007-01-17.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ "Global Temperature for 2005: second warmest year on record" (PDF). Climatic Research Unit, School of Environmental Sciences, University of East Anglia. 2005-12-15. Retrieved 2007-04-13.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "WMO STATEMENT ON THE STATUS OF THE GLOBAL CLIMATE IN 2005" (PDF). World Meteorological Organization. 2005-12-15. Retrieved 2007-04-13.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Mitchell, J. F. B. (2001-01-20). "12.4.3.3 Space-time studies". Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Retrieved 2007-01-04.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Ruddiman, William F. (March 2005). "How Did Humans First Alter Global Climate?" (PDF). Scientific American. 292 (3): 46–53. doi:10.1038/scientificamerican0305-46. PMID 15859211. Retrieved 2007-03-05.
- ^ Schmidt, Gavin A.; Shindell, Drew T.; Harder, Susan (2004-12-10). "A note on the relationship between ice core methane concentrations and insolation". Geophysical Research Letters. 31 (23). doi:10.1029/2004GL021083. S2CID 129005632. L23206. Retrieved 2007-03-05.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Hansen, James (2006-09-26). "Global temperature change" (PDF). PNAS. 103 (39): 14288–14293. doi:10.1073/pnas. PMID 17001018. S2CID 10638657. Retrieved 2007-04-20.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ "The Open University Provides Answers on Global Warming" (PDF) (Press release). Open University. 2004-01-30. Retrieved 2007-03-04.
{{cite press release}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Cohen, Anthony S.; Coe, Angela L.; Harding, Stephen M.; Schwark, Lorenz (February 2004). "Osmium isotope evidence for the regulation of atmospheric CO2 by continental weathering" (PDF). Geology. 32 (2): 157–160. doi:10.1130/G20158.1. Retrieved 2007-03-04.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) - ^ "Summary for Policymakers". Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. 2001-01-20. Retrieved 2007-04-28.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^
Torn, Margaret (2006-05-26). "Missing feedbacks, asymmetric uncertainties, and the underestimation of future warming". Geophysical Research Letters. 33 (10). L10703. Retrieved 2007-03-04.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^
Harte, John (2006-10-30). "Shifts in plant dominance control carbon-cycle responses to experimental warming and widespread drought". Environmental Research Letters. 1 (1). 014001. Retrieved 2007-05-02.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Scheffer, Marten; Brovkin, Victor; Cox, Peter M. (2006-05-26). "Positive feedback between global warming and atmospheric CO2 concentration inferred from past climate change" (PDF). Geophysical Research Letters. 33 (10). doi:10.1029/2005gl025044. S2CID 18457506. Retrieved 2007-05-04.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Stocker, Thomas F. (2001-01-20). "7.2.2 Cloud Processes and Feedbacks". Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Retrieved 2007-03-04.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b "Climate Change 2001: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change". Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. 2001-02-16. Retrieved 2007-03-14.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ a b "Summary for Policymakers" (PDF). Climate Change 2007: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Working Group II Contribution to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Fourth Assessment Report. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. 2007-04-13. Retrieved 2007-04-28.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Church, John A. (2001-01-20). "Executive Summary of Chapter 11". Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Retrieved 2005-12-19.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ The global spread of malaria in a future warmer world. D. Rogers and S. Randolph. Science, 2000.
- ^ Hales, Simon (2002-09-14). "Potential effect of population and climate changes on global distribution of dengue fever: an empirical model" (PDF). The Lancet. 360 (9336): 830–834. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(02)09964-6. PMID 12243917. S2CID 17520947. Retrieved 2007-05-02.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Thomas, Chris D.; Cameron, Alison; Green, Rhys E.; Bakkenes, Michel; Beaumont, Linda J.; Collingham, Yvonne C.; Erasmus, Barend F. N.; De Siqueira, Marinez Ferreira; Grainger, Alan; Hannah, Lee; Hughes, Lesley; Huntley, Brian; Van Jaarsveld, Albert S.; Midgley, Guy F.; Miles, Lera; Ortega-Huerta, Miguel A.; Townsend Peterson, A.; Phillips, Oliver L.; Williams, Stephen E. (2004-01-08). "Extinction risk from climate change" (PDF). Nature. 427 (6970): 145–138. doi:10.1038/nature02121. PMID 14712274. S2CID 969382. Retrieved 2007-03-18.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ a b McLaughlin, John F.; Hellmann, Jessica J.; Boggs, Carol L.; Ehrlich, Paul R. (2002-04-30). "Climate change hastens population extinctions" (PDF). PNAS. 99 (9): 6070–6074. doi:10.1073/pnas.052131199. PMC 122903. PMID 11972020. Retrieved 2007-03-29.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Permesan, Camille (2006-08-24). "Ecological and Evolutionary Responses to Recent Climate Change" (PDF). Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics. 37: 637–669. doi:10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.37.091305.110100. Retrieved 2007-03-30.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "At-a-glance: The Stern Review". BBC. 2006-10-30. Retrieved 2007-04-29.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Tackling climate change. A bargain". The Economist. 2007-05-04. Retrieved 2007-05-04.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Dlugolecki, Andrew (2002). "Climate Risk to Global Economy" (PDF). CEO Briefing: UNEP FI Climate Change Working Group. United Nations Environment Programme. Retrieved 2007-04-29.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ "Kyoto Protocol Status of Ratification" (PDF). United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change. 2006-07-10. Retrieved 2007-04-27.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Revkin, Andrew (2007-04-01). "Poor Nations to Bear Brunt as World Warms". The New York Times. Retrieved 2007-05-02.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Brahic, Catherine (2006-04-25). "China's emissions may surpass the US in 2007". New Scientist. Retrieved 2007-05-02.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Crampton, Thomas (2007-01-04). "More in Europe worry about climate than in U.S., poll shows". International Herald Tribune. Retrieved 2007-04-14.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Summary of Findings". Little Consensus on Global Warming. Partisanship Drives Opinion. Pew Research Center. 2006-07-12. Retrieved 2007-04-14.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Exxon cuts ties to global warming skeptics". MSNBC. 2007-01-12. Retrieved 2007-05-02.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Sandell, Clayton (2007-01-03). "Report: Big Money Confusing Public on Global Warming". ABC. Retrieved 2007-04-27.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Holzer, Jessica (2007-01-18). "Global warming becomes hot topic on Capitol Hill". The Hill. Retrieved 2007-05-02.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Zabarenko, Deborah (2007-05-04). "U.S. rejects 'high cost' global warming scenarios". Reuters. Retrieved 2007-05-04.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "EU agrees on carbon dioxide cuts". BCC. 2007-03-09. Retrieved 2007-05-04.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Angleys, Emmanuel (2007-05-02). "China, India, Brazil hold up climate change talks". Agence France-Presse. Retrieved 2007-05-02.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "U.S. Population 300,888,812 for Jan. 1". Red Orbit. 2006-12-28. Retrieved 2007-05-03.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Coleman, Joseph (2007-05-04). "Report: Climate change plan affordable". Associated Press. Retrieved 2007-05-04.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Malakunas, Karl (2007-05-04). "Experts say nations have means to tackle global warming". Agence France-Presse. Retrieved 2007-05-04.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "The Ocean and the Carbon Cycle". NASA. 2005-06-21. Retrieved 2007-03-04.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Jacobson, Mark Z. (2005-04-02). "Studying ocean acidification with conservative, stable numerical schemes for nonequilibrium air-ocean exchange and ocean equilibrium chemistry" (PDF). Journal of Geophysical Research. 110 (D7). doi:10.1029/2004JD005220. D07302. Retrieved 2007-04-28.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Caldeira, Ken (2005-09-21). "Ocean model predictions of chemistry changes from carbon dioxide emissions to the atmosphere and ocean". Journal of Geophysical Research. 110 (C09S04): 1–12. doi:10.1029/2004JC002671. Retrieved 2006-02-14.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Ocean acidification due to increasing atmospheric carbon dioxide. Royal Society, London, UK.
- ^ Houston, Paul L. (1996-09-13), Ozone Aside, Government 294/Philosophy 294 course at Cornell University, retrieved 2007-04-29
{{citation}}: Check date values in:|date=(help)
Further reading[edit]
- Amstrup, Steven C.; Stirling, Ian; Smith, Tom S.; Perham, Craig; Thiemann, Gregory W. (2006-04-27). "Recent observations of intraspecific predation and cannibalism among polar bears in the southern Beaufort Sea". Polar Biology. 29 (11): 997–1002. doi:10.1007/s00300-006-0142-5. S2CID 34780227.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Association of British Insurers (2005–06). Financial Risks of Climate Change (PDF).
{{cite book}}: Check date values in:|year=(help) - Barnett, T. P.; Adam, J. C.; Lettenmaier, D. P. (2005-11-17). "Potential impacts of a warming climate on water availability in snow-dominated regions". Nature. 438 (7066): 303–309. doi:10.1038/nature04141. PMID 16292301. S2CID 4374104.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Behrenfeld, Michael J.; o'Malley, Robert T.; Siegel, David A.; McClain, Charles R.; Sarmiento, Jorge L.; Feldman, Gene C.; Milligan, Allen J.; Falkowski, Paul G.; Letelier, Ricardo M.; Boss, Emmanuel S. (2006-12-07). "Climate-driven trends in contemporary ocean productivity" (PDF). Nature. 444 (7120): 752–755. doi:10.1038/nature05317. PMID 17151666. S2CID 4414391.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Choi, Onelack (May 2005). "The Impacts of Socioeconomic Development and Climate Change on Severe Weather Catastrophe Losses: Mid-Atlantic Region (MAR) and the U.S." Climate Change. 58 (1–2): 149–170. doi:10.1023/A:1023459216609. S2CID 151074531.
- Dyurgerov, Mark B. (2005). Glaciers and the Changing Earth System: a 2004 Snapshot (PDF). Institute of Arctic and Alpine Research Occasional Paper #58. ISSN 0069-6145.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Emanuel, Kerry A. (2005-08-04). "Increasing destructiveness of tropical cyclones over the past 30 years" (PDF). Nature. 436 (7051): 686–688. doi:10.1038/nature03906. PMID 16056221. S2CID 2368280.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Hansen, James; Nazarenko, Larissa; Ruedy, Reto; Sato, Makiko; Willis, Josh; Del Genio, Anthony; Koch, Dorothy; Lacis, Andrew; Lo, Ken; Menon, Surabi; Novakov, Tica; Perlwitz, Judith; Russell, Gary; Schmidt, Gavin A.; Tausnev, Nicholas (2005-06-03). "Earth's Energy Imbalance: Confirmation and Implications" (PDF). Science. 308 (5727): 1431–1435. doi:10.1126/science.1110252. PMID 15860591. S2CID 10932559.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Hinrichs, Kai-Uwe; Hmelo, Laura R.; Sylva, Sean P. (2003-02-21). "Molecular Fossil Record of Elevated Methane Levels in Late Pleistocene Coastal Waters". Science. 299 (5610): 1214–1217. doi:10.1126/science.1079601. PMID 12595688. S2CID 33263340.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Hirsch, Tim (2006-01-11). "Plants revealed as methane source". BBC.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Hoyt, Douglas V.; Schatten, Kenneth H. (1993). "A discussion of plausible solar irradiance variations, 1700–1992". Journal of Geophysical Research. 98 (A11): 18, 895–18, 906. Bibcode:1993JGR....9818895H. doi:10.1029/93JA01944.
- Kenneth, James P. (2003-02-14). Methane Hydrates in Quaternary Climate Change: The Clathrate Gun Hypothesis. American Geophysical Union.
{{cite book}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Keppler, Frank (2006-01-18). "Global Warming - The Blame Is not with the Plants". Max Planck Society.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Kurzweil, Raymond (2006–07). "Nanotech Could Give Global Warming a Big Chill" (PDF). Forbes / Wolfe Nanotech Report. 5 (7).
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|year=(help) - Lean, J. L.; Wang, Y.-M.; Sheeley, N. R. (2002). "The effect of increasing solar activity on the Sun's total and open magnetic flux during multiple cycles: Implications for solar forcing of climate". Geophysical Research Letters. 29 (24): 2224. Bibcode:2002GeoRL..29.2224L. doi:10.1029/2002GL015880. S2CID 31369370.
{{cite journal}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|1=(help) - Lerner, K. Lee (2006-07-26). Environmental issues : essential primary sources. Thomson Gale. ISBN 1414406258.
{{cite book}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - McLaughlin, Joseph B. (2005-10-06). "Outbreak of Vibrio parahaemolyticus gastroenteritis associated with Alaskan oysters". New England Journal of Medicine. 353 (14). New England Medical Society: 1463–1470. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa051594. PMID 16207848.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)(online version requires registration) - Muscheler, Raimund (2005-07-28). "Climate: How unusual is today's solar activity?" (PDF). Nature. 436 (7012): 1084–1087. doi:10.1038/nature04045. PMID 16049429. S2CID 4383886.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Oerlemans, J. (2005-04-29). "Extracting a Climate Signal from 169 Glacier Records" (PDF). Science. 308 (5722): 675–677. doi:10.1126/science.1107046. PMID 15746388. S2CID 26585604.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Oreskes, Naomi (2004-12-03). "Beyond the Ivory Tower: The Scientific Consensus on Climate Change" (PDF). Science. 306 (5702): 1686. doi:10.1126/science.1103618. PMID 15576594. S2CID 153792099.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Purse, Bethan V.; Mellor, Philip S.; Rogers, David J.; Samuel, Alan R.; Mertens, Peter P. C.; Baylis, Matthew (February 2005). "Climate change and the recent emergence of bluetongue in Europe". Nature Reviews Microbiology. 3 (2): 171–181. doi:10.1038/nrmicro1090. PMID 15685226. S2CID 62802662.
- Revkin, Andrew C (2005-11-05). "Rise in Gases Unmatched by a History in Ancient Ice". The New York Times.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Ruddiman, William F. (2005-12-15). Earth's Climate Past and Future. New York: Princeton University Press. ISBN 0-7167-3741-8.
{{cite book}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Ruddiman, William F. (2005-08-01). Plows, Plagues, and Petroleum: How Humans Took Control of Climate. New Jersey: Princeton University Press. ISBN 0-691-12164-8.
{{cite book}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Solanki, S. K.; Usoskin, I. G.; Kromer, B.; Schüssler, M.; Beer, J. (2004-10-23). "Unusual activity of the Sun during recent decades compared to the previous 11,000 years" (PDF). Nature. 431 (7012): 1084–1087. doi:10.1038/nature02995. PMID 15510145. S2CID 4373732.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Solanki, Sami K. (2005-07-28). "Climate: How unusual is today's solar activity? (Reply)" (PDF). Nature. 436: E4–E5. doi:10.1038/nature04046. S2CID 4420872.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Sowers, Todd (2006-02-10). "Late Quaternary Atmospheric CH4 Isotope Record Suggests Marine Clathrates Are Stable". Science. 311 (5762): 838–840. doi:10.1126/science.1121235. PMID 16469923. S2CID 38790253.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Svensmark, Henrik; Pedersen, Jens Olaf P.; Marsh, Nigel D.; Enghoff, Martin B.; Uggerhøj, Ulrik I. (2007). "Experimental evidence for the role of ions in particle nucleation under atmospheric conditions". Proceedings of the Royal Society A. 463 (2078). FirstCite Early Online Publishing: 385–396. doi:10.1098/rspa.2006.1773. S2CID 59022072.(online version requires registration)
- Walter, K. M.; Zimov, S. A.; Chanton, J. P.; Verbyla, D.; Chapin, F. S. (2006-09-07). "Methane bubbling from Siberian thaw lakes as a positive feedback to climate warming". Nature. 443 (7107): 71–75. doi:10.1038/nature05040. PMID 16957728. S2CID 4415304.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Wang, Y.‐M.; Lean, J. L.; Sheeley, Jr, N. R. (2005-05-20). "Modeling the sun's magnetic field and irradiance since 1713" (PDF). Astrophysical Journal. 625: 522–538. doi:10.1086/429689. S2CID 20573668.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help)
See also[edit]
External links[edit]
Scientific[edit]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC)
- NOAA's Global Warming FAQ
- Discovery of Global Warming – An extensive introduction to the topic and the history of its discovery
- Max Planck Society: Global Warming - The Blame Is not with the Plants
- Caution urged on climate 'risks'
- NASA Finds Sun-Climate Connection in Old Nile Records, March 19, 2007
Educational[edit]
- The EdGCM (Educational Global Climate Modelling) Project free research-quality simulation for students, educators, and scientists alike, with a user-friendly interface that runs on desktop computers
- Daily global temperatures and trends from satellites Interactive graphics — NASA
Other[edit]
- Help Prevent Global Warming A wikiHow article
- UBS Launches First Global Warming Index "UBS-GWI"
- UN: rearing cattle produces more greenhouse gases than driving cars
- Trends in Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide - Mauna Loa
- Science and Technology Librarianship: Global Warming and Climate Change Science – Extensive commented list of Internet resources – Science and Technology Sources on the Internet.
- Union of Concerned Scientists Global Warming page
- Watch and read 'Tipping Point', Australian science documentary about effects of global warming on rare, common, and endangered wildlife
- Newest reports on US EPA website
- IPS Inter Press Service – Independent news on global warming and its consequences.
